The Gut-Brain Axis: How Your Stomach Affects Your Mood
In recent years, the scientific community has increasingly focused on the gut-brain axis, a complex communication network that links our digestive system with our central nervous system. This connection is not just a metaphorical one; it is a bidirectional communication pathway that significantly influences our mood, behavior, and overall mental health. The gut, often referred to as the "second brain," is home to trillions of bacteria that play a crucial role in this communication. Understanding how your gut communicates with your mind is essential for grasping the profound impact it has on your emotional well-being. This article explores 9 fascinating ways in which your gut interacts with your brain, influencing your mood and mental state.
1. The Role of Gut Microbiota

The gut microbiota, consisting of diverse microorganisms, is a key player in the gut-brain axis. These microorganisms help digest food, produce vitamins, and protect against pathogens. However, their most intriguing role is in modulating brain function and mood. The gut microbiota produces neuroactive compounds such as serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which are crucial for regulating mood and anxiety. An imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis, has been linked to depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiota through diet, probiotics, and lifestyle choices is essential for optimal mental health.
2. Serotonin Production

Approximately 90% of the body's serotonin, a neurotransmitter often dubbed the "feel-good" chemical, is produced in the gut. Serotonin plays a vital role in mood regulation, sleep, and appetite. The production of serotonin in the gut is influenced by the types of bacteria present. A healthy balance of gut bacteria can lead to increased serotonin production, promoting a positive mood and emotional stability. Conversely, an imbalance can result in reduced serotonin levels, contributing to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Understanding the link between serotonin and gut health underscores the importance of maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
3. The Vagus Nerve: A Communication Superhighway
The vagus nerve is a critical component of the gut-brain axis, serving as a communication superhighway between the gut and the brain. This nerve transmits signals from the gut to the brain, influencing mood and emotional well-being. Stimulation of the vagus nerve has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, highlighting its role in mood regulation. Practices such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can enhance vagal tone, strengthening this vital communication pathway. By understanding and optimizing vagus nerve function, individuals can improve their mental health and emotional resilience.
4. Gut Inflammation and Mood Disorders

Chronic inflammation in the gut can have a significant impact on mental health. Inflammatory cytokines, which are released during gut inflammation, can cross the blood-brain barrier and affect brain function. This process has been linked to the development of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Factors contributing to gut inflammation include poor diet, stress, and infections. Reducing gut inflammation through anti-inflammatory diets, stress management, and proper medical care can improve mood and mental health outcomes. Recognizing the connection between gut inflammation and mood disorders is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies.
5. Nutrient Absorption and Brain Function

A healthy gut is essential for the proper absorption of nutrients that are critical for brain function. Vitamins and minerals such as B vitamins, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids are vital for neurotransmitter production and brain health. Poor gut health can lead to nutrient deficiencies, negatively impacting mood and cognitive function. Ensuring a nutrient-rich diet and addressing gut health issues can enhance nutrient absorption, supporting optimal brain function and emotional well-being. This highlights the importance of a holistic approach to mental health that includes both diet and gut health management.
6. The Impact of Diet on Gut Health

Diet plays a pivotal role in shaping the gut microbiome and, consequently, mental health. Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to dysbiosis and mood disorders. Conversely, a diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods can promote a healthy gut microbiome, enhancing mood and mental clarity. The Mediterranean diet, in particular, has been associated with improved mental health outcomes due to its emphasis on whole foods and healthy fats. Understanding the impact of diet on gut health is key to optimizing mental health and well-being.
7. Stress and the Gut-Brain Axis
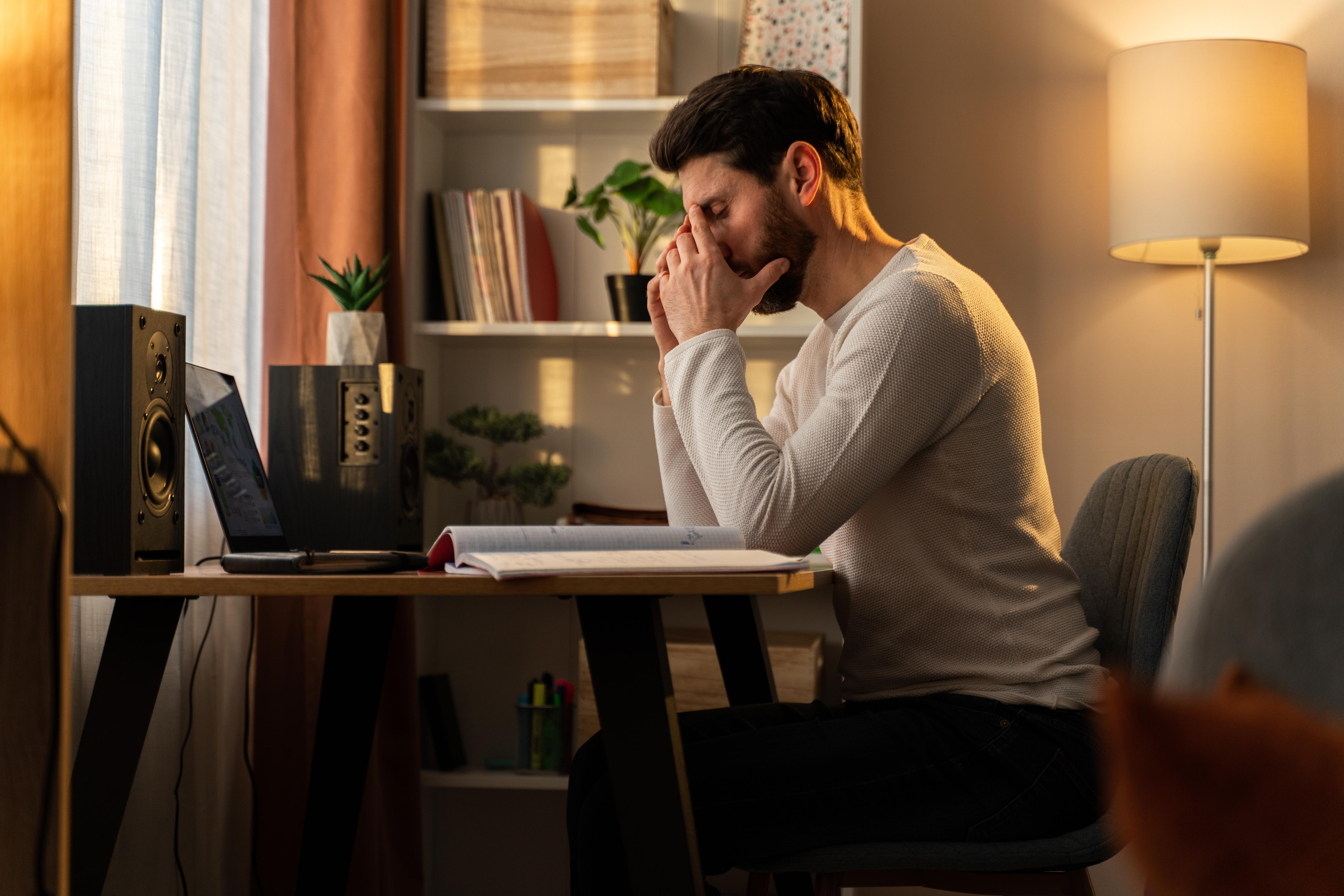

Stress has a profound impact on the gut-brain axis, affecting both gut health and mental well-being. Chronic stress can alter gut microbiota composition, increase gut permeability, and trigger inflammation, all of which negatively impact mood and cognitive function. Stress management techniques such as mindfulness, exercise, and adequate sleep can mitigate these effects, promoting a healthier gut and a more balanced mood. By addressing stress, individuals can break the vicious cycle of stress-induced gut and mood disturbances, paving the way for improved mental health and resilience.
8. Probiotics and Mental Health
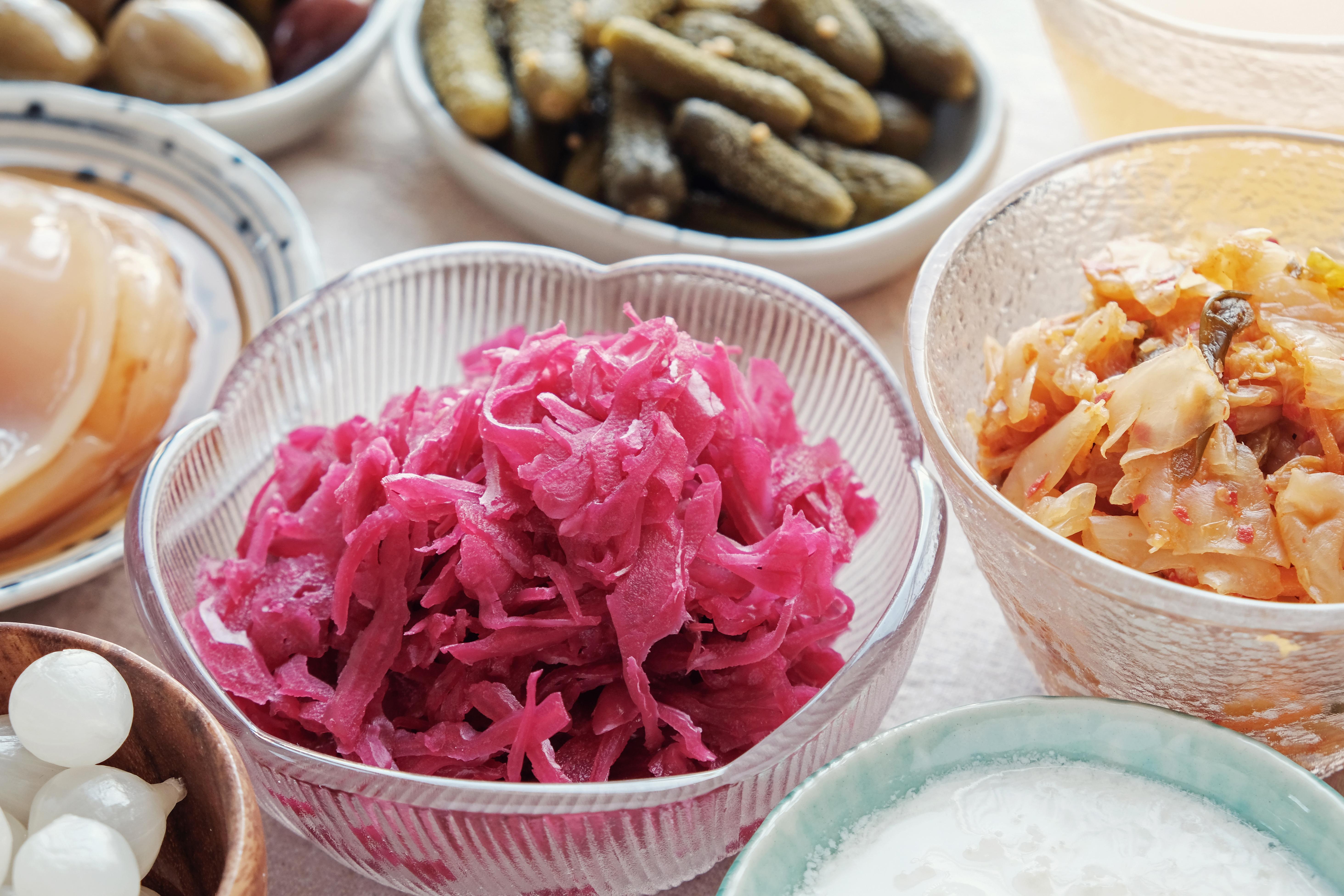

Probiotics, live bacteria that confer health benefits, have gained attention for their potential role in enhancing mental health. Certain probiotic strains have been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety by modulating gut microbiota and promoting the production of neuroactive compounds. Incorporating probiotics through supplements or fermented foods can support a healthy gut microbiome, positively influencing mood and emotional well-being. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms, the emerging evidence suggests that probiotics may be a valuable tool in the management of mood disorders.
9. Nurturing the Gut for Mental Wellness

The intricate relationship between the gut and the brain offers a new perspective on mental health. By understanding and nurturing this connection, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their mood and emotional well-being. From maintaining a balanced diet and managing stress to incorporating probiotics and enhancing vagal tone, there are numerous strategies to support a healthy gut-brain axis. As research continues to illuminate the profound impact of the gut on mental health, embracing a holistic approach that includes gut health as a cornerstone of mental wellness becomes increasingly important.
The Future of Gut-Brain Research
The field of gut-brain research is rapidly evolving, with exciting implications for mental health treatment. Advances in technology and a growing understanding of the gut-brain axis are paving the way for innovative therapies targeting gut health to improve mental well-being. Personalized medicine approaches that consider individual gut microbiota profiles hold promise for more effective and tailored treatments for mood disorders. As research continues to uncover the complexities of the gut-brain connection, the potential for transformative mental health interventions grows, offering hope for those struggling with mood disorders.