Beyond the Itch: The Infection Risks You Face When You Over-Scratch Bug Bites
When a mosquito leaves its mark or a flea finds its way to your skin, the immediate reaction is to scratch the itch away. However, beneath this seemingly harmless action lies a world of unseen risks and potential infections. While the itch might be a minor inconvenience, the consequences of over-scratching can be far more severe. This article delves into the lesser-known dangers associated with scratching bug bites, exploring how this common reaction can lead to infections and other health complications. We will examine the science behind the itch, the types of infections that can arise, and the broader health implications, offering insights into how to protect yourself effectively.
The Science Behind the Itch: Why Bug Bites Make Us Scratch
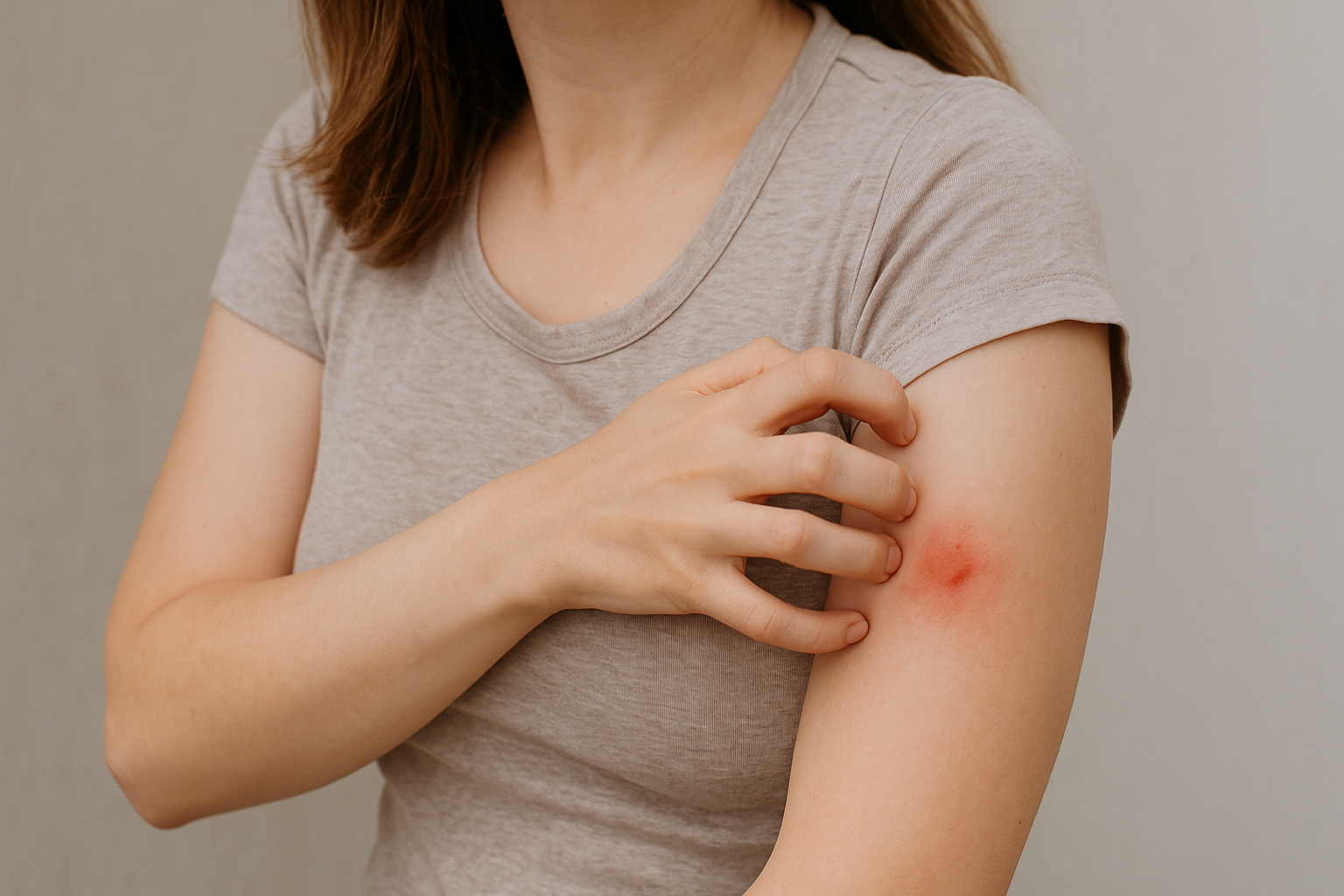

Understanding why bug bites itch is crucial to comprehending the risks of over-scratching. When an insect bites, it injects saliva that contains anticoagulants and proteins, causing an immune response. This response releases histamines, which are chemicals that trigger inflammation and the itch sensation. Scratching provides temporary relief by distracting the brain with a mild pain signal, but it can exacerbate the inflammation. Furthermore, scratching can cause the skin to break, creating an entry point for bacteria and other pathogens. Recognizing the biological processes at play helps us understand the importance of resisting the urge to scratch.
The Skin Barrier: Your First Line of Defense

The skin is the body's largest organ and serves as a crucial barrier against environmental threats, including infections. Over-scratching compromises this barrier by creating micro-tears and abrasions. These small injuries can become entry points for bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, which can lead to skin infections like impetigo or cellulitis. The integrity of the skin is vital for keeping harmful microorganisms at bay. Therefore, preserving the skin's protective function through proper care and avoiding excessive scratching is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing infections.
Common Infections Resulting from Over-Scratching
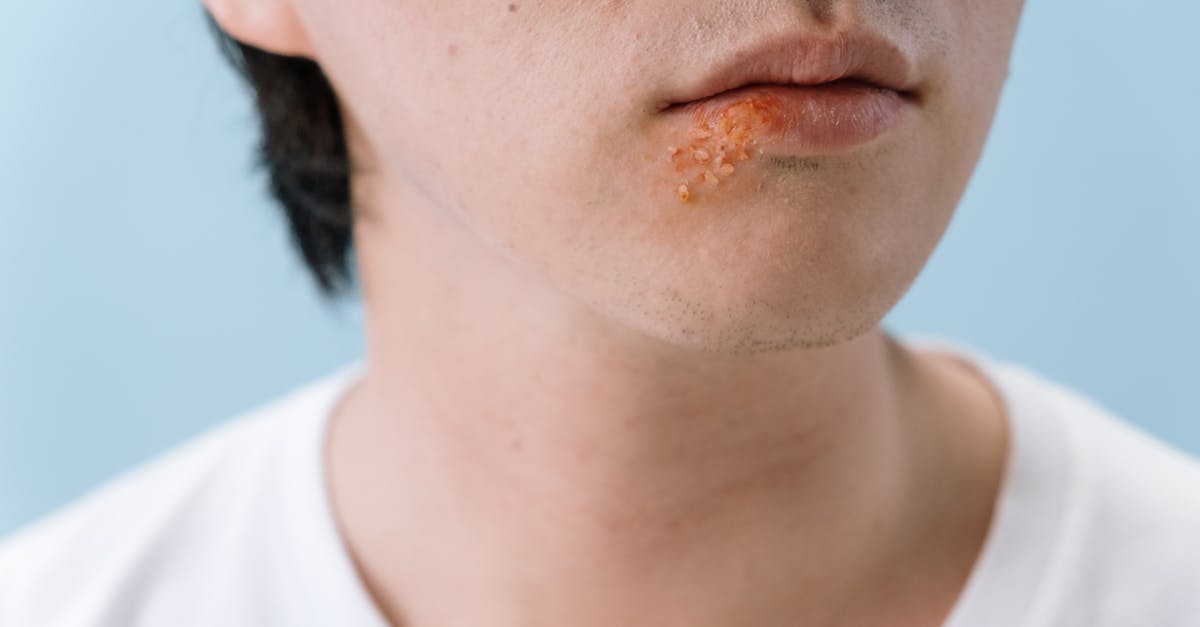
When the skin barrier is breached due to over-scratching, it opens the door to a range of infections. Bacterial infections are the most common, with impetigo being a frequent consequence of broken skin. This contagious infection results in red sores that can ooze and crust over, often requiring antibiotic treatment. In severe cases, cellulitis can develop, characterized by swollen, red, and tender areas that spread rapidly. Fungal infections, such as ringworm, can also exploit the compromised skin. Understanding these potential outcomes underscores the importance of treating bug bites with care and avoiding the temptation to scratch.
The Role of Hygiene in Preventing Infections
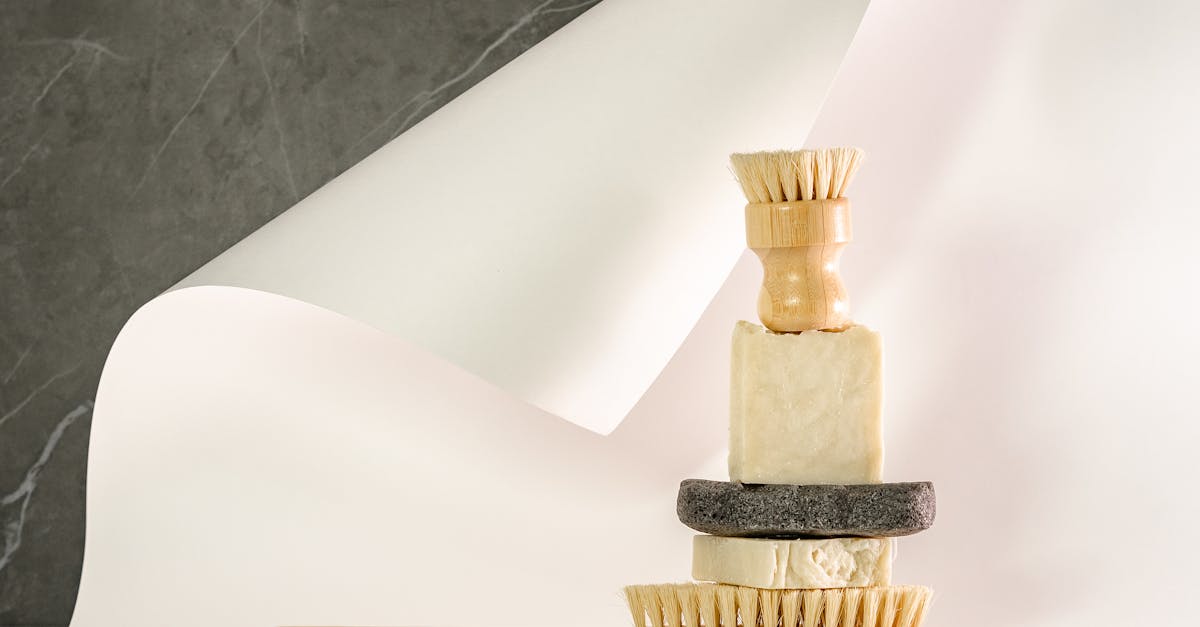

Maintaining good hygiene is a critical factor in preventing infections from bug bites. Thoroughly cleaning the affected area with soap and water can help remove irritants and reduce the risk of bacterial invasion. Applying antiseptic creams or ointments can further protect the skin and promote healing. Additionally, keeping fingernails short and clean minimizes the chance of transferring bacteria during scratching. These simple yet effective hygiene practices are essential in safeguarding against infections and maintaining skin health, emphasizing the role of personal care in infection prevention strategies.
Allergic Reactions and Secondary Skin Conditions

Beyond infections, over-scratching can lead to allergic reactions and secondary skin conditions. Continuous scratching can cause a condition known as lichen simplex chronicus, where the skin becomes thickened and leathery due to persistent irritation. This condition can exacerbate the itch-scratch cycle, leading to further complications. In some cases, individuals may experience allergic contact dermatitis, where the skin reacts to substances introduced through scratching. Recognizing these potential outcomes highlights the importance of managing bug bites promptly and effectively to prevent escalating skin issues.
Psychological Impacts: The Itch-Scratch Cycle
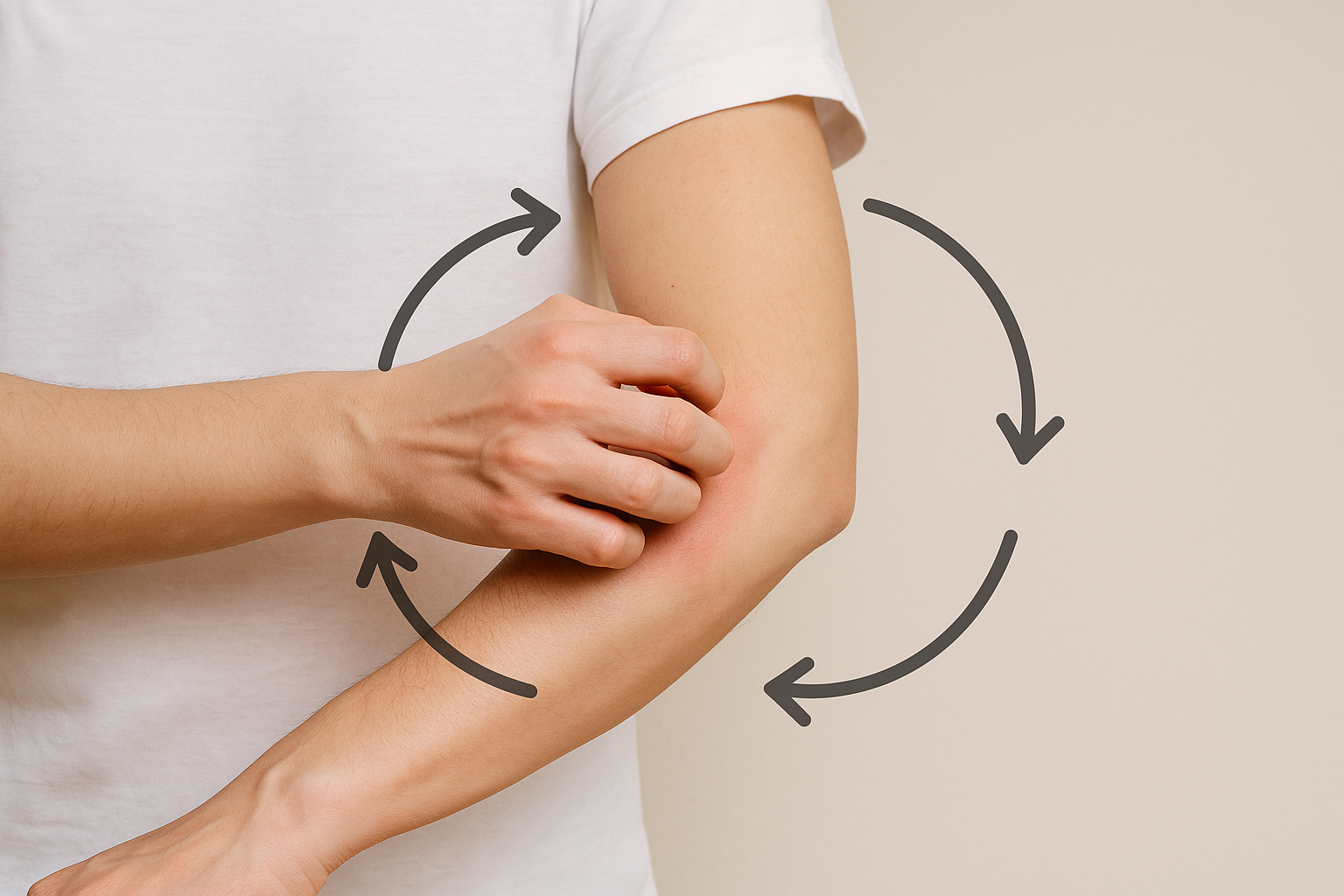
The itch-scratch cycle is not just a physical phenomenon; it has psychological implications as well. The persistent itch can lead to significant discomfort and distress, affecting sleep and overall quality of life. This discomfort can create a cycle of anxiety and stress, which in turn can exacerbate the perception of itchiness. Understanding the psychological aspect of scratching behavior is crucial for developing comprehensive strategies to manage bug bites. Techniques such as mindfulness and cognitive-behavioral approaches can help break the itch-scratch cycle, reducing both physical and emotional impacts.
Vulnerable Populations: Who's at Greater Risk?

Certain populations are more vulnerable to the risks associated with over-scratching bug bites. Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with diabetes or undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk for infections. Children, with their delicate skin and tendency to scratch, are also more susceptible to developing complications. Additionally, people with pre-existing skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis may experience heightened sensitivity and a greater likelihood of infection. Identifying these at-risk groups allows for targeted education and prevention efforts to minimize the health impacts of bug bites.
Effective Treatments and Alternatives to Scratching
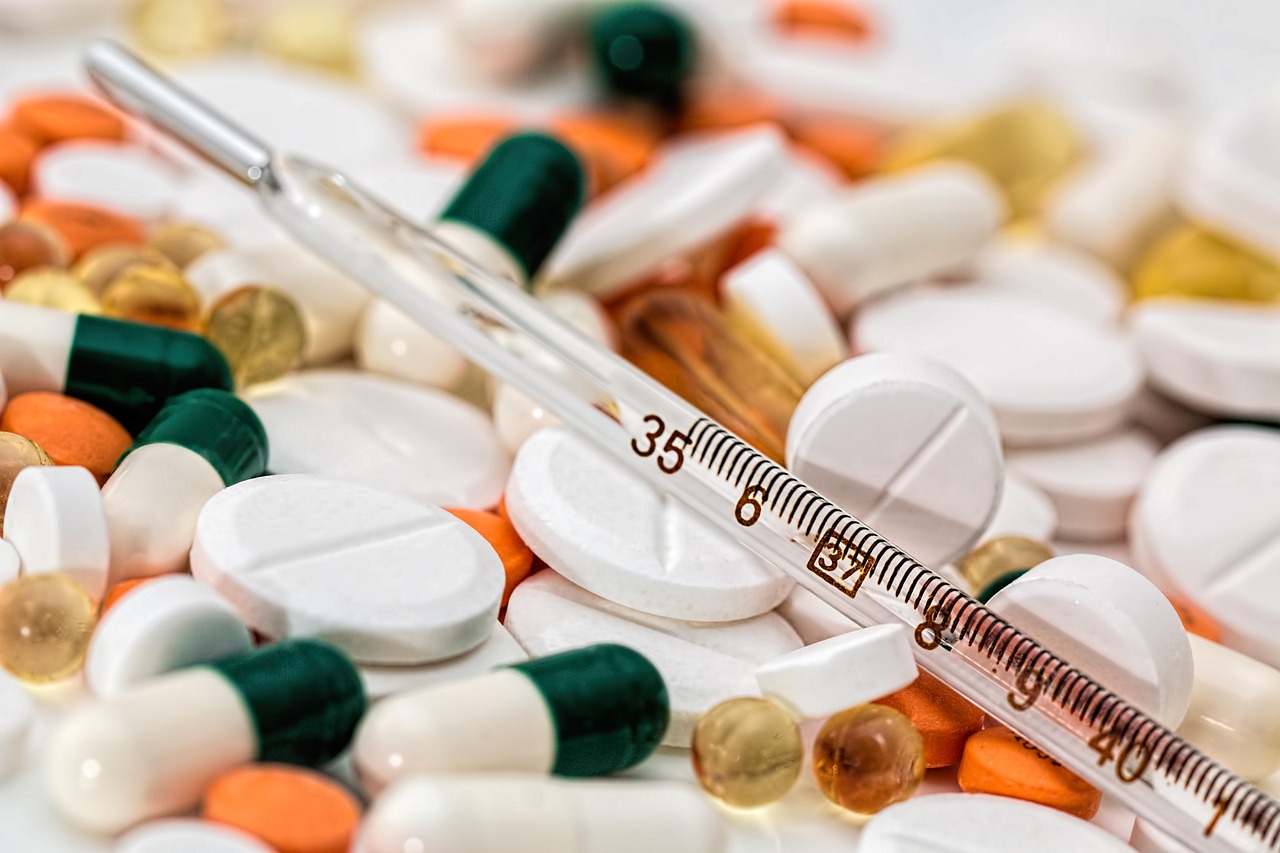
Preventing the urge to scratch begins with effective treatments for bug bites. Over-the-counter antihistamines can help reduce the itch by blocking histamine release. Topical corticosteroids can also alleviate inflammation and soothe the skin. Natural remedies, such as aloe vera and calamine lotion, provide cooling relief and can be used as alternatives to pharmaceuticals. Employing these treatments can reduce the need to scratch, preserving the skin's integrity and preventing infections. Exploring a range of treatment options ensures that individuals can find the most suitable solutions for their needs.
Preventative Measures: Reducing Bug Bite Incidence

Reducing the incidence of bug bites is a proactive approach to minimizing the risks associated with over-scratching. Using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and installing screens on windows can significantly decrease exposure to biting insects. Additionally, eliminating standing water and maintaining clean environments can reduce breeding grounds for mosquitoes. Educating communities about these preventative measures can empower individuals to protect themselves and their families from bug bites, ultimately reducing the need to scratch and the risk of infection.
Embracing Awareness and Prevention

While the immediate reaction to scratch a bug bite is natural, the potential for infection and other complications calls for greater awareness and preventive action. By understanding the biological, psychological, and environmental factors at play, individuals can make informed decisions to protect their skin and overall health. Emphasizing hygiene, utilizing effective treatments, and adopting preventative measures are key strategies in mitigating the risks associated with over-scratching. As we move beyond the itch, embracing these practices can lead to healthier outcomes and a greater sense of well-being.