10 Hidden Clues Every Woman Should Know About Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants itself outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. This condition is not only rare but also potentially life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated promptly. As women navigate their reproductive health, understanding the nuances of ectopic pregnancy becomes crucial. This article aims to uncover 10 hidden clues every woman should be aware of, offering a comprehensive guide to recognizing, preventing, and managing this condition. An ectopic pregnancy can be challenging to diagnose due to its subtle symptoms that often mimic those of a normal pregnancy. However, the consequences of an undiagnosed ectopic pregnancy can be severe, leading to complications such as internal bleeding and infertility. Our goal is to provide a thorough understanding that will help women identify potential red flags and seek medical advice when necessary.
1. The Anatomy of Ectopic Pregnancy: Where It All Begins
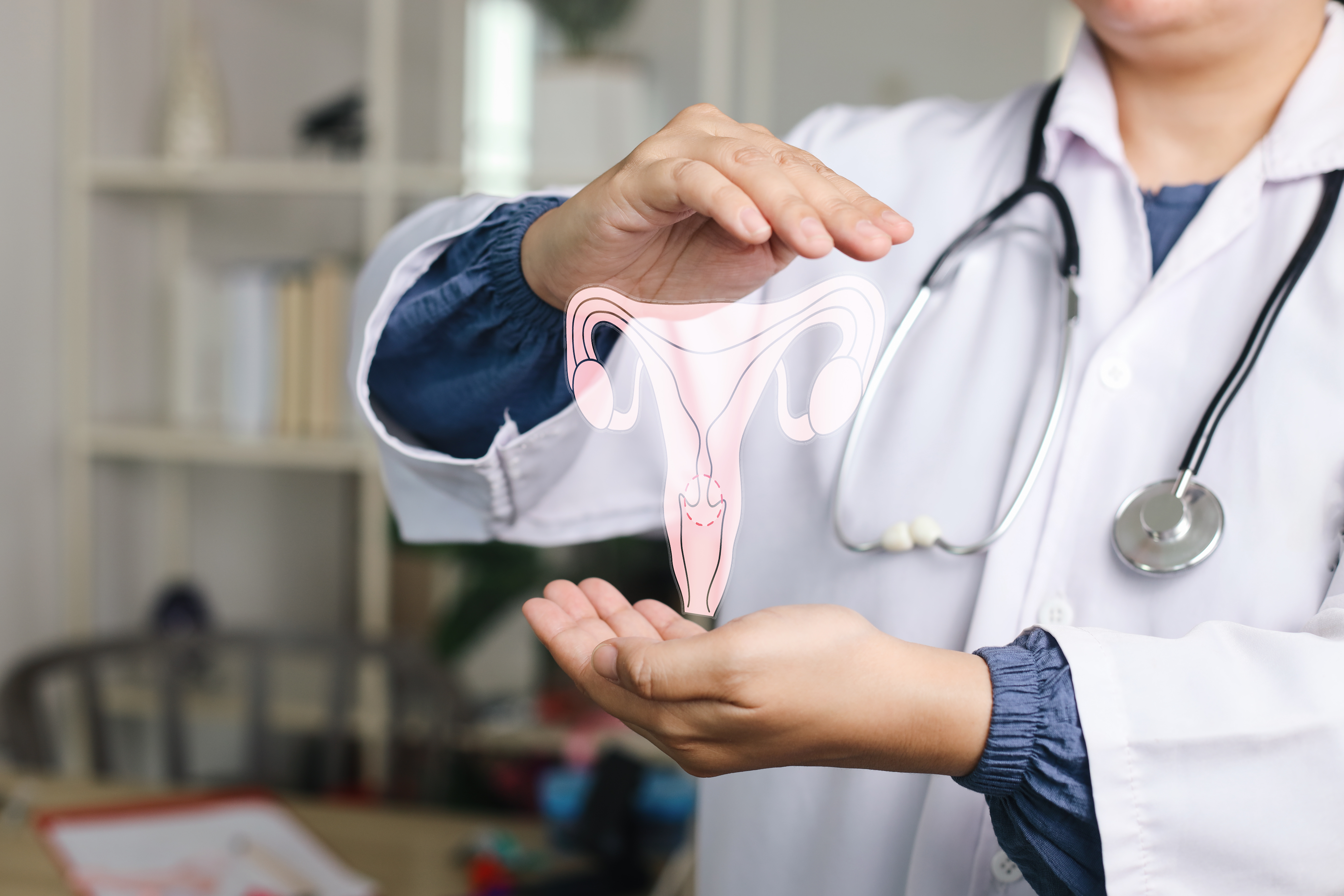
Ectopic pregnancies primarily occur in the fallopian tubes, known as tubal pregnancies, but they can also implant in the abdominal cavity, ovaries, or cervix. Understanding the anatomy of ectopic pregnancies is crucial because it affects the symptoms and treatment options available. In a normal pregnancy, the fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube and implants in the uterine lining. However, in an ectopic pregnancy, this journey is disrupted, and implantation occurs elsewhere. This anomaly can be attributed to various factors, including scarring or inflammation of the fallopian tubes, often due to infections like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or previous surgeries. The location of the ectopic pregnancy determines the severity of symptoms and potential complications. For instance, a tubal pregnancy may cause the fallopian tube to rupture, leading to internal bleeding and severe pain. In contrast, an abdominal pregnancy might not present symptoms until later stages, making it more challenging to diagnose early. Understanding these anatomical nuances helps in recognizing the subtle signs of an ectopic pregnancy, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention to prevent life-threatening situations.
2. Common Symptoms and Early Warning Signs

Recognizing the early warning signs of an ectopic pregnancy is essential for timely medical intervention. The symptoms often resemble those of a normal pregnancy, such as missed periods, breast tenderness, and nausea, which can make detection challenging. However, some distinct symptoms may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, including sharp or stabbing pain in the abdomen or pelvis, light vaginal bleeding, and dizziness or fainting. These symptoms may vary depending on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and the extent of the condition. Pain is one of the most common indicators of an ectopic pregnancy and can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. It may be localized to one side of the abdomen and can radiate to the shoulder or neck due to internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm. Additionally, vaginal bleeding in an ectopic pregnancy is usually lighter than a normal menstrual period and may be accompanied by a feeling of pressure in the rectum. Women experiencing these symptoms should seek immediate medical attention, as early diagnosis is crucial in preventing complications and preserving fertility.
3. Risk Factors: Who is More Susceptible?

Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing an ectopic pregnancy, making it important for women to be aware of their personal risk profile. One of the primary risk factors is a history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can cause scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes. Other risk factors include previous ectopic pregnancies, surgeries on the reproductive organs, fertility treatments, and the use of intrauterine devices (IUDs). Additionally, smoking and age over 35 are also associated with a higher risk of ectopic pregnancies. Women with a history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are at greater risk due to the potential for scarring and inflammation in the reproductive tract. Understanding these risk factors can help women and their healthcare providers make informed decisions about monitoring and managing their reproductive health. For those with known risk factors, regular check-ups and early pregnancy scans can be instrumental in detecting ectopic pregnancies early, allowing for timely intervention and reducing the risk of complications.
4. Diagnosis: Medical Tests and Procedures

Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy involves a combination of medical tests and procedures to confirm the condition and determine its location. The first step in the diagnostic process is usually a pelvic exam, followed by a series of blood tests to measure the levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy. In a normal pregnancy, hCG levels double every two to three days, but in an ectopic pregnancy, these levels may rise more slowly or plateau. Ultrasound imaging is a critical tool in diagnosing ectopic pregnancies, as it allows healthcare providers to visualize the reproductive organs and identify the location of the pregnancy. A transvaginal ultrasound is often used to provide a detailed view of the fallopian tubes and other structures. In some cases, a laparoscopy may be necessary, which involves inserting a small camera through an incision in the abdomen to directly observe the reproductive organs. These diagnostic procedures are essential in confirming an ectopic pregnancy and determining the appropriate course of treatment.
5. Treatment Options: From Medication to Surgery

The treatment of ectopic pregnancy depends on its location, size, and the severity of symptoms. Early detection often allows for less invasive treatment options, such as medication. Methotrexate is a common medication used to terminate an ectopic pregnancy by stopping the growth of the fertilized egg and allowing the body to absorb the tissue. This option is most effective when the pregnancy is detected early and the fallopian tube has not ruptured. In cases where medication is not suitable or the ectopic pregnancy is more advanced, surgical intervention may be necessary. Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to remove the ectopic tissue and repair or remove the affected fallopian tube. In severe cases where the fallopian tube has ruptured, emergency surgery may be required to control internal bleeding and prevent further complications. While surgery can be more invasive, it is often necessary to preserve the woman's health and future fertility.
6. Emotional Impact: Coping with the Diagnosis

The diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy can be emotionally devastating, as it often involves the loss of a desired pregnancy and concerns about future fertility. Women may experience a range of emotions, including grief, anger, and anxiety, which can be compounded by the physical recovery process. It is important for women to have access to emotional support during this time, whether through counseling, support groups, or loved ones who can provide comfort and understanding. Coping with the emotional impact of an ectopic pregnancy involves acknowledging and processing these feelings. Many women find it helpful to talk about their experiences with others who have gone through similar situations, as this can provide validation and a sense of community. Healthcare providers should also be sensitive to the emotional needs of their patients, offering resources and support to help them navigate this challenging time. Understanding that healing is a gradual process can empower women to take the necessary steps toward emotional recovery.
7. Long-term Health Considerations

After experiencing an ectopic pregnancy, it is important for women to be aware of the potential long-term health considerations. One of the primary concerns is the impact on future fertility, as damage to the fallopian tubes can affect the ability to conceive naturally. Women who have had an ectopic pregnancy may have an increased risk of recurrence, making it essential to work closely with healthcare providers to monitor subsequent pregnancies. Regular follow-up appointments and fertility assessments can help women understand their reproductive health and explore options for future family planning. In some cases, assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), may be recommended to bypass damaged fallopian tubes and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying health conditions, and avoiding risk factors can contribute to improved reproductive health and reduce the likelihood of future complications.
8. Preventive Measures: Reducing the Risk
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of ectopic pregnancy, there are several measures women can take to reduce their risk. Maintaining good reproductive health is paramount, which includes practicing safe sex to prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and seeking prompt treatment for any infections that do occur. Regular gynecological check-ups and screenings can help detect potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention and reducing the risk of complications. Women with known risk factors, such as a history of pelvic inflammatory disease or previous ectopic pregnancies, should discuss their concerns with their healthcare providers and consider early pregnancy monitoring. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy weight, can also contribute to reducing the risk of ectopic pregnancies. By taking proactive steps to protect their reproductive health, women can minimize their risk and increase their chances of having a healthy pregnancy in the future.
9. The Role of Healthcare Providers

Healthcare providers play a crucial role in the prevention, diagnosis, and management of ectopic pregnancies. Their expertise and guidance are essential in helping women navigate the complexities of this condition. By providing comprehensive education and support, healthcare providers can empower women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health. This includes discussing risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, as well as offering emotional support and resources for coping with the diagnosis. Effective communication between women and their healthcare providers is key to ensuring timely diagnosis and treatment. Providers should encourage open dialogue and address any concerns or questions women may have about their reproductive health. By fostering a collaborative relationship, healthcare providers can help women feel more confident and informed about their health, ultimately contributing to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
10. The Impact on Future Pregnancies: What to Expect Next

After an ectopic pregnancy, many women worry about their chances of conceiving again and carrying a pregnancy to term. While having one ectopic pregnancy increases the risk of another, many women go on to have successful pregnancies. The key is early monitoring and working closely with healthcare providers to assess risk factors. In some cases, doctors may recommend early ultrasounds to confirm implantation in the uterus. For those with significant fallopian tube damage, assisted reproductive technologies like IVF can offer alternative paths to conception. Understanding what to expect in future pregnancies can provide reassurance and a sense of control in family planning after an ectopic pregnancy.
Empowerment Through Knowledge

The journey through understanding ectopic pregnancy is one of empowerment through knowledge. By recognizing the hidden clues and understanding the complexities of this condition, women can take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being. Awareness and education are powerful tools in preventing complications and ensuring timely intervention. As women become more informed about ectopic pregnancies, they can advocate for their health and seek the support they need during challenging times. The insights gained from this article aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of ectopic pregnancy, from its causes and symptoms to its emotional and physical impact. By equipping women with this knowledge, we hope to foster a sense of empowerment and resilience, enabling them to navigate their reproductive health with confidence and clarity. Remember, knowledge is not just power—it's a pathway to better health and a brighter future.
