21 Simple Strength Moves to Prevent Muscle Loss After 50
What if the true "fountain of youth" wasn't a mythical spring, but rather the empowering clang of weights and the satisfying burn of a well-executed strength move? As we navigate life's chapters, the desire isn't just for more years, but for more vibrant, capable years. The secret often lies in preserving our body's powerhouse: our muscles. After 50, sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss) can quietly begin to sap strength and vitality, but this is far from an irreversible fate! We believe mastering the art of longevity means actively building resilience. That's why we've significantly expanded our guide, now unveiling 21 essential strength moves specifically designed to help you defy muscle loss, boost energy, and stride confidently into your best decades yet. Get ready to discover the exercises that will keep you strong, active, and truly thriving!
1. Understanding Sarcopenia: The Silent Muscle Thief
Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass and strength, is a silent yet significant threat to longevity. It typically begins around the age of 30 and accelerates after 50, leading to a decline in physical performance and an increased risk of falls and fractures. The underlying causes of sarcopenia are multifaceted, involving hormonal changes, reduced protein synthesis, and decreased physical activity. Understanding these factors is crucial in developing effective strategies to counteract muscle loss. Research indicates that regular strength training can significantly mitigate the effects of sarcopenia. By engaging in targeted exercises that stimulate muscle growth and enhance neuromuscular function, individuals can maintain their strength and improve their quality of life. This section delves into the science of sarcopenia, highlighting its impact on the aging population and the importance of proactive measures in preserving muscle health.
2. The Role of Nutrition in Muscle Maintenance
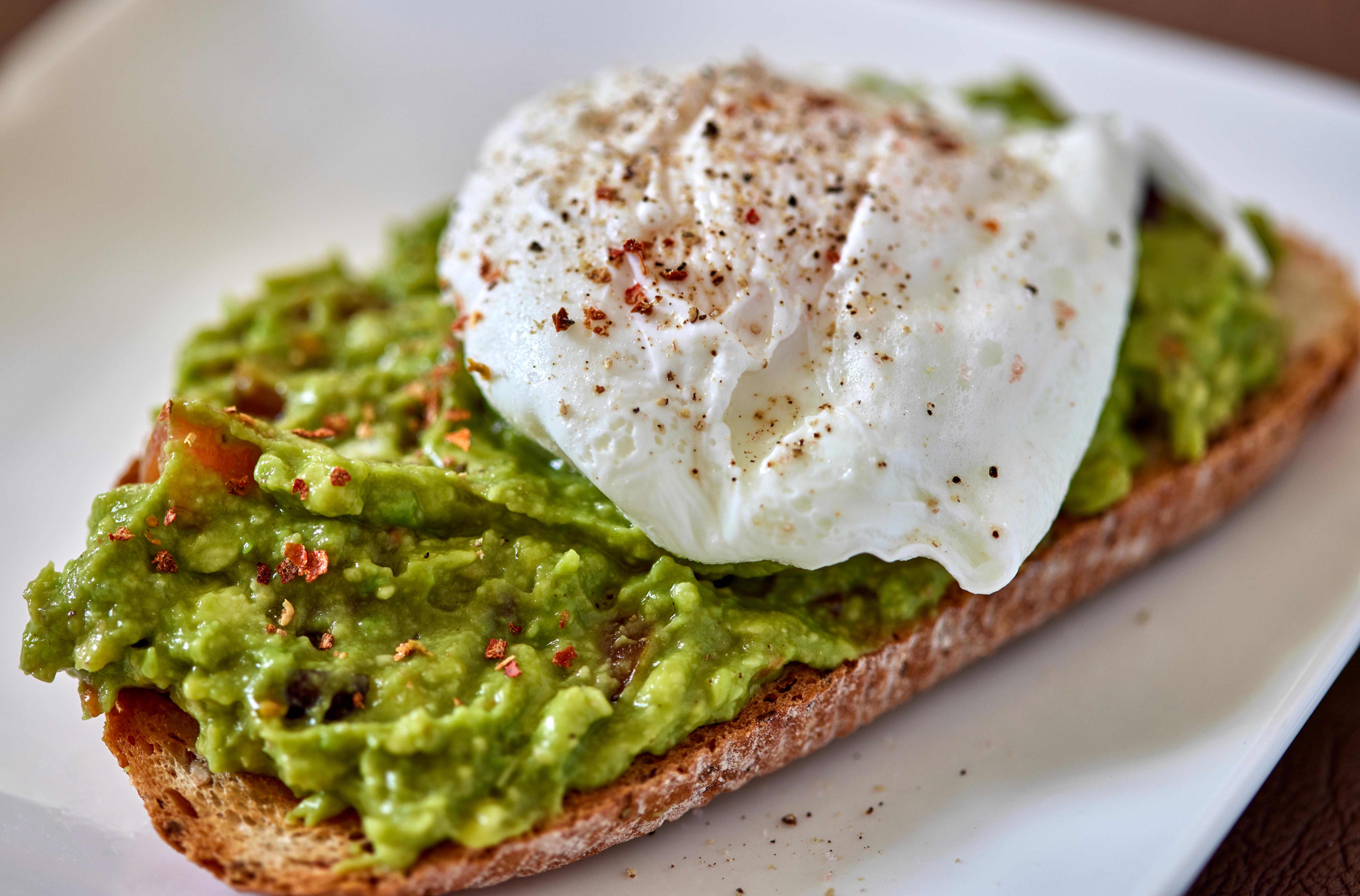

Nutrition plays a pivotal role in combating muscle loss and promoting longevity. As we age, our bodies require more protein to maintain muscle mass and repair tissues. A diet rich in high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins is essential. Additionally, adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin D and calcium, supports bone health and muscle function. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, have also been shown to enhance muscle protein synthesis and reduce inflammation. This section explores the nutritional strategies that complement strength training, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet in supporting muscle health. By understanding the synergistic relationship between nutrition and exercise, individuals can optimize their efforts to maintain strength and vitality as they age.
3. The Importance of Mind-Muscle Connection
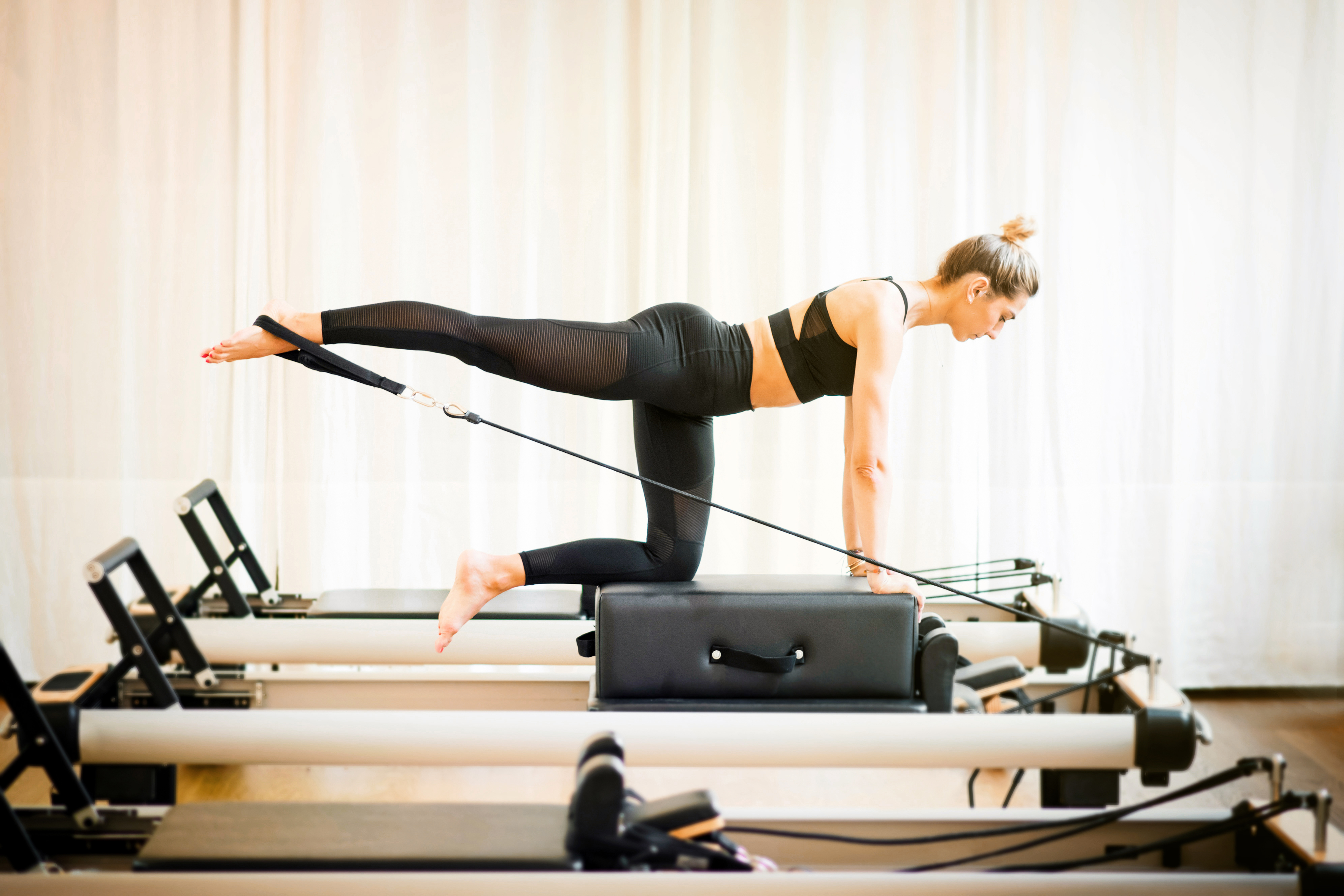

The mind-muscle connection is a crucial yet often overlooked aspect of strength training. This concept involves focusing on the muscle being worked during an exercise, enhancing neuromuscular activation and improving exercise effectiveness. As we age, maintaining a strong mind-muscle connection becomes increasingly important in preventing muscle loss. By concentrating on the quality of each movement and engaging the target muscles, individuals can maximize the benefits of their workouts. This section examines the techniques for developing a strong mind-muscle connection, including mindfulness practices and visualization. By integrating these methods into their training routines, individuals can enhance their strength gains and combat the effects of aging on muscle health.
4. Squats: The Foundation of Strength

Squats are a fundamental exercise for building lower body strength and combating muscle loss. They engage multiple muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core, making them an efficient and effective strength move. Squats also improve balance and stability, reducing the risk of falls in older adults. This section provides a detailed guide to performing squats correctly, addressing common mistakes and offering modifications for different fitness levels. By incorporating squats into their training regimen, individuals can maintain lower body strength and enhance their overall functional fitness. The benefits of squats extend beyond muscle maintenance, contributing to improved mobility and a higher quality of life.
5. Deadlifts: Building a Strong Back and Core
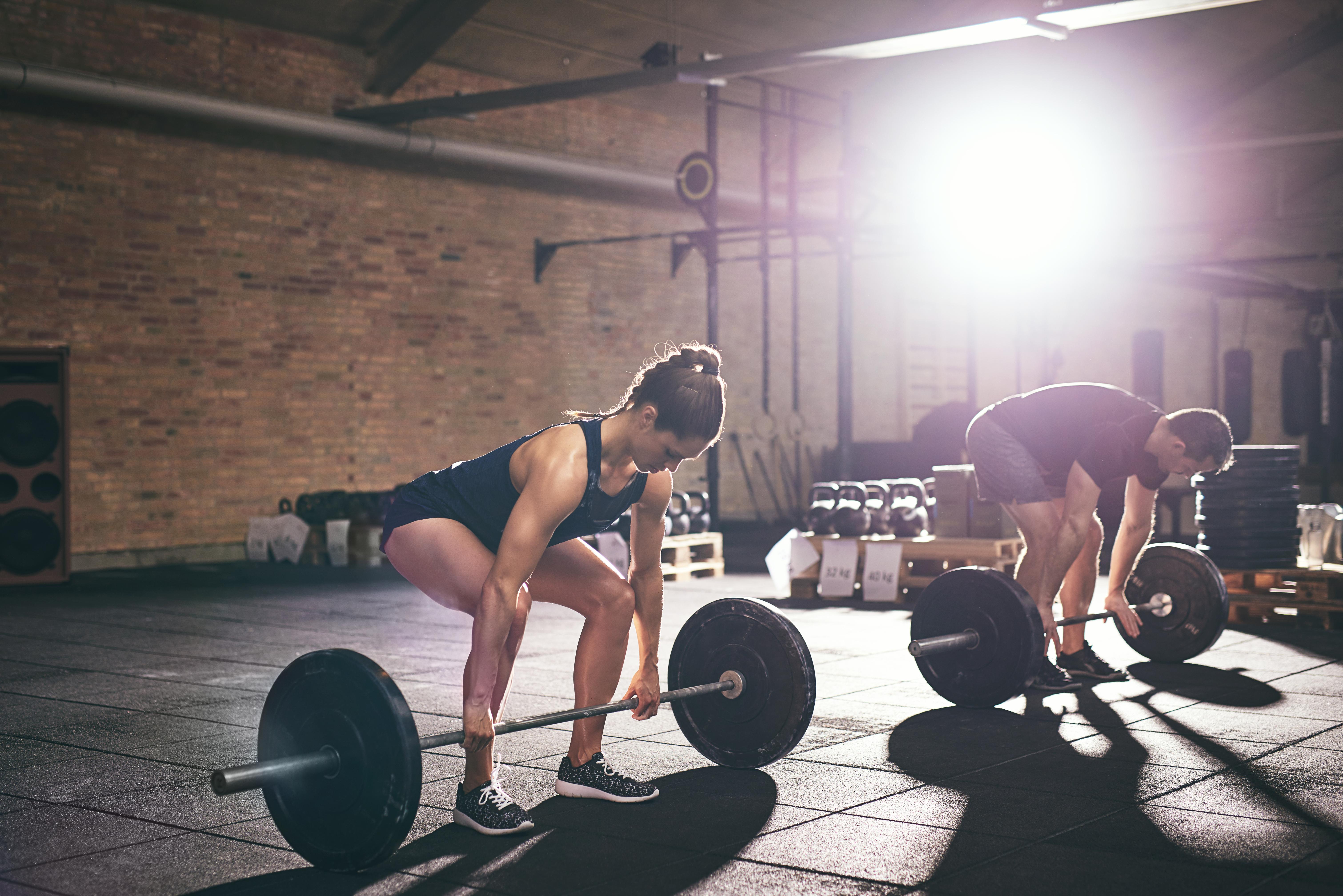

Deadlifts are a powerful exercise for strengthening the posterior chain, including the back, glutes, and hamstrings. They also engage the core, promoting stability and balance. As we age, maintaining a strong back is crucial in preventing posture-related issues and reducing the risk of injury. This section explores the benefits of deadlifts in combating muscle loss and enhancing functional strength. It provides step-by-step instructions for performing deadlifts safely and effectively, with variations to accommodate different fitness levels. By incorporating deadlifts into their routine, individuals can build a resilient back and core, essential components of longevity and vitality.
6. Push-Ups: Enhancing Upper Body Strength
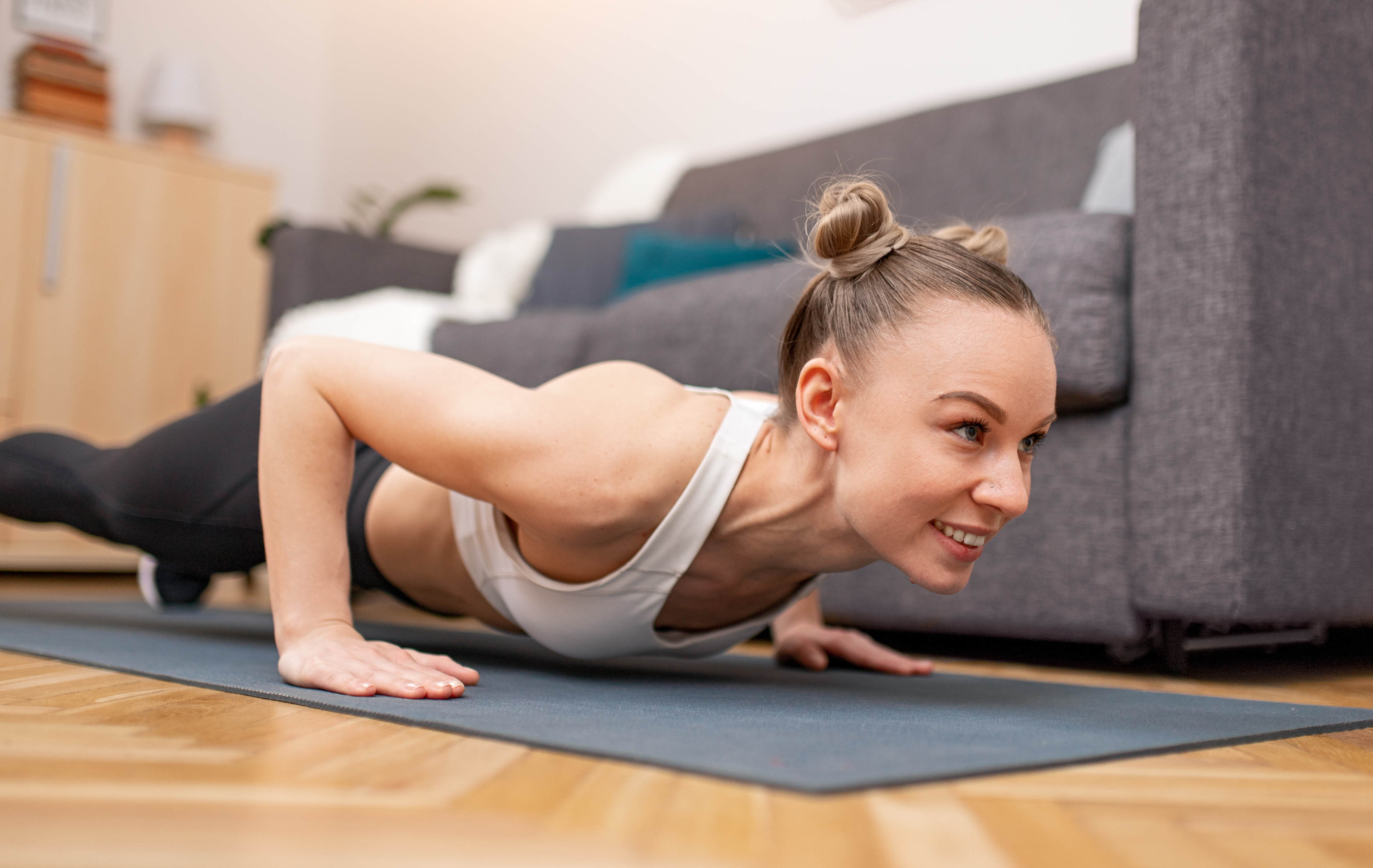

Push-ups are a versatile exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, triceps, and core. They are an excellent way to build upper body strength and combat muscle loss. Push-ups can be performed anywhere, making them a convenient option for maintaining strength as we age. This section offers a comprehensive guide to performing push-ups with proper form, addressing common challenges and providing modifications for different abilities. By incorporating push-ups into their training regimen, individuals can enhance their upper body strength and improve their overall fitness. The benefits of push-ups extend beyond muscle maintenance, contributing to better posture and increased functional capacity.
7. Lunges: Improving Balance and Coordination
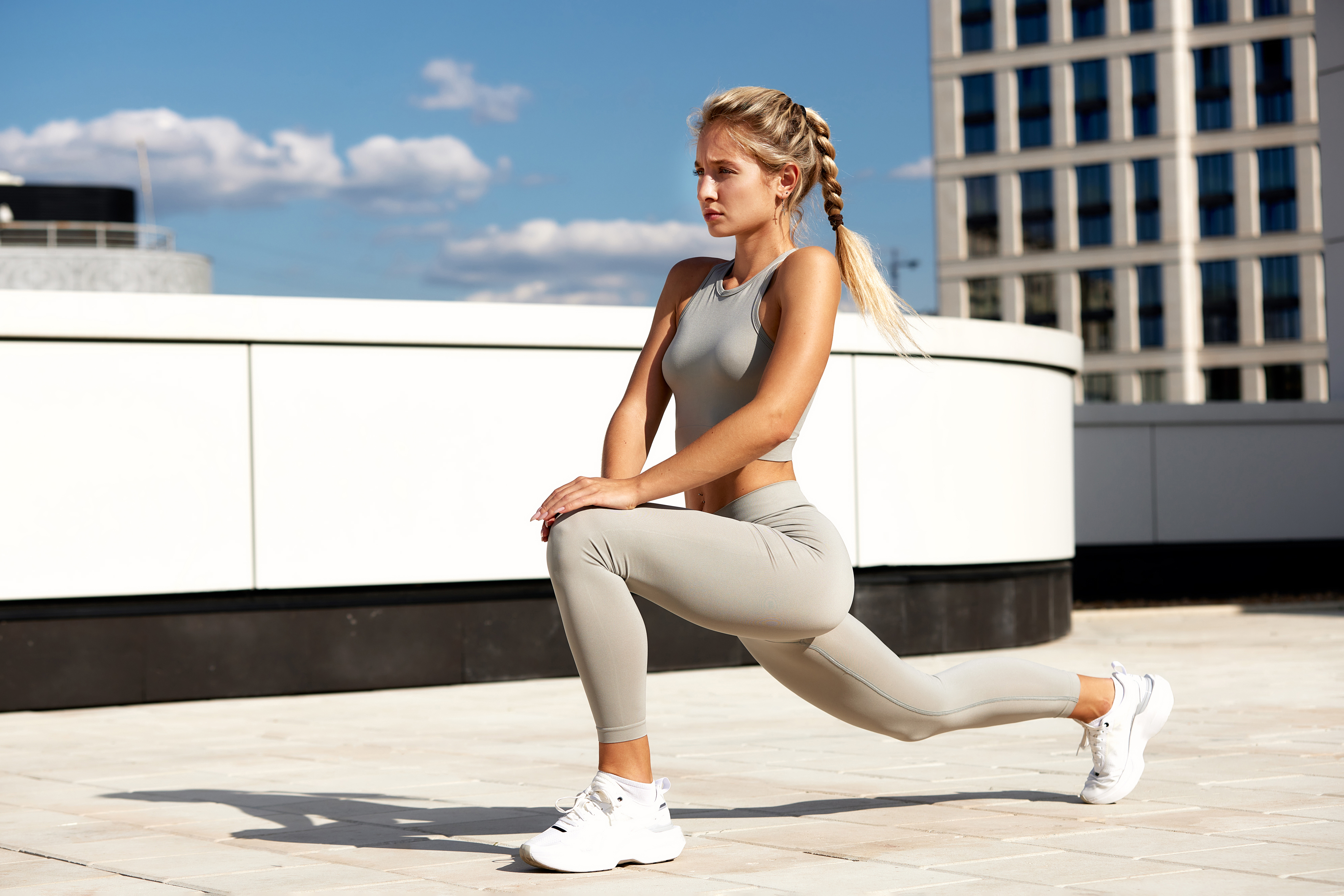

Lunges are a dynamic exercise that targets the lower body, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. They also improve balance and coordination, essential components of longevity. As we age, maintaining balance becomes increasingly important in preventing falls and injuries. This section explores the benefits of lunges in combating muscle loss and enhancing functional fitness. It provides detailed instructions for performing lunges safely and effectively, with variations to accommodate different fitness levels. By incorporating lunges into their routine, individuals can maintain lower body strength and improve their balance, contributing to a higher quality of life.
8. Planks: Building Core Stability
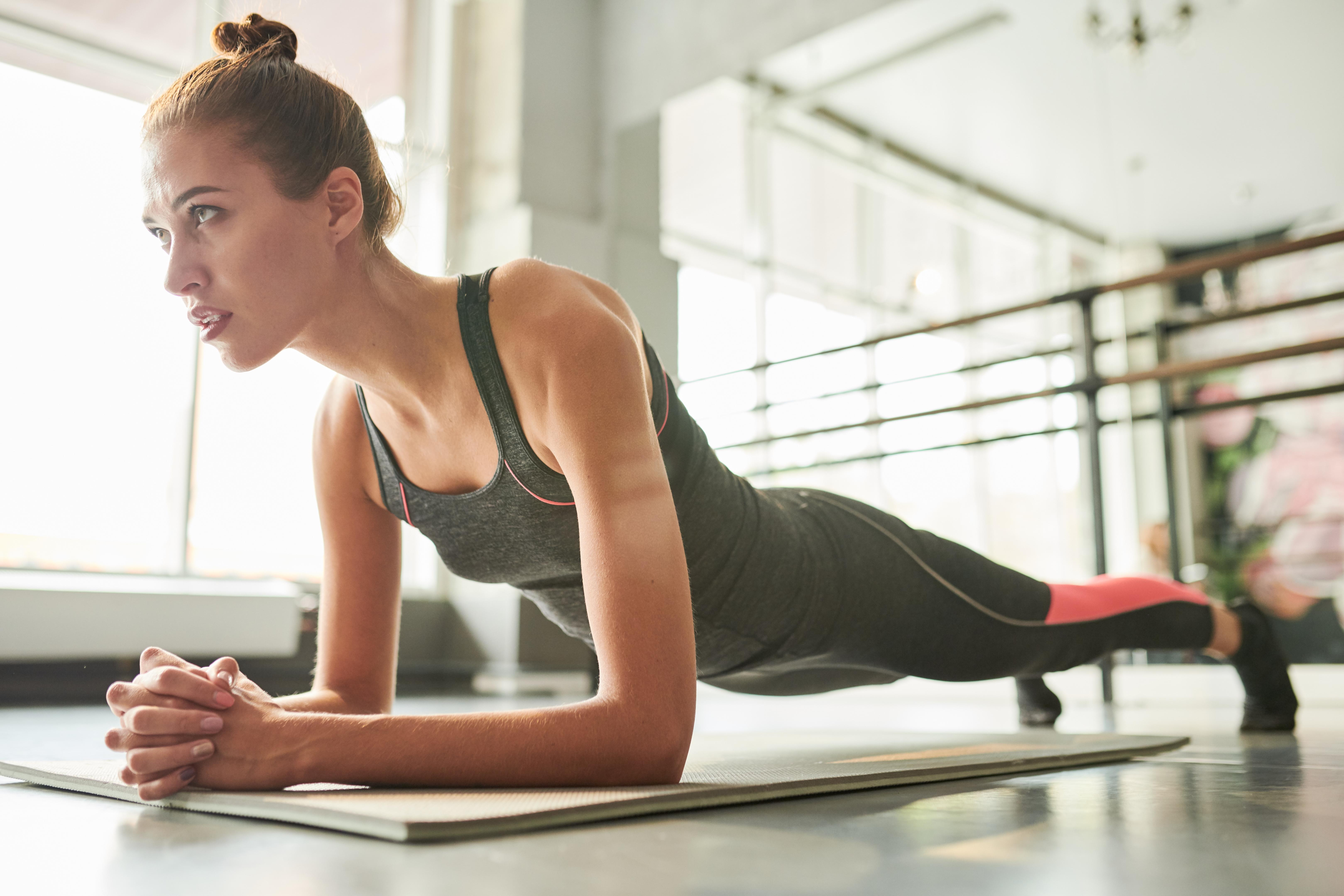

Planks are a highly effective exercise for building core stability and strength. They engage the entire core, including the abdominals, obliques, and lower back, promoting better posture and reducing the risk of injury. As we age, maintaining a strong core is crucial in supporting overall functional fitness. This section examines the benefits of planks in combating muscle loss and enhancing core stability. It provides step-by-step instructions for performing planks with proper form, addressing common challenges and offering modifications for different abilities. By incorporating planks into their training regimen, individuals can build a strong core and improve their overall strength and stability.
9. Bent-Over Rows: Strengthening the Upper Back

Bent-over rows are an effective exercise for strengthening the upper back, shoulders, and arms. They are particularly beneficial for combating muscle loss and improving posture. As we age, maintaining a strong upper back is crucial in preventing posture-related issues and reducing the risk of injury. This section explores the benefits of bent-over rows in enhancing upper body strength and overall functional fitness. It provides detailed instructions for performing bent-over rows safely and effectively, with variations to accommodate different fitness levels. By incorporating bent-over rows into their routine, individuals can build a resilient upper back and improve their posture, contributing to a higher quality of life.
10. Glute Bridges: Enhancing Hip and Lower Back Strength

Glute bridges are an excellent exercise for strengthening the hips, glutes, and lower back. They are particularly beneficial for combating muscle loss and improving hip mobility. As we age, maintaining strong hips is crucial in supporting overall functional fitness and reducing the risk of injury. This section examines the benefits of glute bridges in enhancing lower body strength and stability. It provides step-by-step instructions for performing glute bridges with proper form, addressing common challenges and offering modifications for different abilities. By incorporating glute bridges into their training regimen, individuals can build strong hips and improve their overall strength and mobility.
11. Overhead Press: Building Shoulder and Arm Strength

The overhead press is a powerful exercise for building shoulder and arm strength. It engages the shoulders, triceps, and upper chest, promoting better posture and reducing the risk of injury. As we age, maintaining upper body strength is crucial in supporting overall functional fitness. This section explores the benefits of the overhead press in combating muscle loss and enhancing upper body strength. It provides detailed instructions for performing the overhead press safely and effectively, with variations to accommodate different fitness levels. By incorporating the overhead press into their routine, individuals can build strong shoulders and arms, contributing to a higher quality of life.
12. Farmer's Walks: Building Real-World Resilience
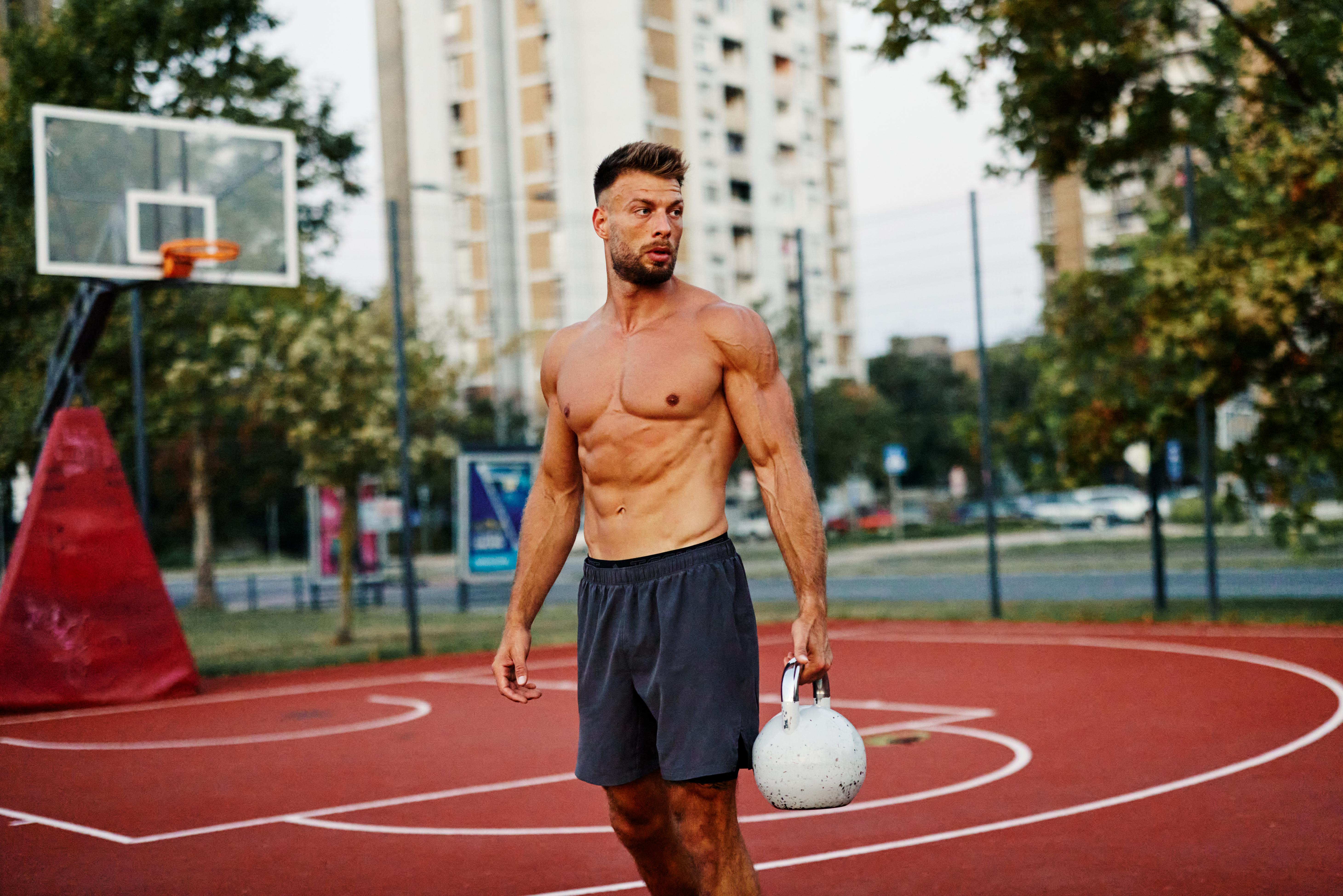

Imagine carrying heavy groceries or suitcases with ease – that’s the power of Farmer’s Walks. This deceptively simple exercise involves holding weights (dumbbells, kettlebells, or even heavy bags) at your sides and walking for a set distance or time. It’s phenomenal for building formidable grip strength – crucial for daily tasks – as well as challenging your core stability, improving posture, and enhancing overall endurance. Farmer's Walks translate directly to real-world strength, making everyday activities feel significantly lighter and safer as you age.
13. Pallof Press: The Anti-Rotation Guardian

Protect your spine and build a rock-solid core with the Pallof Press. Using a cable machine or resistance band anchored at chest height, you'll hold the handle at your chest and press it straight out, resisting the rotational force trying to pull you sideways. This anti-rotational exercise is incredible for strengthening deep core stabilizers, like the obliques and transverse abdominis, which are vital for preventing back pain and maintaining stability during dynamic movements. It’s a subtle but mighty move for long-term core integrity.
14. Bird Dog: Balancing Strength and Stability

The Bird Dog is a fantastic low-impact exercise for enhancing core strength, spinal stability, and balance. Starting on all fours, you’ll extend one arm straight forward and the opposite leg straight back, holding your core tight to prevent your torso from rotating or sagging. This movement improves proprioception (your body's awareness in space) and strengthens the muscles that support your spine, crucial for maintaining good posture and reducing the risk of falls. It’s an excellent foundational exercise for all ages, promoting controlled, coordinated movement.
15. Step-Ups: Elevating Leg Power and Balance

Mimicking the essential life skill of climbing stairs, Step-Ups are a brilliant exercise for building unilateral (one-sided) leg strength, improving balance, and boosting cardiovascular health. Simply step up onto a sturdy bench or platform with one leg, bringing the other knee up, then step back down. This move targets your quads, glutes, and hamstrings individually, helping to correct strength imbalances between legs. You can add weights as you progress, making it a versatile and highly functional addition to your routine for everyday power.
16. Face Pulls: The Posture Perfecter

Combat the forward hunch that can come with age and screen time by incorporating Face Pulls. Using a resistance band or cable machine anchored at chest or head height, grasp the ends and pull the band towards your face, aiming your hands towards your ears while squeezing your shoulder blades together. This exercise specifically targets the often-neglected muscles of the upper back and rotator cuff, crucial for improving posture, enhancing shoulder health, and preventing injuries. It's a game-changer for upright, confident bearing.
17. Single-Leg Romanian Deadlifts (RDLs): Unilateral Balance & Strength

Challenge your balance and build robust hamstring, glute, and lower back strength with the Single-Leg RDL. Standing on one leg (with a slight knee bend), hinge at your hips to lower your torso towards the ground while extending the other leg straight back for balance, keeping your back flat. This unilateral movement not only strengthens the posterior chain but also significantly improves balance and proprioception, vital for stability and fall prevention. Start with bodyweight and gradually add light dumbbells as you master the form.
18. Wall Slides (Scapular Wall Slides): Reclaiming Shoulder Mobility

Improve shoulder mobility, upper back engagement, and posture with gentle yet effective Wall Slides. Stand with your back against a wall, feet slightly away. Bend your elbows to 90 degrees, pressing your forearms, wrists, and the backs of your hands against the wall. Slowly slide your arms up the wall as high as you can while maintaining contact, then slowly slide them back down. This exercise helps activate and strengthen the muscles around your shoulder blades, countering rounded shoulders and promoting better overhead movement.
19. Calf Raises (Standing & Seated): Foundation for Mobility

Often overlooked, strong calf muscles are vital for balance, walking, and propelling movement. Standing Calf Raises (lifting your heels off the ground) target the gastrocnemius, while Seated Calf Raises (performed with knees bent, lifting heels) focus on the soleus muscle. Strengthening both contributes to ankle stability, better push-off during walking, and can even aid in venous return (blood flow back to the heart). These simple movements are essential for maintaining your foundational mobility and preventing lower leg weakness.
20. Band Pull-Aparts: Shoulder's Best Friend

For a simple yet incredibly effective exercise to bolster shoulder health and upper back strength, look no further than Band Pull-Aparts. Hold a resistance band with both hands, arms straight out in front of you at shoulder height. Keeping your arms straight (or with a slight bend), pull the band apart by squeezing your shoulder blades together. This movement strengthens the rhomboids and rear deltoids, crucial for good posture and stabilizing the shoulder joint, helping to prevent common aches and pains.
21. Side-Lying Hip Abductions: Stabilizing Your Stride
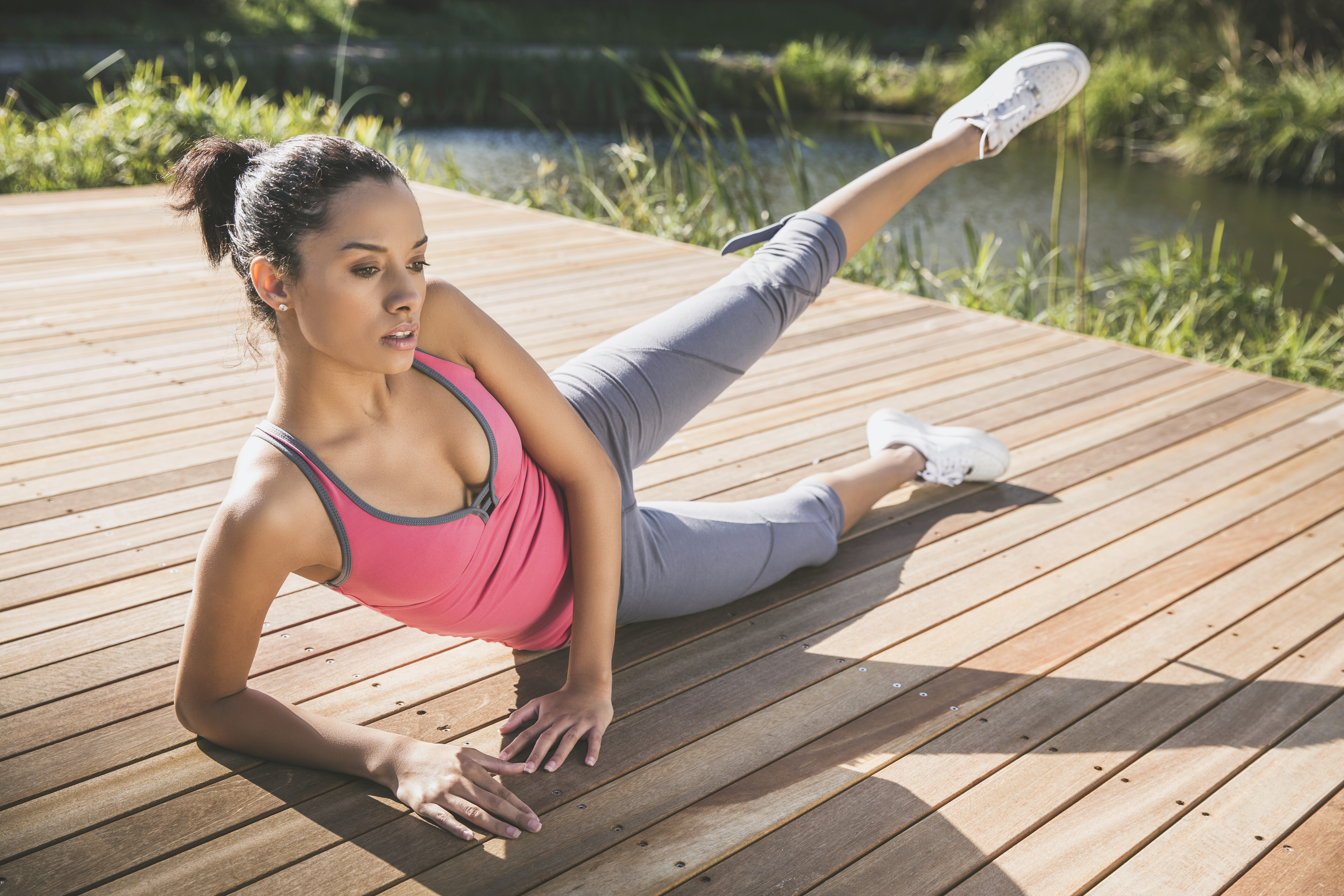

Strengthen your hip abductor muscles (like the gluteus medius) with Side-Lying Hip Abductions to improve balance, walking stability, and reduce the risk of knee and hip pain. Lie on your side with legs straight and stacked. Keeping your top leg straight and core engaged, lift the top leg towards the ceiling without letting your hips roll backward. This targeted movement is key for maintaining pelvic stability during single-leg activities like walking or climbing stairs, crucial for graceful and pain-free movement as you age.
A Holistic Approach to Longevity

Mastering the art of longevity involves a holistic approach that encompasses physical health, mental well-being, and emotional resilience. By incorporating these 21 essential strength moves into their training regimen, individuals can combat muscle loss and maintain their vitality beyond the age of 50. This article has explored the science of sarcopenia, the role of nutrition, and the importance of the mind-muscle connection in promoting muscle health. By understanding these factors and implementing effective strategies, individuals can lead an active, fulfilling life as they age. The journey to longevity is a lifelong commitment, but with the right tools and mindset, it is a journey that can be both rewarding and enriching.