Immunity 360: 12 Ways to Strengthen Your Body From the Inside Out
Building stronger immunity doesn't mean hunting for a single "silver bullet." Instead, a 360-degree approach combines everyday habits, targeted nutrition, smart supplementation, and informed clinical options. This article lays out twelve practical steps that work together to support immune resilience—from the small daily choices you can make right away to clinical tools that may help when there are real nutrient gaps or recovery needs. Each item pairs clear actions you can try, reasons why those steps matter, and when it makes sense to get a healthcare professional involved. Our aim is to give you practical, realistic strategies that fit busy lives and changing needs. Some readers will be focusing on baseline prevention; others may need help during recovery or while managing chronic conditions. Wherever you are, these suggestions honor that progress happens steadily, not instantly. Along the way, we'll flag where evidence is strong, where claims are mostly industry-based, and where more study is needed. If you're considering supplements, IV therapies, or other clinical options, use this guide as a starting point and bring your questions to a trusted clinician. Small, consistent habits often create the biggest long-term benefits for how you feel and how your immune system functions.
1. Prioritize Sleep Quality
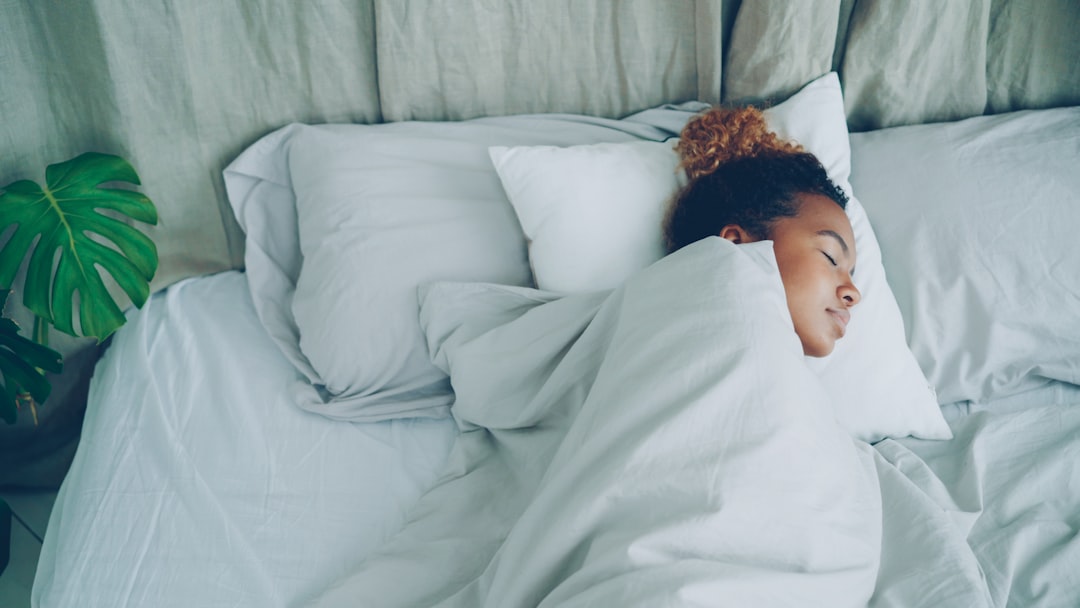

Quality sleep is one of the most reliable foundations for a resilient immune system. During deep sleep, the body carries out repair tasks and helps immune cells consolidate memory so they respond better to infections. Short, disrupted sleep weakens these processes. Start by creating a regular bedtime routine that signals rest to your nervous system. That could be dimming lights, avoiding screens for 30–60 minutes before bed, and keeping the room cool and quiet. Aim for a consistent sleep schedule—even on weekends—because regularity helps the body’s internal clock and supports hormone rhythms tied to immunity. If falling asleep is hard, try brief relaxation practices before bed, like diaphragmatic breathing or a five-minute guided meditation. For older adults, consider light exposure earlier in the day to support circadian rhythm and avoid heavy meals before bedtime. If you suspect sleep apnea, chronic insomnia, or restless legs are interfering with rest, speak with a healthcare provider for testing and treatment. Better sleep doesn't require perfection: layered small changes add up and often improve both energy and resistance to illness over time.
2. Nourish with an Anti-Inflammatory, Whole-Food Diet
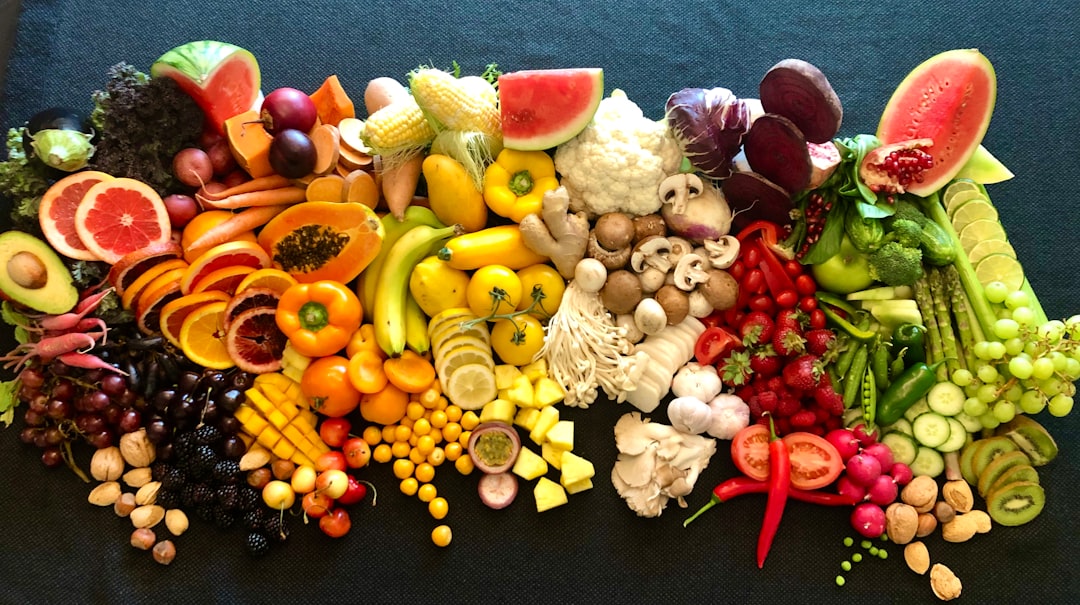

Food is everyday medicine when it comes to immune-supporting nutrients and inflammation control. Emphasize a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, which deliver vitamins, minerals, and polyphenols that modulate immune response. Include whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish for steady energy, plant-based fiber, and omega-3 fats that support healthy inflammation signaling. Aim for meals that combine a lean protein, vegetables, a whole grain or starchy vegetable, and a healthy fat to stabilize blood sugar and supply building blocks for immune cells. Simple swaps can make a difference—choose berries instead of sugary snacks, roast a sheet pan of mixed vegetables for easy reheats, or add a serving of oily fish twice a week. Avoid diets overly high in ultra-processed foods and added sugars, which can promote chronic inflammation and blunt immune function over time. For people with specific needs—food intolerances, dietary restrictions, or chronic conditions—work with a registered dietitian to create a sustainable eating plan that supports both vitality and immune health.
3. Manage Stress with Daily Practices
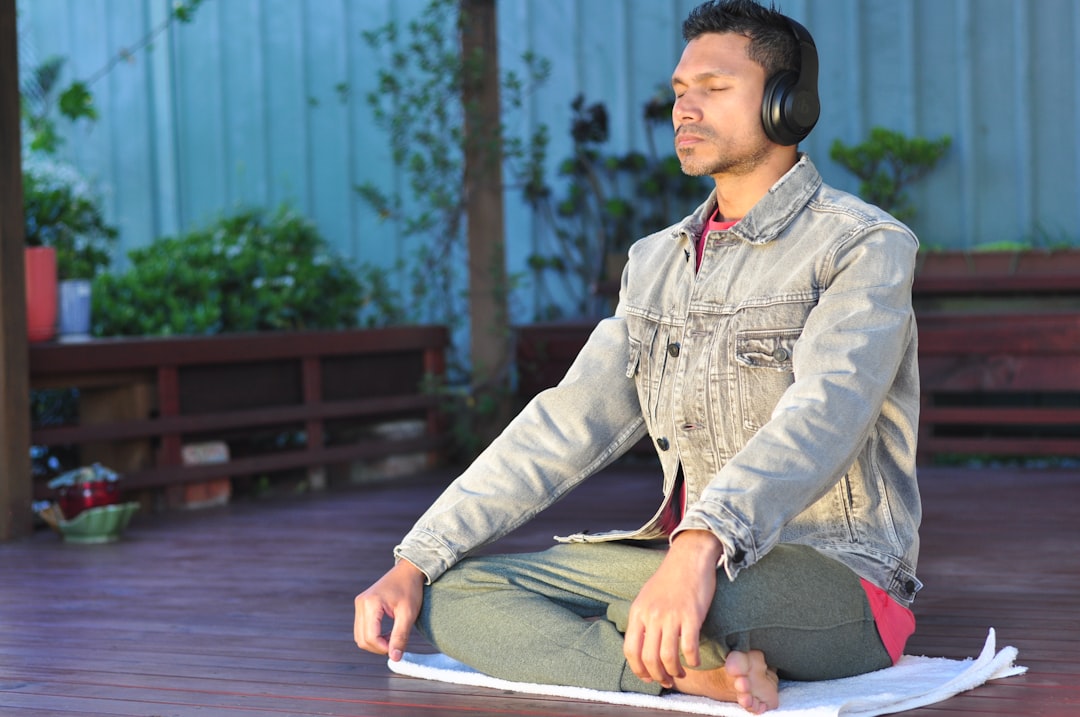

Chronic stress affects hormones like cortisol and can shift immune responses in ways that make it harder to fight infections or recover from illness. That doesn't mean stress-free living is the goal; rather, practical ways to lower daily stress build resilience. Pick short, repeatable practices you can use anywhere. Ten deep breaths at your desk, a five-minute progressive muscle relaxation before bed, or a daily walk without screens are all concrete tools. Social connection also buffers stress—regular chats with friends or family contribute to wellbeing and immune balance. When life feels particularly demanding, prioritize small, replenishing actions: a brief stretch break, a cup of tea without multitasking, or a quick gratitude note. If anxiety or persistent stress interferes with sleep, appetite, or daily functioning, seek support from a mental health professional. Over time, consistent stress-care is one of the most compassionate investments you can make in both mood and immune health.
4. Move Regularly with Aerobic and Strength Work
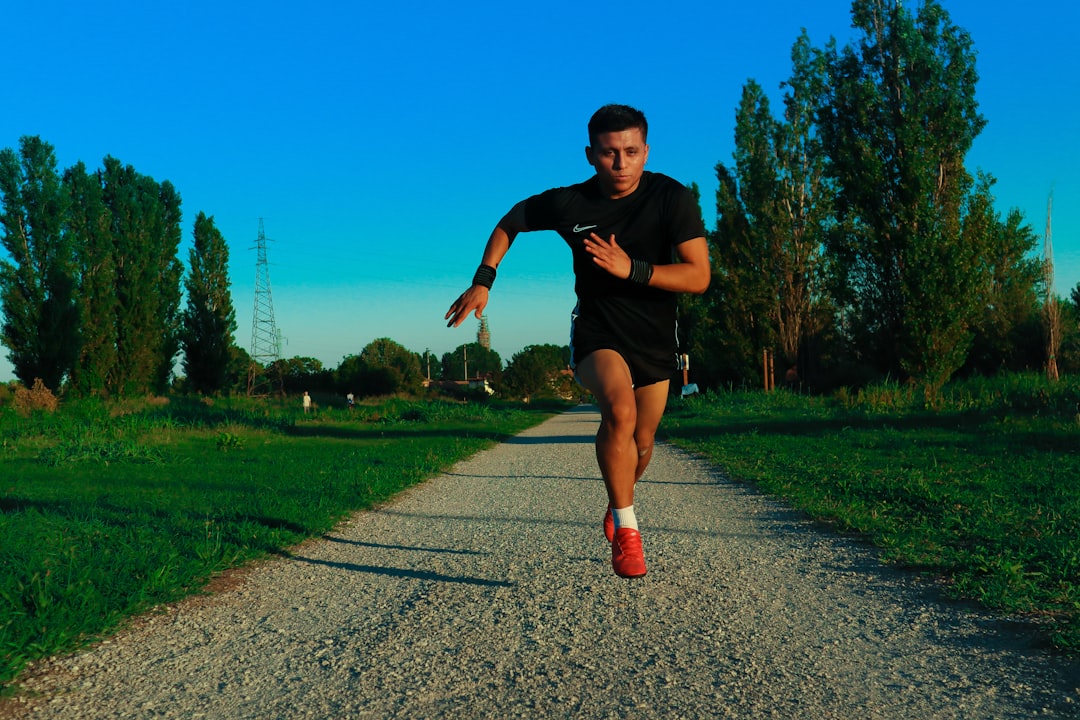

Regular physical activity supports immune surveillance, circulation, and recovery. Moderate aerobic exercise—walking, cycling, swimming—encourages healthy immune cell distribution and reduces inflammation. Strength training preserves muscle mass and protein reserves that the body uses during recovery from illness, which is especially important as we age. Aim for a mix: moderate aerobic movement most days and two to three strength sessions per week. Sessions can be brief; even two 20–30 minute workouts deliver benefits. Gentle flexibility work and balance exercises help reduce injury risk and keep movement sustainable. Importantly, avoid sudden spikes of very intense training without recovery, which can temporarily suppress immune function. If you're returning to exercise after a long break or managing chronic conditions, start slowly and consider working with a trainer or physical therapist for a tailored plan. Movement should be enjoyable and achievable—pick activities you like so consistency becomes part of daily life.
5. Support Gut Health: Prebiotics, Probiotics, and Fiber
The gut microbiome plays a major role in immune education and the body’s response to pathogens. A diverse diet rich in fiber feeds beneficial microbes and supports mucosal defenses. Include prebiotic foods like onions, garlic, leeks, bananas, and whole grains to nourish helpful bacteria. Fermented foods—yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, miso—offer live cultures that can support gut balance for many people. For targeted situations, certain probiotic strains have evidence for reducing respiratory and gastrointestinal infections in specific populations; choose products backed by reputable manufacturers and look for strain-specific studies when possible. If you take antibiotics, a probiotic can help reduce antibiotic-associated diarrhea, but discuss timing and product choice with your clinician. Avoid treating probiotics as a cure-all: a food-first approach is foundational, and testing or specialist input can be useful for persistent gut issues or complex health conditions. Small, consistent changes to diet often translate to meaningful improvements in digestive comfort and immune-linked outcomes.
6. Keep Vitamin D in a Healthy Range

Vitamin D supports immune cell function and mucosal defenses, and many adults have levels lower than optimal—especially in winter or with limited sun exposure. Aim to get vitamin D status checked if you have risk factors such as darker skin, obesity, limited sun exposure, or certain chronic conditions. Safe sun exposure can boost vitamin D naturally, but supplementation is often the practical method to correct deficiency. Work with a provider to test levels and determine an appropriate dose rather than guessing. Typical daily maintenance doses vary by individual; higher doses to correct deficiency should be supervised medically. Food sources include fortified dairy or plant milks, fatty fish, and eggs, but those foods alone often don't supply enough for people with low levels. Maintaining a healthy vitamin D range supports immune balance but is one piece of a broader strategy that includes sleep, nutrition, and activity.
7. Prioritize Key Micronutrients: Zinc, Selenium, and Protein

Certain micronutrients are especially important for immune cell function and repair. Zinc helps with immune cell development and wound healing; selenium supports antioxidant enzymes and immune responses. Good food sources of zinc include oysters, lean meats, beans, and nuts. Selenium appears in foods like Brazil nuts, seafood, and whole grains; just a single Brazil nut can provide a substantial portion of a daily selenium need, so be mindful of portion sizes. Protein matters too—adequate protein supports the formation of antibodies and tissue repair after illness. Aim for a serving of high-quality protein at meals, adjusting portions to individual needs and health status. While supplements can correct clear deficiencies, they should be used thoughtfully since excess intake can cause harm. If you suspect dietary gaps, consider a lab test or consult a registered dietitian to prioritize targeted, safe interventions.
8. Hydration, Alcohol Moderation, and Gut-Friendly Habits

Staying well-hydrated supports mucosal barriers in the nose and throat—the first line of defense against pathogens. Hydration needs vary with body size, activity level, and climate, but regular fluid intake throughout the day helps maintain circulation and supports cellular functions. Plain water is effective; include herbal teas and water-rich foods if you prefer. Alcohol has short- and long-term effects on immune function and sleep, and high consumption can impair immune defenses. If you drink, aim for moderation and consider alcohol-free days each week. Gut-friendly habits—like chewing slowly, eating regular meals, and avoiding high-sugar beverages—also support digestion and the microbiome. Small shifts such as carrying a water bottle, swapping one daily cocktail for sparkling water with citrus, or choosing plain yogurt as a snack add up to better overall resilience and daily wellbeing.
9. Smart Supplement Use: Vitamin C, Zinc, and Evidence-Based Formulas

Supplements can help when dietary intake or testing shows a shortfall, but they are not a replacement for a healthy diet and lifestyle. Vitamin C and zinc are two commonly used supplements for short-term immune support; evidence suggests they may shorten the duration of some colds when used appropriately. Choose reputable brands and check ingredient lists for doses and form—some forms are easier on digestion than others. Read labels for third-party testing seals to reduce the risk of contaminants or dose inconsistencies. Avoid megadoses without medical supervision since excessive intake can cause side effects and interfere with other nutrients. If you're taking medications or managing chronic conditions, consult your clinician or pharmacist about interactions. Treat supplements as targeted tools: useful in specific contexts, but part of a layered approach rather than a standalone solution.
10. Cellular Support: CoQ10, NAD+ and Metabolic Health

Immune cells rely on healthy cellular energy and mitochondrial function to respond to threats effectively. Nutrients such as CoQ10 support energy production in cells, and metabolic health—regulated by sleep, nutrition, and activity—underpins immune resilience. Emerging therapies like NAD+ supplementation or IV-based NAD+ claim benefits for cellular repair and energy; research is still developing and evidence varies by condition. For most people, focusing first on metabolic health through balanced meals, movement, regular sleep, and stress management offers the greatest benefit with the least risk. If you are exploring supplements or advanced therapies for cellular support, discuss goals and potential risks with a clinician who understands your medical history. Where clinical treatments are pursued, prioritize providers who use testing, monitor vital signs, and explain realistic outcomes rather than promising rapid fixes.
11. IV Nutrition and Wellness Shots: Pros, Cons, and Questions to Ask

IV nutrition and wellness shots deliver vitamins and minerals directly into the bloodstream and are offered by clinics as a fast way to raise nutrient levels. Some clinics emphasize the advantage of bypassing the digestive system for better absorption when oral routes are insufficient. However, many claims around IV therapy come from commercial providers and are not yet confirmed by large, peer-reviewed studies for general immune boosting. There are situations where intravenous or intramuscular nutrient delivery is medically appropriate—such as diagnosed deficiencies, malabsorption syndromes, or perioperative care—but these approaches should be guided by tests and a licensed clinician. Before trying IV therapy, ask about credentials, sterile technique, the evidence for proposed benefits, potential risks, and less invasive alternatives. Always consider cost, safety, and whether the treatment complements foundational habits. When used selectively and responsibly, such therapies can be part of a broader plan—but they are seldom a substitute for consistent lifestyle-based immunity support.
12. Personalized Preventive Care: Vaccination, Screenings, and Professional Guidance
Preventive healthcare is a cornerstone of any immune-strengthening strategy. Staying current with recommended vaccinations reduces risk for specific serious illnesses and supports community health. Routine screenings and chronic disease management—blood pressure checks, diabetes screening, and thyroid evaluation, for example—identify conditions that can affect immune function and are best managed proactively. Work with your primary care provider to build a tailored preventive plan that considers age, medical history, and lifestyle. For older adults and those with chronic conditions, personalized guidance often includes nutrition counseling, medication reviews, and referrals to specialists when needed. A strong partnership with trusted clinicians helps you prioritize interventions, interpret lab results, and decide when advanced therapies or supplements are appropriate. Prevention is both practical and empowering; it lets you allocate time and resources where they matter most for long-term resilience and quality of life.
A Practical, Compassionate Path to Stronger Immunity

Immunity 360 is about combining steady daily habits with thoughtful, evidence-aligned choices. The steps above are not a checklist of one-off fixes; they're a layered roadmap that begins with sleep, food, movement, and stress care, and moves toward targeted supplements or clinical options when appropriate. Remember that progress is gradual, and small, consistent changes produce ripple effects in energy, recovery, and resistance to illness. When considering supplements, IV therapy, or newer metabolic treatments, prioritize reputable sources of information, third-party testing, and conversations with clinicians who know your health history. Celebrate the small wins: an extra hour of sleep, a colorful plate at dinner, a short walk after lunch—these build real resilience over months and years. Finally, be kind to yourself through the process and aim for steady improvements rather than perfection. A supportive, whole-person approach honors the wisdom of your life experience while giving your body the practical care it needs to stay strong from the inside out.