10 Mind-Boggling Facts on Unraveling the Mystery of Pulsatile Tinnitus
Imagine hearing your own heartbeat, not as a subtle life rhythm, but as a constant, thumping drum echoing in your ears, perfectly in sync with your pulse. This isn't science fiction; it's the unsettling reality for those with pulsatile tinnitus, a rare and often misunderstood condition far different from the common "ringing in the ears." This internal percussion can be deeply distracting, a relentless reminder of bodily processes typically unheard. More than just an auditory anomaly, pulsatile tinnitus often whispers of underlying, sometimes serious, health issues—from quirky blood vessel formations to conditions needing urgent attention. Prepare to delve into this medical enigma as we unravel its complexities with 10 truly mind-boggling facts that illuminate the mystery behind hearing your own pulse, offering insights that could change your understanding of this extraordinary phenomenon.
1. Hearing Test
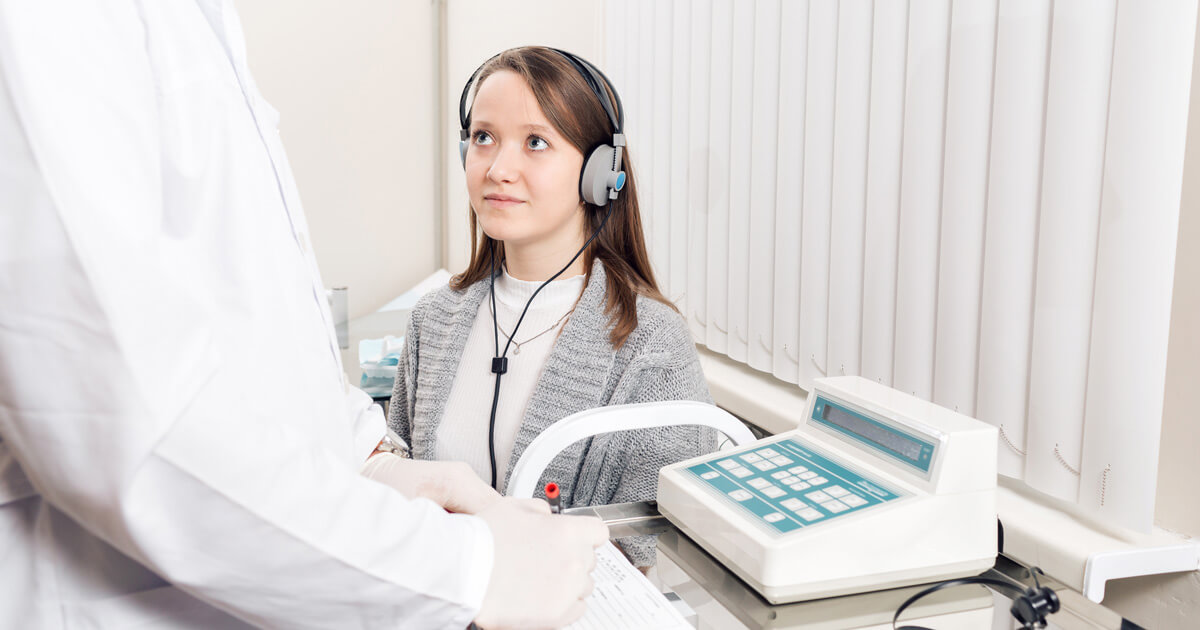

The exact method of diagnosis for pulsatile tinnitus may vary depending on the case. If patients don't need emergency medical treatment, they may be referred to a specialist called an otolaryngologist. This doctor will typically perform a hearing test or multiple hearing tests as the first method of diagnosis. During a pure tone audiometry test, a doctor will measure the pitches and volumes patients are able to hear. Some individuals may have trouble hearing because the pulsatile tinnitus drowns out other sounds. Hearing loss can also occur when patients have intracranial hypertension, which causes increased pressure on the brain, ears, and eyes. Damage to the ears may make patients unable to hear certain tones or process sounds clearly.
2. Electrocochleography
An electrocochleography may be used as a further form of hearing test. This technique allows doctors to record the electrical potentials the patient's auditory nerve and inner ear generate when they hear sounds. The test involves the placing of an electrode into the tympanic membrane or ear canal. Typically, this type of diagnostic test is only performed by an otologist or audiologist who has been specially trained in its application. The electrocochleography results will help detect whether there's elevated pressure against the patient's inner ear. In cases of intracranial hypertension, this technique is very helpful when diagnosing the underlying issue, such as pulsatile tinnitus. In cases that don't involve increased pressure, the test can rule out emergency conditions like intracranial hypertension.
3. Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response
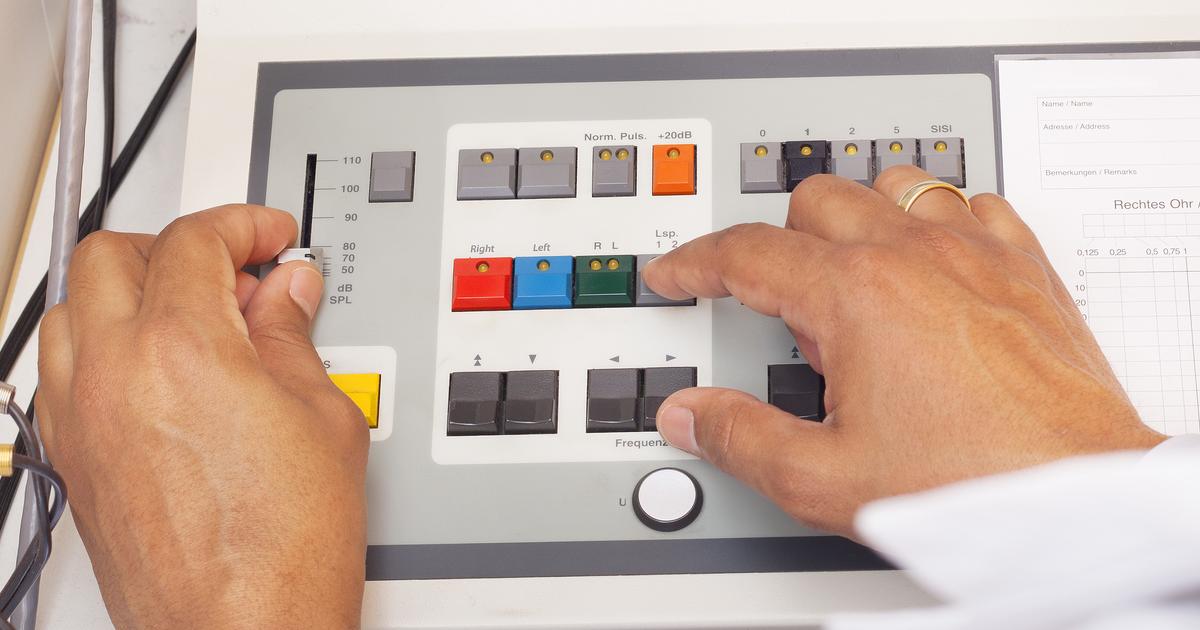

A brainstem auditory evoked response test, more commonly called a BAER test, is a diagnostic tool that measures how well a patient's brain processes sounds. This can help determine whether the cause of pulsatile tinnitus is in the ear itself or neurologically-based. BAER tests record the feedback of the patient's brainwaves when they're exposed to certain audio tones or a series of clicks. The test helps determine the cause and severity of hearing loss in multiple different cases. It also helps diagnose nervous system issues that lead to auditory processing problems. BAER tests are most frequently used with young children, newborns, and individuals unable to partake in standard hearing tests.
4. Tinnitus Retraining

The best course of treatment will vary depending on the underlying cause of the tinnitus. Doctors will typically focus on treating the underlying cause first. Oftentimes, when the underlying cause has been cured or sufficiently managed, the symptoms of pulsatile tinnitus resolve. However, some patients may experience the sound on a permanent or semi-permanent basis. In these cases, tinnitus retraining can be helpful. This therapy method is used for those with permanent tinnitus to help them cope with their condition both subconsciously and consciously. Tinnitus retraining incorporates three main principles. First, the doctor collects extensive information about the patient's medical history and living habits. Then, they use electronic devices to generate noise and direct the patient's attention from their tinnitus. The third component is integrated psychological therapy that teaches the patient how to ignore their tinnitus.
5. Underlying Condition Treatment

Pulsatile tinnitus is generally caused by an underlying condition that requires treatment. Doctors will focus on treating the condition and see if the symptoms resolve. If they don't, the patient may then move on to tinnitus retraining. One potentially fatal condition is intracranial hypertension. When this occurs, patients may have strange neurological symptoms that accompany the tinnitus. Intracranial hypertension requires emergency care to prevent permanent, potentially fatal brain injuries. If individuals have a blood vessel that has burst or become abnormally shaped, they may need surgery to repair it. Reparation of the blood vessels typically causes tinnitus symptoms to ease. Some patients may need to manage a blood vessel condition by using blood pressure medication or other medications.
6. The Doctor Can Hear It Too? The Phenomenon of Objective Pulsatile Tinnitus

Perhaps one of the most mind-boggling aspects of pulsatile tinnitus is that, in some cases, it's not just subjective. Unlike typical tinnitus which only the patient perceives, certain forms of pulsatile tinnitus are "objective," meaning a doctor might actually be able to hear the rhythmic sound by using a stethoscope carefully placed around the patient’s ear, head, or neck! This occurs when the underlying cause, often a vascular issue, generates a sound loud enough to be externally detectable. This shareable perception makes objective pulsatile tinnitus a particularly unique and verifiable auditory phenomenon, offering a crucial diagnostic clue.
7. Turbulent Tides Within: Unmasking the Source of the Sound

Ever wondered why you hear that rhythmic beat? The "whooshing" or "thumping" of pulsatile tinnitus isn't random; it often mirrors the turbulent, rather than smooth, flow of blood through vessels near your ear. Think of a kinked garden hose making a sputtering sound. When blood vessels are narrowed, twisted, or have abnormal connections (like an arteriovenous malformation), the blood flow becomes chaotic. This turbulence creates vibrations that are then picked up by the delicate structures of your inner ear and perceived as a pulse-synchronous sound, a direct acoustic window into your circulatory system.
8. Body Posture's Puzzling Power: When Simple Movements Change the Beat

A truly perplexing yet common feature of pulsatile tinnitus is its sensitivity to changes in body posture or head position. Many individuals report that their internal rhythm intensifies, diminishes, or even changes character when they lie down, turn their head a certain way, stand up, or even during physical exertion. This isn't just a coincidence; it’s a vital clue. Such changes often indicate a vascular origin, as movement can alter blood pressure and flow dynamics within specific vessels near the ear, directly impacting the audible pulse. Tracking these positional variations can provide valuable diagnostic information.
9. Beyond Blood Vessels: Surprising Systemic Culprits and Connections

While vascular issues are the usual suspects, the mystery of pulsatile tinnitus sometimes extends to seemingly unrelated systemic conditions. For instance, severe anemia can lead to thinner blood that flows more rapidly and turbulently, potentially causing a pulsing sound. Similarly, an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) can increase heart rate and blood flow, sometimes manifesting as pulsatile tinnitus. Even something as seemingly distant as intracranial hypertension (high pressure around the brain) can transmit the pulse to the ear. These connections highlight how intricately our body systems are linked, making diagnosis a comprehensive detective work.
10. The Imaging Breakthrough: Peering Inside to Pinpoint the Elusive Pulse
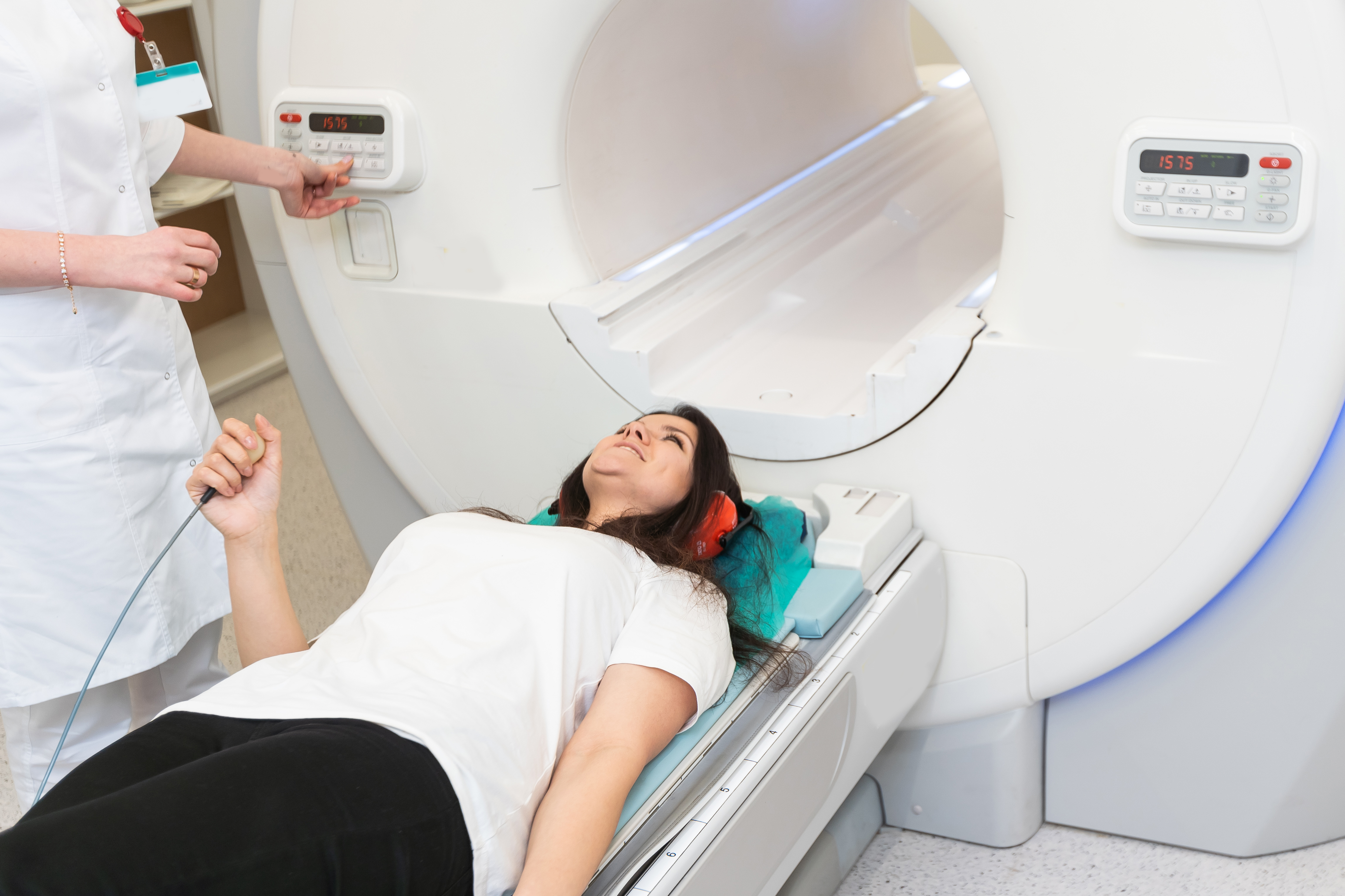
Unraveling the mystery of pulsatile tinnitus heavily relies on seeing the unseen. Advanced medical imaging techniques are the modern-day keys to unlocking the cause of this often-elusive sound. Technologies like Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA), Magnetic Resonance Venography (MRV), Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA), and sometimes traditional angiography, allow doctors to create detailed maps of the blood vessels in the head and neck. These scans can reveal the tiny abnormalities, constrictions, or unusual connections that might be generating the rhythmic sound, guiding precise treatment and often bringing immense relief to those affected.
Decoding the Pulse: Hope in Understanding
Unraveling the mystery of pulsatile tinnitus reveals a condition far more complex and intriguing than a simple "ringing in the ears." As these ten mind-boggling facts illustrate, hearing your own pulse can be a window into the intricate workings of your vascular system, a sign of underlying health conditions, and a truly unique auditory experience. From sounds a doctor can also hear to the critical role of advanced imaging in pinpointing elusive causes, the journey to understanding pulsatile tinnitus is one of careful investigation. While the experience can be distressing, knowledge empowers. Recognizing its potential significance and seeking thorough medical evaluation are the crucial first steps towards diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and ultimately, quieting the internal drum to reclaim a sense of peace.
