What Increases The Risk Of Eye Melanoma?
Eye melanoma is a form of cancer that develops in the melanocytes or cells that give the eyes their coloring. Most often, eye melanomas will develop in the region of the eye that cannot be seen upon looking into a mirror. Eye melanoma also doesn't cause any early signs or symptoms. Both of these factors make this type of cancer particularly difficult to detect. When symptoms do manifest, they will usually include a growing dark spot on the iris, a change in pupil shape, blurry vision in one eye, peripheral vision loss, and a sensation of specks or flashes in the vision. These changes typically occur quickly once the melanoma has become advanced. A primary concern with eye melanoma is the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
While most causes of eye melanoma are unknown, numerous factors will put certain individuals at a higher risk of developing it.
Ocular Melanocytosis
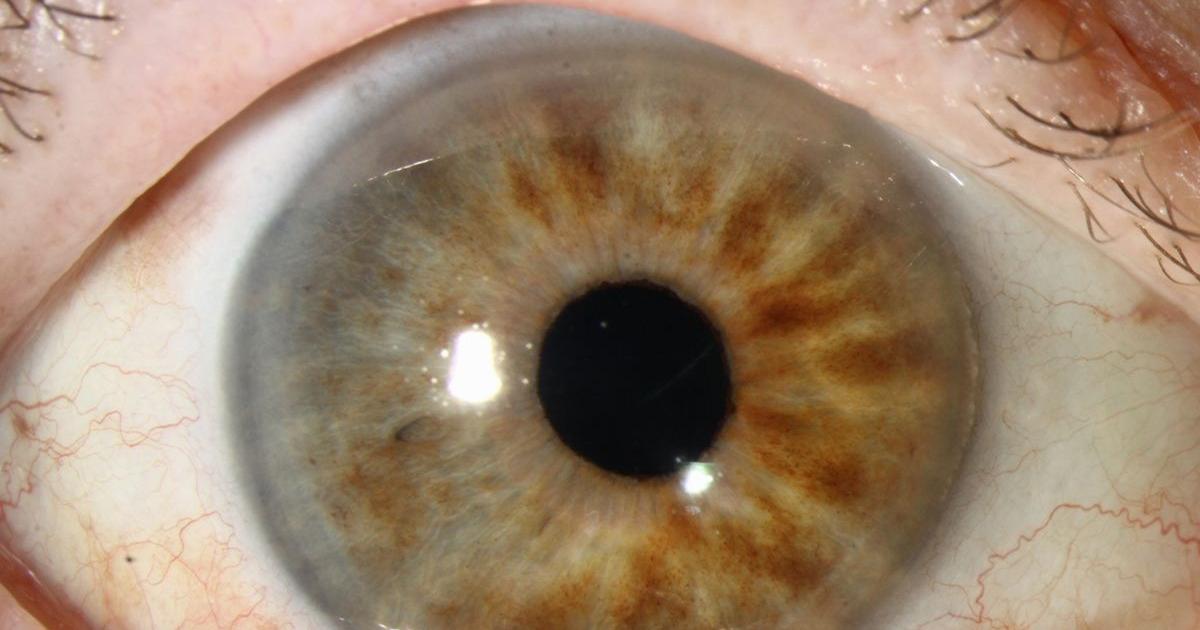
Ocular melanocytosis or melanosis oculi is a congenital eye disease where there is an increased number of melanocytes in the iris or the colored region of the eye, the choroid or vascular eye layer, and surrounding areas. It can present itself in several ways including iris heterochromia or different colored eyes, blue or gray discoloration in the sclera or the white outer eyeball layer, and other discolored lesions around the pupil. Essentially, an individual who has ocular melanocytosis has freckles and discolored spots in their eyes due to the abnormal clumping together of melanocytes or pigment-producing cells. Just like discolorations such as freckles or moles on the skin increase the risk of developing skin melanoma, these freckles or discolorations in the eye due to ocular melanocytosis can also increase an individual's risk of developing eye melanoma. In addition, roughly half of all diagnosed skin melanomas are known to originate from existing moles and skin discolorations. Because the mechanism of eye melanoma is similar to that of skin melanoma, it is likely a considerable percentage of eye melanomas also originate from the eye spots that occur in individuals with ocular melanocytosis.
Learn more about what can increase the risk of eye melanoma now.
Lighter Eye Color
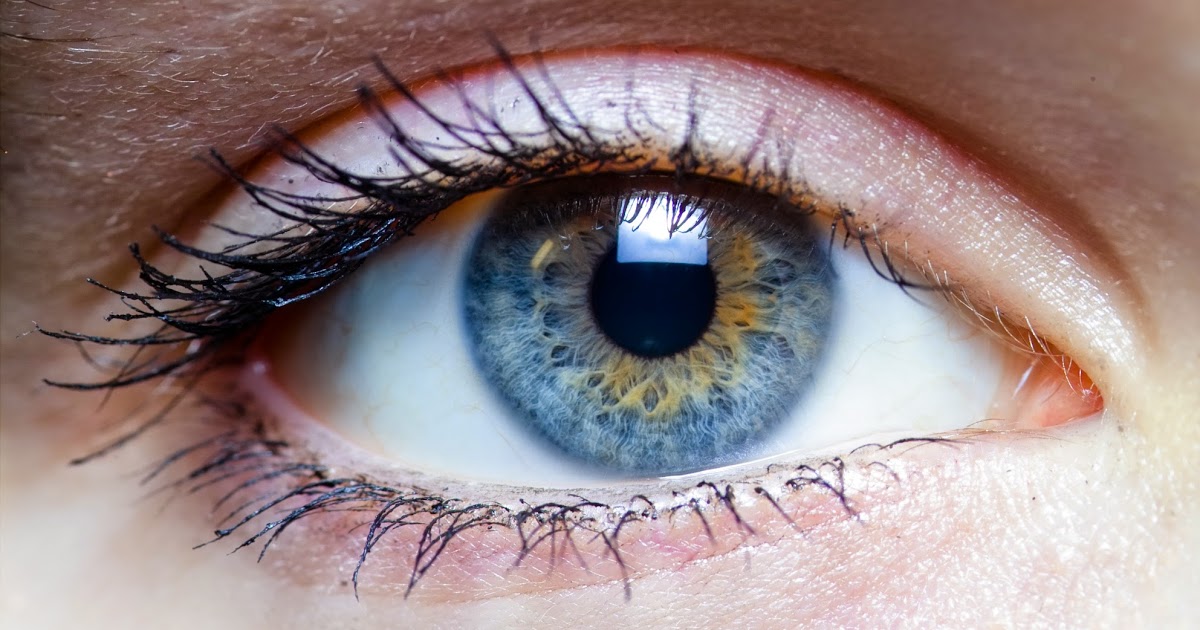
Eye melanoma is a type of cancerous tumor that develops in the cells of the iris or the pigmented part of the eye. Individuals with lighter eye colors have a higher susceptibility to developing eye melanoma because they have less protection against harmful UV rays. When the iris contains more melanin, that melanin helps stop the harmful light from penetrating into the eye. The way melanin works to protect cells from ultraviolet light is by absorbing the UV energy and redirecting it away from healthy cells. Because darker pigments are a result of higher levels of protective melanin, individuals with darker colored eyes have a lower risk of developing eye melanoma than individuals with lighter eyes.
Keep reading for more details on the risk factors for eye melanoma now.
Exposure To Ultraviolet Light
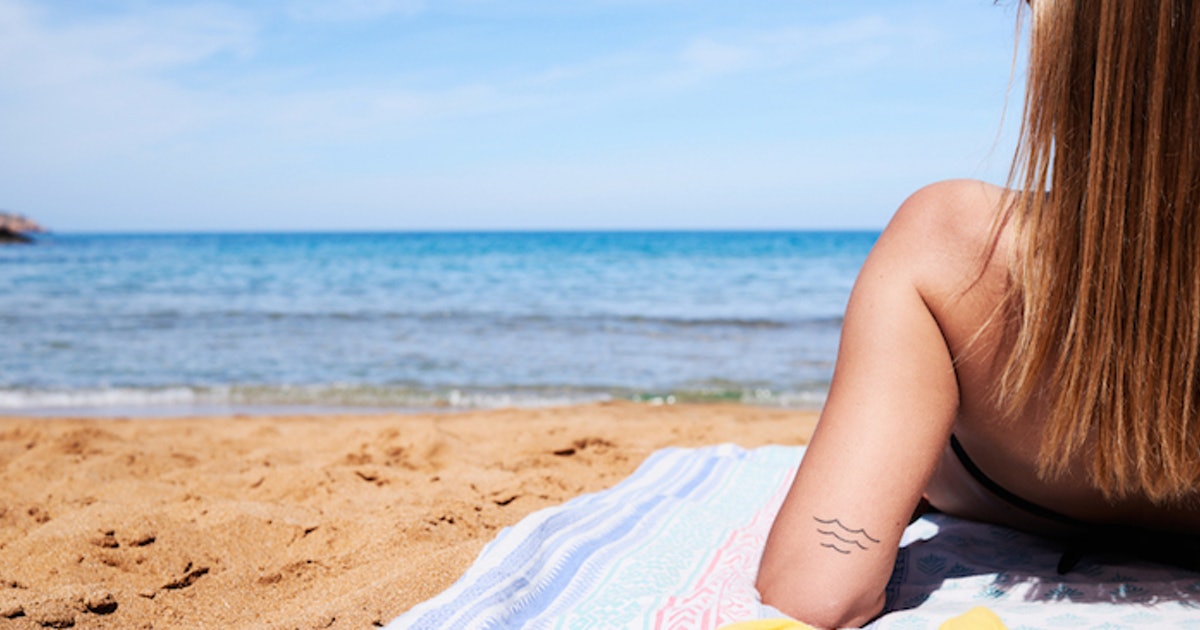

Ultraviolet (UV) light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that comes from the sun and a few other sources. This radiation is projected in the form of particles or waves in numerous frequencies and wavelengths. There are three main types of UV light rays. UVC rays have the highest amount of energy, but they cannot penetrate the atmosphere enough to cause cancer. UVA rays have less energy then UVC and UVB rays, however, they can age the skin and sometimes cause cancer. UVB rays are the highest energy rays that are able to penetrate the earth's atmosphere, and they directly damage the DNA in human and animal cells. Cancer starts developing when this damage occurs to the part of the cellular DNA containing the genes that control cell growth. Ultraviolet light is also able to damage the cellular DNA repair process, and this provides a way for mutated cells to acquire the ability to evade cellular death. The key to prevention of eye melanoma is to limit eye exposure to ultraviolet light. Ultraviolet light is most damaging to the cells in the eye at specific times of the day, during certain seasons, in locations closer to the equator, at higher altitudes, and in conditions of minimal cloud cover.
Get the details on more risk factors for eye melanoma now.
Dysplastic Nevus Syndrome
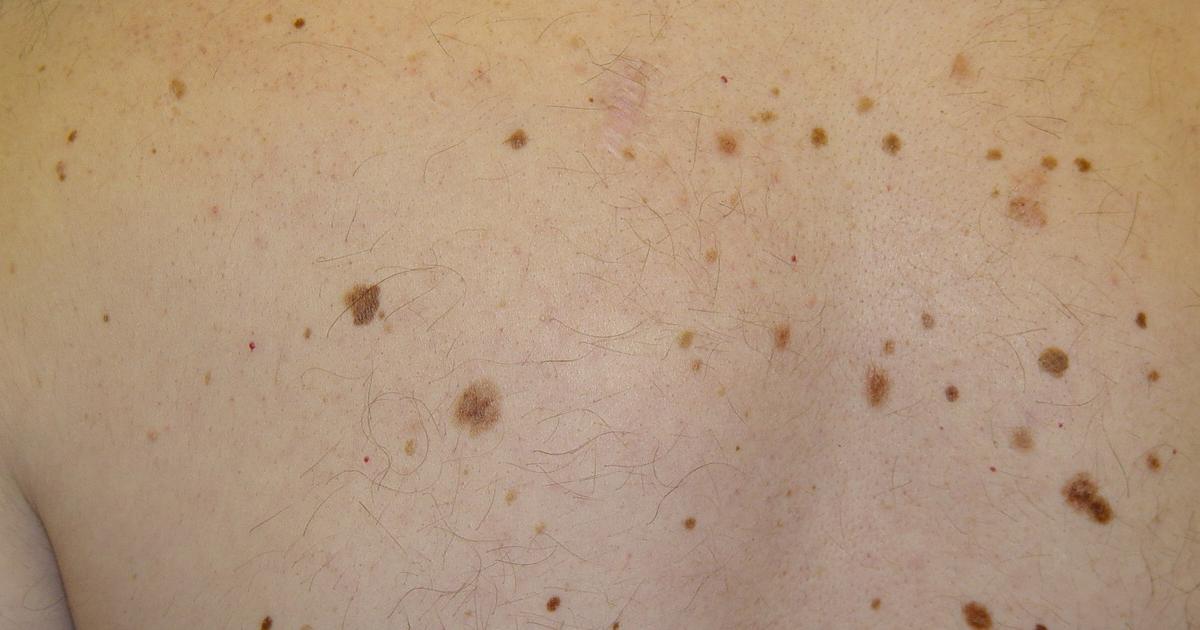
Dysplastic nevus syndrome is a skin condition that manifests itself through the presence of a large number of atypical moles around the body. When dysplastic nevus syndrome is inherited, it is most likely a result of DNA mutations in the CDKN2A gene. The excessive irregular moles that occur in dysplastic nevua syndrome patients are caused by overstimulation of the system of cells that create melanin or the melanocytic system. However, this overstimulation is not isolated to just the skin tissues. This also occurs in the colored region of the eye. The overstimulation causes an increased incidence of localized spots of melanocytic proliferation or melanocyte overgrowth in the eye. This overgrowth is what is responsible for discolorations or spots in the colored region of the eye. Because eye melanoma often originates from eye spots and discolorations, individuals with dysplastic nevus syndrome are at a higher risk for developing it.
Uncover the next risk factor for eye melanoma now.
Being Caucasian

Eye melanoma is more common in individuals with lighter skin tones than it is in individuals with darker skin. This occurs because individuals with light skin have less melanin in their body overall. Melanin is what gives the eyes, hair, and skin its pigmentation. Melanin also protects cells by absorbing and deflecting the UV energy away from healthy cells in the interior tissues of the body. Individuals who have less melanin in their skin are more likely to have less melanin in the iris or the colored part of the eye. Less melanin in these areas results in less protection from the harmful and damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation from the sun and other sources. In addition, individuals with lighter skin tend to have more discolorations in their iris and on their skin such as freckles and moles. The group of individuals in the population who have fair skin tones and blue colored eyes are the most affected by eye melanoma. Even though having a light eye color and being Caucasian are independent risk factors of this type of cancer, an individual with both of these characteristics is at a higher risk than someone who only has one of them.
