10 Serious Indicators Of Wernicke's Encephalopathy
Your mind is a powerhouse, constantly converting fuel into the energy it needs to function. But what happens when that vital energy supply is critically low? Wernicke's encephalopathy is a serious, often sudden, neurological emergency stemming from a severe deficiency of thiamine (Vitamin B1) – the very nutrient essential for your brain's energy production. Often appearing as a shocking twist in a larger, complex syndrome, Wernicke's demands immediate attention. Overlooking its subtle yet critical warning signs can have devastating consequences, potentially progressing to irreversible brain damage. Understanding these 10 serious indicators isn't just about recognizing symptoms; it's about potentially saving cognitive function, and even lives. Let's delve into what your body might be trying to tell you.
1. Ataxia
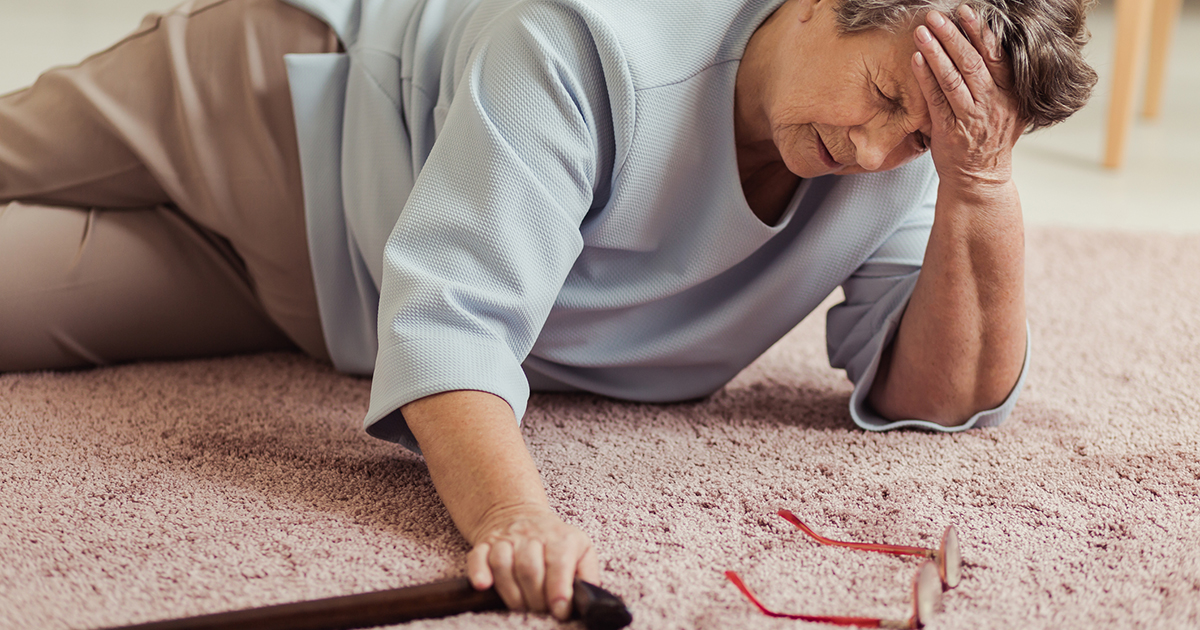

Ataxia is a condition that occurs when the nervous system's functioning degenerates. Individuals with ataxia may look like they're drunk, as they tend to stumble, fall, lack coordination, and slur their words. These symptoms are caused by degeneration of the cerebellum, which coordinates a person's movements. There are a number of diseases under the ataxia umbrella that present with the condition alone, but the onset of the condition can also indicate an underlying problem. With Wernicke's encephalopathy, a severe thiamine deficiency has led the brain's functions to degenerate because there's not enough energy. Ataxia patients often have wide stances and take short steps because of their trouble balancing. They may need others to help them stand up and move around. Patients may also experience general weakness in the legs and arms. Even if the cause isn't Wernicke's encephalopathy, the sudden onset of these symptoms is a serious sign something is neurologically wrong. If individuals experience these symptoms without warning or explanation, they should seek emergency medical treatment.
2. Confusion
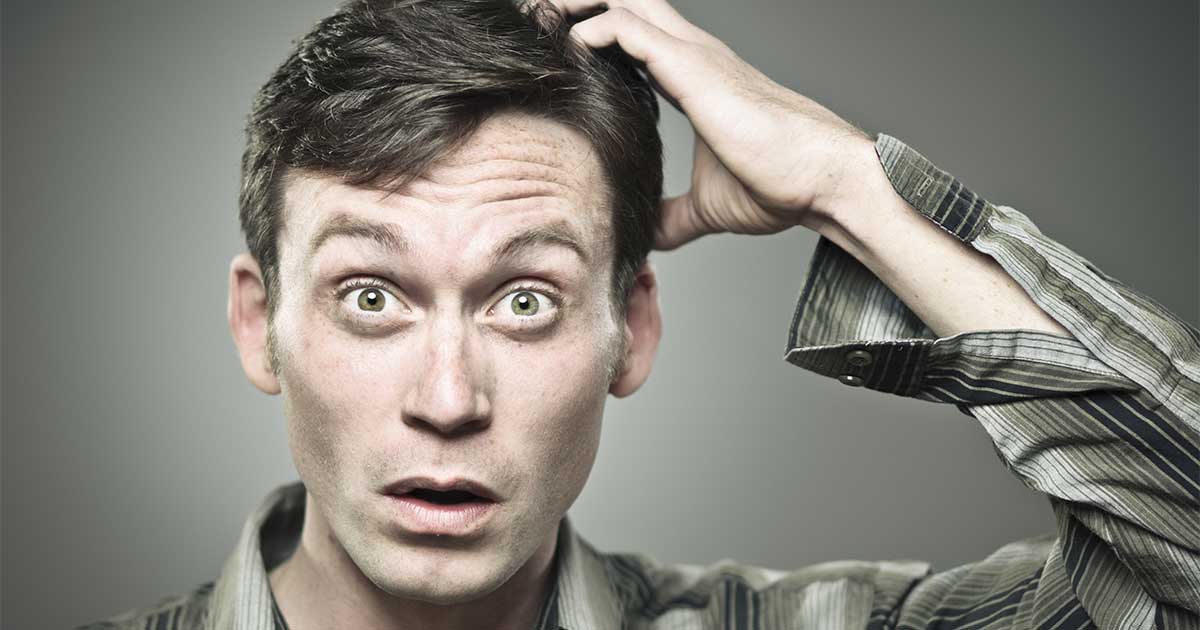

Confusion is another one of the major symptoms of Wernicke's encephalopathy. Patients with this symptom may be confused about what's going on around them. They might have trouble following a conversation, remembering where they are, or remembering what they're doing. The confusion might be accompanied by a general loss of interest in the outside world. Wernicke's encephalopathy patients sometimes find it's too difficult to sort through the mental fog, and they don't have the will to connect to the outside world. This kind of mental confusion is another symptom that occurs because of the brain's decreased ability to function. Thought processes and interpretation of sensory data both become muddled, and the ability to feel emotions may also be somewhat dulled.
3. Ophthalmoplegia
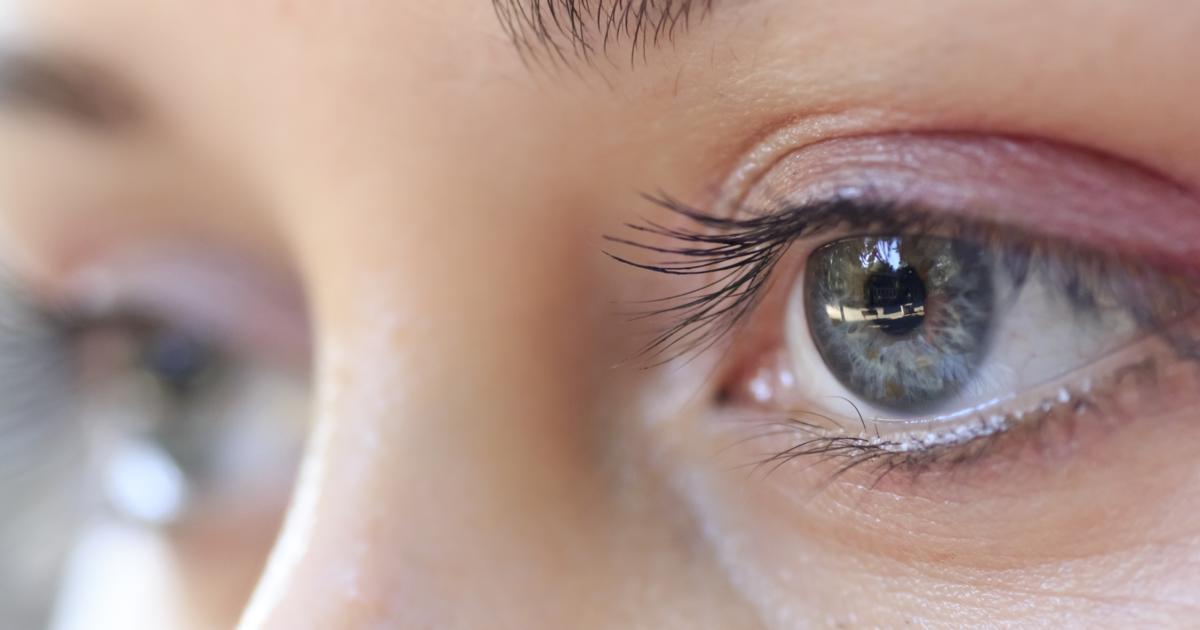
Eye problems are the third major symptom of Wernicke's encephalopathy. With ophthalmoplegia, the eye muscles become weak or completely paralyzed. There are six muscles that control the movement of the eyes, and this condition might affect one or more. The most common symptoms are blurring or double vision. Some individuals might have difficulty positioning their eyes in sync, or they may find this completely impossible. Many patients present with drooping eyelids. The most common causes of ophthalmoplegia are multiple sclerosis, trauma, muscle disorders, or mitochondrial diseases. However, brain injuries and nervous system degeneration like what's seen in Wernicke's encephalopathy can also lead to this. Infections, brain tumors, strokes, migraines, and thyroid diseases may also be underlying causes. The condition can often be treated, but patients with Wernicke's encephalopathy must have their underlying thiamine deficiency treated to keep the condition from progressing.
4. Vision Or Hearing Loss
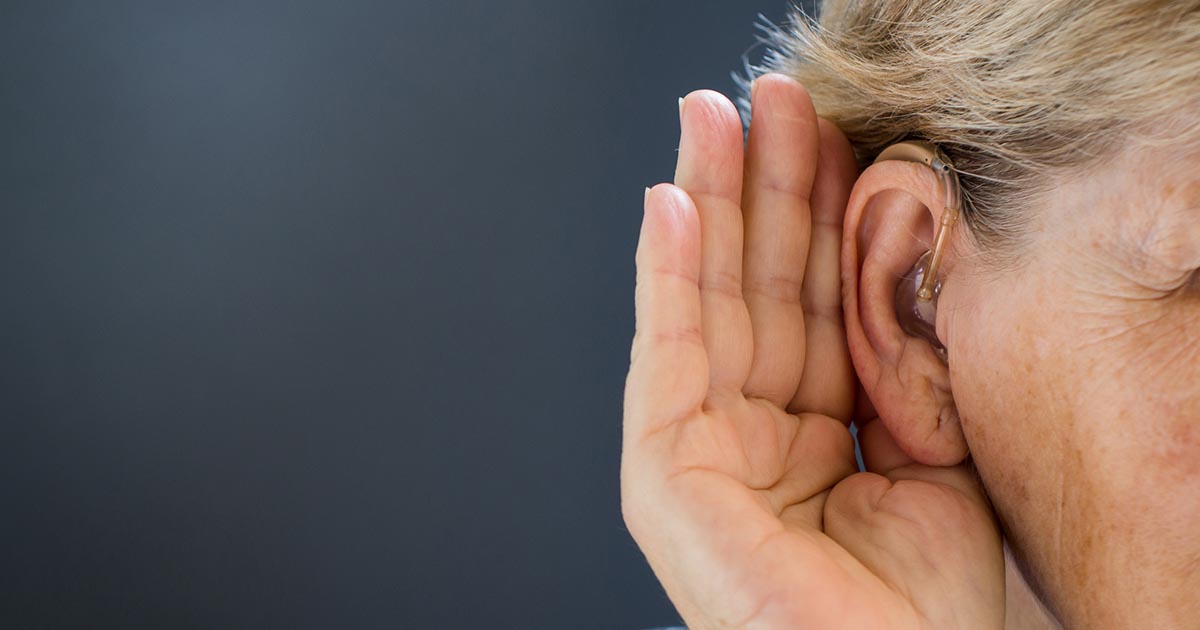

Wernicke's encephalopathy can present with vision or hearing loss. Vision loss tends to be related to the eye abnormalities. If a patient's eye muscles are weak or paralyzed, and their eyes are misaligned, they may not be able to interpret visual data correctly. Hearing loss, on the other hand, tends to occur more rarely. It's only been recorded in a handful of cases, but the correlation is significant enough that researchers recommend considering Wernicke's encephalopathy as a diagnosis when patients present with hearing loss, eye abnormalities, ataxia, and confusion. In one study, a sixty-one-year-old woman had acute hearing loss in both ears followed by acute and vague disturbances in her vision. In fact, the hearing loss was severe enough that she was almost deaf. After she was treated with IV thiamine, her hearing, eye movements, and cognition became markedly improved within just twelve hours. She had almost returned to her baseline after the first twenty-four hours of treatment.
5. Retinal Hemorrhage
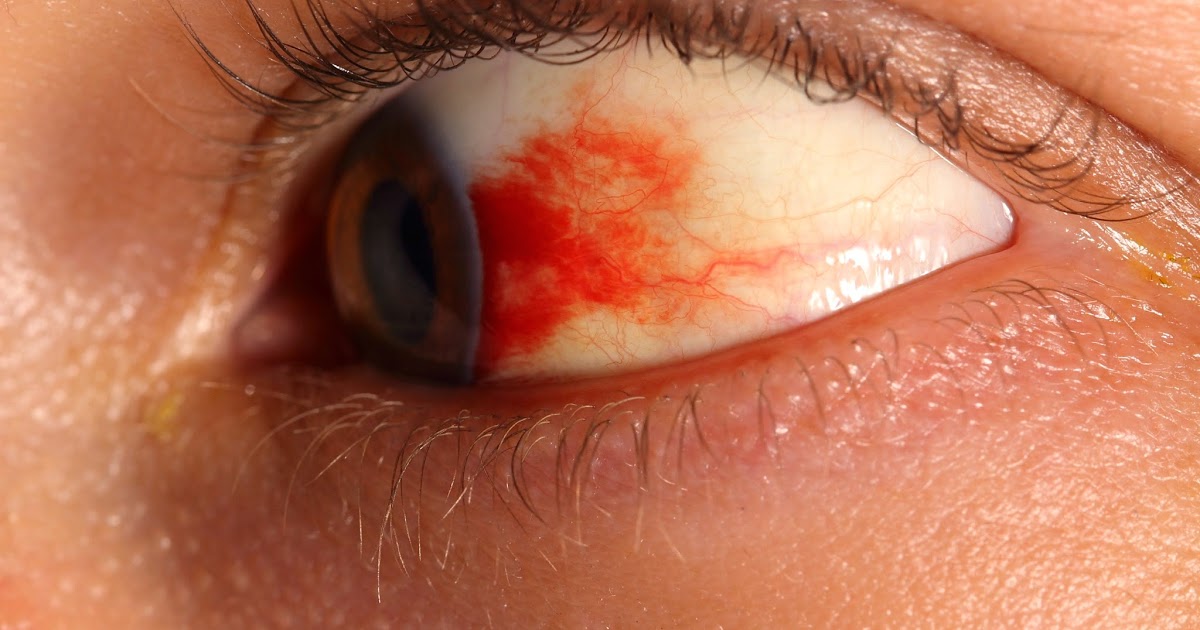
Retinal hemorrhage occurs when there's bleeding inside the retina, which is responsible for interpreting visual data. There are a number of medical conditions that might lead to retinal hemorrhage, including blockage of a retinal vein, hypertension, leukemia, anemia, and diabetes mellitus. Though hemorrhages that occur outside the eye's macula might not be detected for years, others can cause severe vision impairment. Another condition that may occur is optic disk edema, which causes the optic disk to swell because of an increase in pressure inside the skull. Though these aren't the most common eye abnormalities in Wernicke's encephalopathy, they're still significant. Hemorrhages need immediate treatment if they've caused serious vision impairment.
6. Sudden Hypotension (Low Blood Pressure)
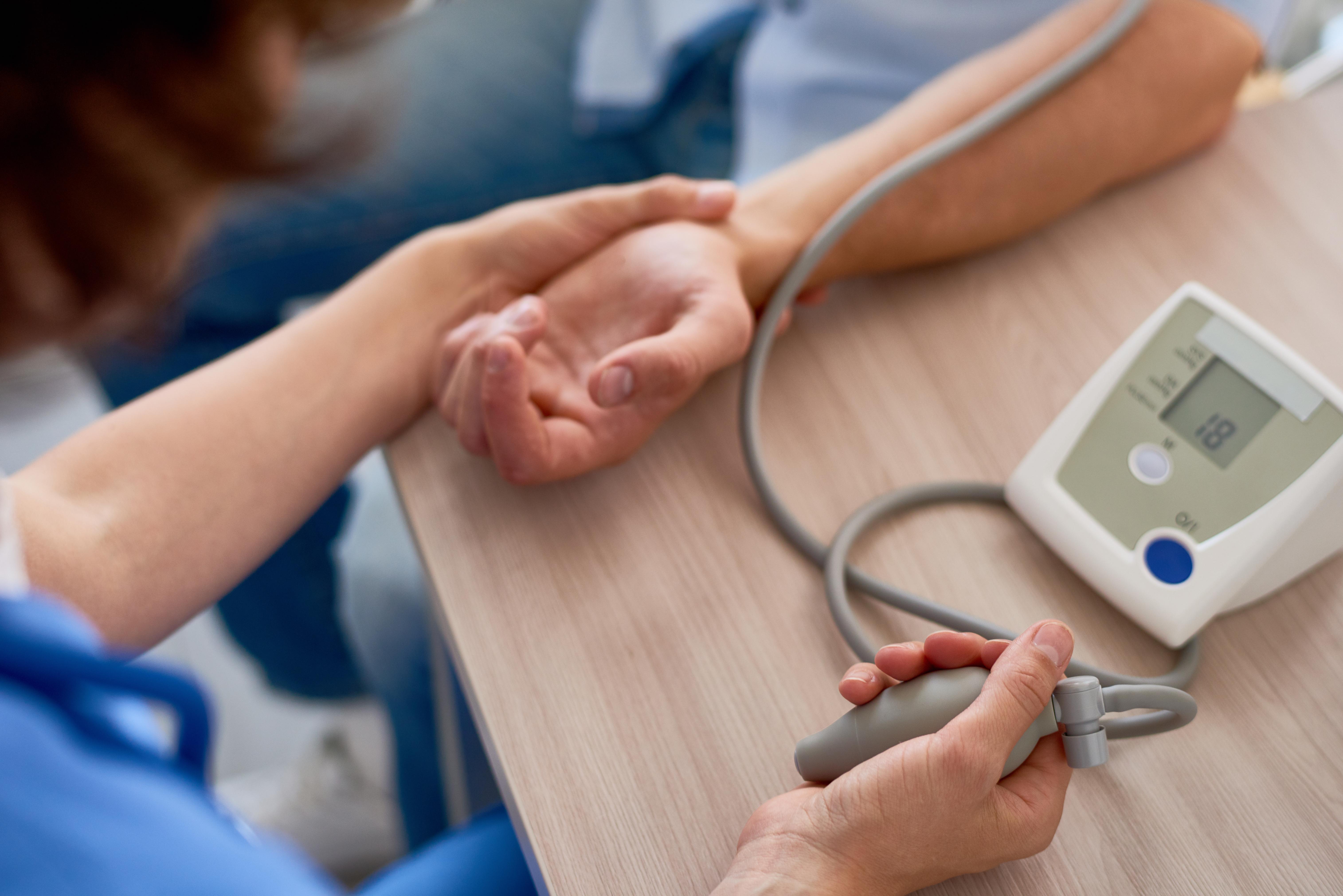

While less commonly highlighted than the neurological symptoms, a sudden and unexplained drop in blood pressure (hypotension) can be a critical, underlying indicator of Wernicke's encephalopathy. This occurs because severe thiamine deficiency can impair the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary bodily functions like blood pressure and heart rate. If a patient presents with sudden weakness, dizziness, or fainting alongside other cognitive or movement issues, especially without obvious cardiac causes, Wernicke's should be considered. It's a vital sign of systemic dysfunction.
7. Hypothermia (Abnormally Low Body Temperature)
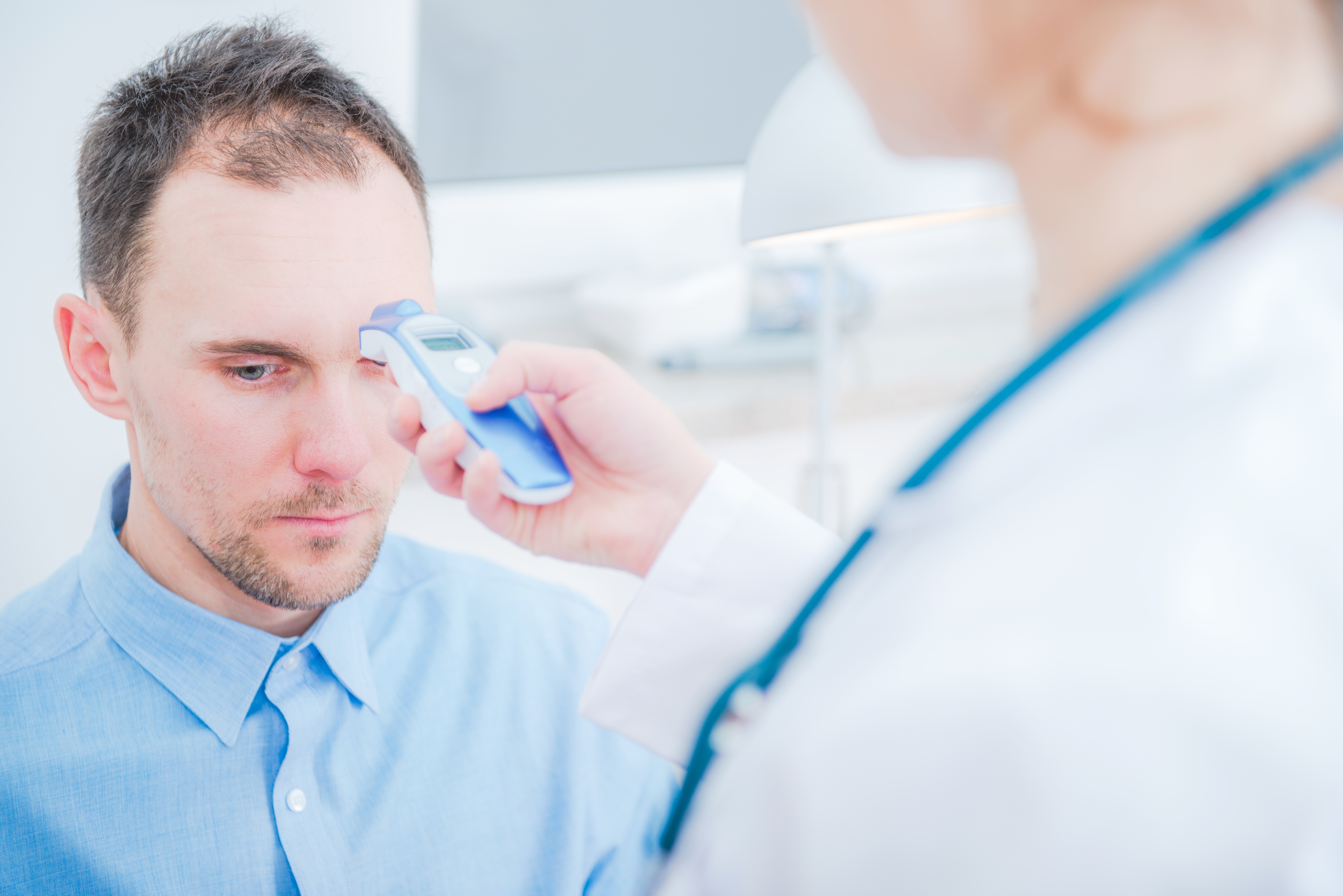
Another surprising autonomic nervous system dysfunction seen in Wernicke's encephalopathy is hypothermia – an abnormally low body temperature. The brain's hypothalamus, which controls thermoregulation, relies on thiamine for proper function. When energy production is compromised, this vital regulatory center can fail, leading to a dangerous drop in core body temperature. This often occurs even in warm environments and can be a subtle, yet serious, clue when combined with mental changes or gait abnormalities.
8. Memory Impairment (Acute Onset)

While severe, chronic memory loss is characteristic of Korsakoff syndrome (the later stage), a sudden, acute onset of severe memory impairment can be a critical sign of Wernicke's encephalopathy. This isn't just typical confusion; it's a pronounced inability to form new memories (anterograde amnesia) or recall recent events. Patients may repeatedly ask the same questions or be unable to remember conversations from minutes prior. This acute amnesia, alongside other neurological symptoms, points directly to severe thiamine-related brain dysfunction requiring immediate intervention.
9. Peripheral Neuropathy (New or Worsening)

Thiamine is essential for healthy nerve function throughout the body. Therefore, a sudden onset or rapid worsening of peripheral neuropathy – nerve damage outside the brain and spinal cord – can be a serious indicator. Symptoms might include unexplained numbness, tingling, burning sensations, or weakness in the extremities (hands and feet). While many conditions cause neuropathy, its acute appearance alongside other neurological symptoms like ataxia or confusion should strongly raise suspicion for Wernicke's encephalopathy, signaling widespread thiamine deficiency.
10. General Malnutrition & Weight Loss

While not a direct neurological symptom, unexplained or severe general malnutrition and significant weight loss are crucial contextual indicators that should immediately flag Wernicke's encephalopathy as a possibility. Thiamine deficiency rarely occurs in isolation; it's often a hallmark of broader nutritional neglect, commonly seen in chronic alcoholism, severe eating disorders, or prolonged vomiting. When neurological signs appear in a visibly malnourished individual, clinicians should prioritize immediate thiamine supplementation even before a definitive diagnosis.
Recognizing and Responding to Wernicke's

Wernicke's encephalopathy is a medical emergency where time is literally brain. These 10 serious indicators — from pronounced confusion and gait instability to subtle autonomic disruptions and acute memory loss — demand immediate medical attention. While often associated with alcoholism, Wernicke's can arise from any severe thiamine deficiency, affecting a wider range of individuals than commonly assumed. Recognizing these critical warning signs is the first, vital step towards prompt diagnosis and life-saving thiamine treatment. Don't delay; early intervention can dramatically improve outcomes, preserving cognitive function and preventing the progression to irreversible brain damage. Your vigilance could make all the difference.
