10 Signs of Arthritis You Should Never Ignore
Arthritis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the joints, affects millions worldwide, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. Despite its prevalence, many individuals remain unaware of the early warning signs that could indicate the onset of arthritis. Recognizing these red flags early can make a significant difference in managing the condition effectively and improving quality of life. This guide aims to unveil the top 10 key arthritis red flags that you cannot afford to overlook. By understanding these signs, individuals can seek timely medical intervention, potentially slowing the progression of the disease and alleviating symptoms. This comprehensive exploration will delve into each red flag, offering insights into their implications, how they manifest, and why they are crucial for early diagnosis and management of arthritis.
1. Persistent Joint Pain
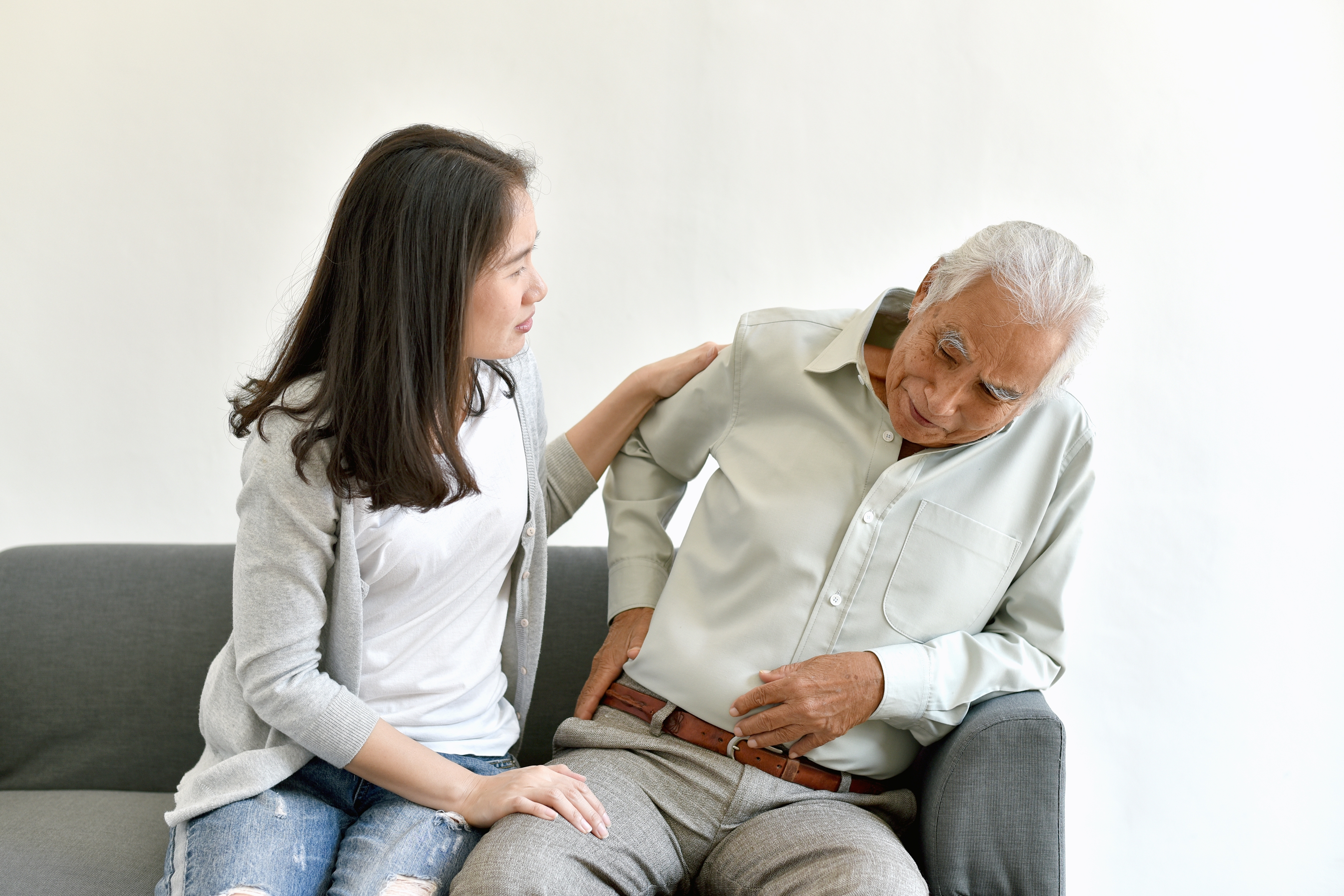

One of the most common and significant red flags for arthritis is persistent joint pain. Unlike temporary discomfort that might result from overexertion or minor injury, arthritis-related joint pain is chronic and often worsens over time. This pain typically manifests in the hands, knees, hips, or spine, and can be both dull and sharp, varying in intensity. It is crucial to pay attention to pain that persists for more than a few weeks, as it may indicate underlying joint inflammation. Early recognition of persistent joint pain can lead to prompt medical evaluation, enabling healthcare providers to determine whether arthritis or another condition is the cause. Understanding the nature of this pain and its potential impact on daily activities can empower individuals to seek help sooner rather than later.
2. Joint Stiffness
Joint stiffness, particularly when it occurs first thing in the morning or after periods of inactivity, is another key indicator of potential arthritis. This stiffness is often most pronounced in the hands and knees and can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours. For some, the stiffness diminishes with movement, but for others, it can persist throughout the day, significantly impacting mobility and quality of life. Recognizing and addressing joint stiffness early is essential, as it may signal the beginning stages of arthritis. Differentiating between stiffness caused by arthritis and that resulting from other factors, such as muscle strain, is critical. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help clarify the cause and guide appropriate management strategies.
3. Swelling and Tenderness

Swelling and tenderness around the joints are hallmark symptoms of arthritis, often accompanying joint pain and stiffness. Swelling occurs due to inflammation in the joint tissues, leading to an accumulation of fluid. This can cause the affected area to appear visibly enlarged and feel warm to the touch. Tenderness, on the other hand, refers to the discomfort experienced when pressure is applied to the joint. These symptoms can significantly interfere with daily activities, making tasks such as gripping objects or walking difficult. Noticing persistent swelling and tenderness should prompt an evaluation by a healthcare professional, as these symptoms may indicate active inflammation requiring treatment. Early intervention can prevent further joint damage and preserve function.
4. Reduced Range of Motion

A reduced range of motion in the joints is a common consequence of arthritis, often resulting from both pain and structural changes within the joint. Individuals may find it challenging to fully bend or straighten their joints, which can hinder activities such as climbing stairs, typing, or even dressing. This limitation can progressively worsen if not addressed, leading to decreased independence and a reduced quality of life. Identifying a reduction in joint mobility early on is vital, as it can signal the need for therapeutic interventions, such as physical therapy, to maintain flexibility and strength. By focusing on exercises that enhance range of motion, individuals can manage symptoms more effectively and retain functional abilities.
5. Fatigue and Malaise

Beyond the physical symptoms directly affecting the joints, arthritis can also cause systemic symptoms like fatigue and malaise, which are often overlooked. Fatigue in arthritis is not merely a feeling of tiredness; it is a profound, persistent exhaustion that can affect mental clarity and emotional well-being. Malaise, a general feeling of discomfort or unease, often accompanies fatigue and can be debilitating. These symptoms may result from the body's inflammatory response or the stress of coping with chronic pain. Recognizing the impact of fatigue and malaise is crucial, as they can significantly affect an individual's ability to perform daily tasks and maintain social interactions. Addressing these symptoms through lifestyle modifications, stress management, and medical interventions can improve overall well-being.
6. Unexplained Weight Loss

Unexplained weight loss can be an alarming symptom associated with various health conditions, including arthritis. Inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can increase metabolic rate and reduce appetite, leading to unintended weight loss. This loss of weight, especially when coupled with other symptoms like joint pain and fatigue, should not be ignored. It may indicate an underlying inflammatory process that requires medical attention. Understanding the relationship between arthritis and weight loss can guide individuals in seeking appropriate care and nutritional support. Addressing weight loss early can help prevent further complications and ensure that individuals maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial for joint health and overall well-being.
7. Fever and Inflammation

Fever, although not commonly associated with arthritis, can occur, particularly in inflammatory types such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. A low-grade fever may accompany joint inflammation, reflecting the body's immune response. While a fever can be attributed to various causes, its presence alongside other arthritis symptoms warrants medical evaluation. Inflammation, the body's response to injury or infection, is a central feature of arthritis and can cause widespread effects beyond the joints. Understanding the role of inflammation in arthritis is essential for effective management, as it can guide treatment decisions aimed at reducing inflammatory activity and alleviating symptoms. Timely recognition of fever and inflammation can lead to more accurate diagnoses and targeted therapies.
8. Numbness and Tingling

Numbness and tingling, particularly in the hands and feet, can be indicative of arthritis-related nerve involvement. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can lead to nerve compression or damage, resulting in these sensations. Numbness and tingling can affect dexterity and balance, posing challenges to daily activities and increasing the risk of falls. Recognizing these symptoms as potential red flags for arthritis is important, as they may indicate the need for further neurological evaluation. Early intervention can prevent permanent nerve damage and improve outcomes. Understanding the connection between arthritis and nerve symptoms can help individuals seek appropriate care and implement strategies to protect nerve health.
9. Changes in Skin and Nails

Arthritis can also manifest in changes to the skin and nails, providing additional clues to its presence. Psoriatic arthritis, for example, is often associated with skin lesions and nail changes such as pitting or separation from the nail bed. These changes can serve as important diagnostic indicators, particularly when they occur alongside joint symptoms. Recognizing skin and nail changes as potential signs of arthritis can facilitate early diagnosis and treatment, improving both joint and dermatological outcomes. Consulting with a healthcare professional when these changes are observed can lead to a more comprehensive evaluation and tailored management plan.
10. Eye Inflammation

Eye inflammation, or uveitis, is another potential red flag for certain types of arthritis, such as juvenile idiopathic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis. Symptoms may include redness, pain, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light. Eye inflammation can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly, underscoring the importance of recognizing this symptom as a possible indication of underlying arthritis. Understanding the connection between eye inflammation and arthritis can guide individuals in seeking timely ophthalmologic and rheumatologic care. Early detection and treatment can prevent vision loss and improve overall disease management, highlighting the need for awareness of this often-overlooked symptom.
Early Diagnosis and Effective Management

Recognizing the red flags of arthritis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. The symptoms discussed—persistent joint pain, stiffness, swelling, reduced range of motion, fatigue, weight loss, fever, numbness, skin changes, and eye inflammation—serve as important indicators that should not be ignored. By understanding these signs and seeking timely medical evaluation, individuals can take proactive steps to manage arthritis, potentially slowing its progression and improving quality of life. This guide underscores the importance of awareness and vigilance in identifying arthritis symptoms, encouraging individuals to act promptly and seek appropriate care. Through education and early intervention, those affected by arthritis can achieve better outcomes and maintain a higher level of function and well-being.
