10 Antibiotics That Will Treat Prostatitis
Prostatitis is a group of conditions affecting the prostate gland including acute bacterial infections to chronic pain disorders. Symptoms also vary, and patients can expect urinary obstruction, fever, myalgias, low sex drive or impotence, painful ejaculation, and low-back pain. Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis is usually treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. When the infection is bacterial-caused, antibiotic treatments are required for up to several months. A number of antibiotics are available based on individual diagnoses.
1. Levofloxacin
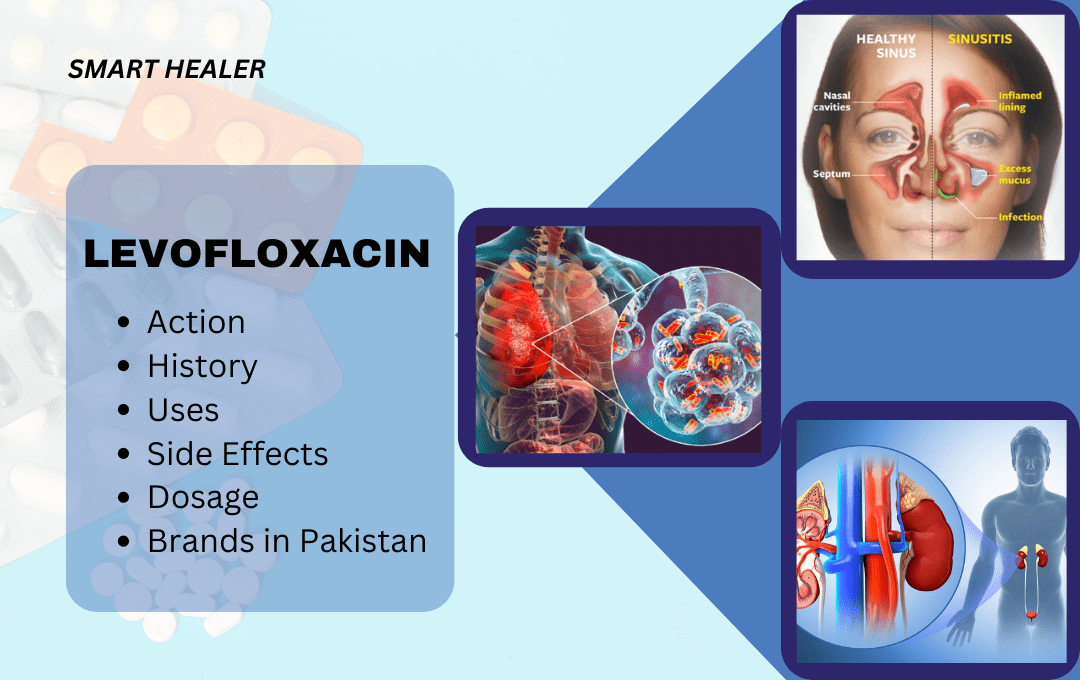
Levofloxacin is used to combat the ill effects of the bacteria Escherichia coli, E faecalis, or Staphylococcus epidermidis. It can be used on its own and has been an effective treatment for Pseudomonas species as well as pneumococcus. Side effects of its use include nausea, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, lightheadedness, or trouble sleeping, but prescriptions are made to those whose benefits will outweigh the side effects. Other serious side effects pose threats to the kidney, liver, and stomach.
2. Ceftriaxone
Taken by injection, ceftriaxone kills bacteria associated with prostatitis, as well as other bacterial infections. The powder is mixed with a liquid before use, and the positive results are seen within the first few days. Typical side effects of the drug include pain, tenderness, or hardness surrounding the area of injection, as well as pale skin, weakness, shortness of breath, and diarrhea. More serious side effects include chest pain, problems urinating, and seizures.
3. Carbenicillin
Carbenicillin is an antibiotic belonging to the carboxypenicillin subgroup of the penicillins.
4. Cefazolin
Unlike many antibiotics taken orally, cefazolin is usually injected at the doctor’s office or hospital. Those doing injections at home have to make sure their dose is free of debris and is not clouded or discolored. Minor side effects are typical, and users may expect nausea, loss of appetite, and mild diarrhea, but in rare cases, users have experienced a change in skin color, pain, leg and foot swelling, and tenderness.
5. Minocycline
Minocycline is in the class of tetracycline drugs. This antibiotic is used for bacterial infections and is not effective for viruses, but can be useful for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Common products like iron supplements, multivitamins, calcium supplements, antacids, and laxatives should not be taken in combination with minocycline. Typical side effects of the drug include nausea, diarrhea, headaches, and muscle pain. Any signs of organ problems need to be addressed immediately.
