What Can Cause Individuals To Bruise Easily?
A bruise is a visible discoloration of the skin that occurs in response to an injury to an individual's soft tissues. Local capillaries in the affected area break and allow red blood cells to leak. A bruise usually appears purple or red initially, and will not lose color when pressure is placed on it. As the body begins to reabsorb blood components, the bruise begins to heal. Bruises typically go through color phases of black and blue that eventually lighten up to brown and green before fully fading away. Bruising in healthy individuals is attributed to a minor or moderate blunt injury. However, an individual who bruises easily maybe have some underlying mechanism or condition. Some causes of easy bruising are very benign and are not of significant concern, while others can be serious and life-threatening. Learn about them now.
Thinner Skin Due To Age

Many individuals will experience thinner skin due to age and start to bruise easily. As the body ages, normal tissue growth processes begin to slow down. Old bone tissue that is broken down does not get replaced with new bone as quick, and the body takes longer to repair minor tissue injuries. Special proteins that make up an individual's skin keep it moist, firm, strong, and elastic. However, these proteins do not get produced as often as the body ages, resulting in a lower rate of replacement of skin cells that regularly shed off. This mechanism causes the skin to become thinner in individuals of advanced age, and tissues that make up the blood vessels become weaker. Bruises occur when trauma damages or ruptures the blood vessels in the skin, causing blood to leak into the surrounding tissue. The fatty components in and underneath the skin help absorb the shock of blows and help protect vessels to a certain extent, but those fatty tissues become less ample as the body ages. Less trauma is needed to produce a bruise, and bruises occur more frequently in the elderly as a result of these changes in the body.
Blood Thinners

Individuals who take blood thinners regularly to manage certain conditions are known to bruise easily. These medications are meant to stop the formation and further development of any existing blood clots. Disorders that cause the blood to clot abnormally, heart defects, heart disease, and other conditions that increase an individual's risk of developing clots may all be treated with the use of blood-thinning medications. While blood-thinning medications are effective at the prevention of strokes and heart attacks in certain individuals, they do produce adverse side effects. Therefore, these drugs are only used when their benefits outweigh their risks.
There are two main classifications of blood-thinning drugs. Anticoagulants function by slowing down the coagulation cascade or process of blood clot formation. Antiplatelet drugs inhibit the action of platelets so they do not stick to one another or the blood vessel walls. While these mechanisms help keep existing clots from becoming larger and new clots from developing, they also impair the healthy clotting process in situations where it is warranted. Bruises occur when minor trauma causes blood vessels to burst and leak blood. The clotting system doesn't work as it should with these medications, allowing blood to leak into surrounding tissues for a longer period. This causes the affected individual to bruise more frequently and more severely than others.
Vitamin Deficiencies

Certain vitamin deficiencies in an individual can cause them to bruise easier than others. Vitamins are an important part of an individual's diet required for their body to carry out numerous important processes. Ascorbic acid or vitamin C enhances antioxidant and immune system activity in the body, and it is required to produce a protein called collagen that can be found in the skin, hair, and nails. Vitamin K is extremely important because it functions as an enzyme cofactor required for the coagulation cascade to take place. Without adequate amounts of vitamin K, easy bruising can occur because the coagulation process is impaired. Vitamin B9 (folic acid) is important because it works with other vitamins such as vitamin C and vitamin B12 to assist with the production, use, and breakdown of proteins. Vitamin B12 is important for actions related to proteins, and a deficiency causes elevated levels of a compound called homocysteine in the affected individual's blood. Homocysteine disables the DNA repair process and causes blood vessels to become damaged. A shortage of vitamins C, K, B9, or B12 can result in easy bruising because they have roles involving blood vessels and bleeding.
Liver Disease

Liver disease patients may bruise easily as a result of their condition. Proteins in the blood called clotting factors are responsible for a chain reaction that forms clots to stop an individual from bleeding too much. These clotting factors are all synthesized in an individual's liver, the abdominal organ just above the stomach that is responsible for helping remove toxins from the blood. Liver disease can be caused by many mechanisms. Scarring of the liver occurs when the body attempts to repair damaged liver tissues with tissues more dense and fibrous than normal liver tissue. As this scarring builds up, the function of the liver decreases. Several complications occur from poor liver function, including decreases in most or all coagulation proteins in the blood. These deficiencies also have adverse effects on the platelets, prothrombin, and fibrinogen in the blood, which all play roles in healthy blood clotting. Bruising in individuals with liver disease occurs more frequently and is more severe because the body cannot repair damaged blood vessels the way it should.
Von Willebrand Disease
Individuals diagnosed with Von Willebrand disease, a condition they are born with, are known to bruise easier than others. This disorder is inherited from an affected individual's parents. The genetic mutation that causes Von Willebrand disease is one that affects the way a certain blood-clotting protein is produced. When levels of this clotting factor are too low or absent in an individual, platelets cannot adhere to one another properly and cannot effectively bind themselves to the walls of an injured blood vessel. Some individuals affected by this disorder have a deficiency in the clotting factor VIII. Symptoms that occur in these individuals involve bleeding excessively during surgical procedures, menstrual cycles, dental work, and spontaneously from the nose. Lumpy bruises and easy bruising is common in Von Willebrand disease patients because the body is unable to repair injured blood vessels in a timely manner.
Corticosteroids

Corticosteroids are drugs prescribed to help individuals who have compromised immune systems. Some of the most common corticosteroid drugs on the market are prednisone, hydrocortisone, and cortisone, and they treat a wide variety of different conditions. Corticosteroids are sometimes used to treat allergic reactions and rashes, which can occur when the immune system releases histamine into the body. They can also be used to treat inflammation and inflammatory conditions. One inflammation-related condition these drugs are used for is asthma, which causes the respiratory system to become inflamed and blocked with mucus. Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis are often treated with corticosteroids. At the same time, these drugs have the potential for serious side effects, one of which is easy bruising. Topical corticosteroids can cause the skin to become thinner where the medication is applied, which sometimes contributes to the easy bruising. Patients can talk to their doctor about ways to limit the potential side effects of corticosteroids.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a type of pain reliever. Some of them can be purchased over-the-counter, while others are available in prescription doses from a doctor. Most doctors don't recommend using anti-inflammatories for long term treatment of chronic conditions, because they can lead to kidney damage and damage to other organs. Patients should always talk to a doctor before taking any new medications to manage a condition, even over-the-counter medicines. There are several effects anti-inflammatories have on the body, one of which is they reduce the blood's ability to clot. In thinning the blood, individuals might experience more bleeding than usual. When the bleeding occurs outside the skin, it's a wound. However, when it occurs underneath the skin, it's a bruise. It's also possible for NSAIDs to cause stomach problems like constipation, diarrhea, gas, vomiting, nausea, and heartburn.
Hemophilia

Hemophilia is a rarely occurring disorder that happens when blood doesn't have the right proteins for clotting. Some patients make the correct proteins, but don't make enough of them. This lack of normal blood clotting causes them to bleed for longer times than the average individual would following an injury. Lack of clotting factors is also what leads to easy bruising in hemophilia patients. Those with severe hemophilia may sometimes experience deep bleeding inside their bodies, otherwise known as internal bleeding. Random internal bleeding can become life-threatening. Hemophilia occurs genetically, and while it doesn't have a cure, it can be treated by regularly replacing the deficient clotting factors in the body. Some patients with severe deficiencies experience spontaneous bleeding, but those with a mild form of the disease might only bleed heavily after they're injured or undergo surgery. It's important to be aware of the signs of spontaneous bleeding. If individuals have deep or large bruises that aren't explained, this is often a sign their body is experiencing spontaneous bleeding.
Vasculitis
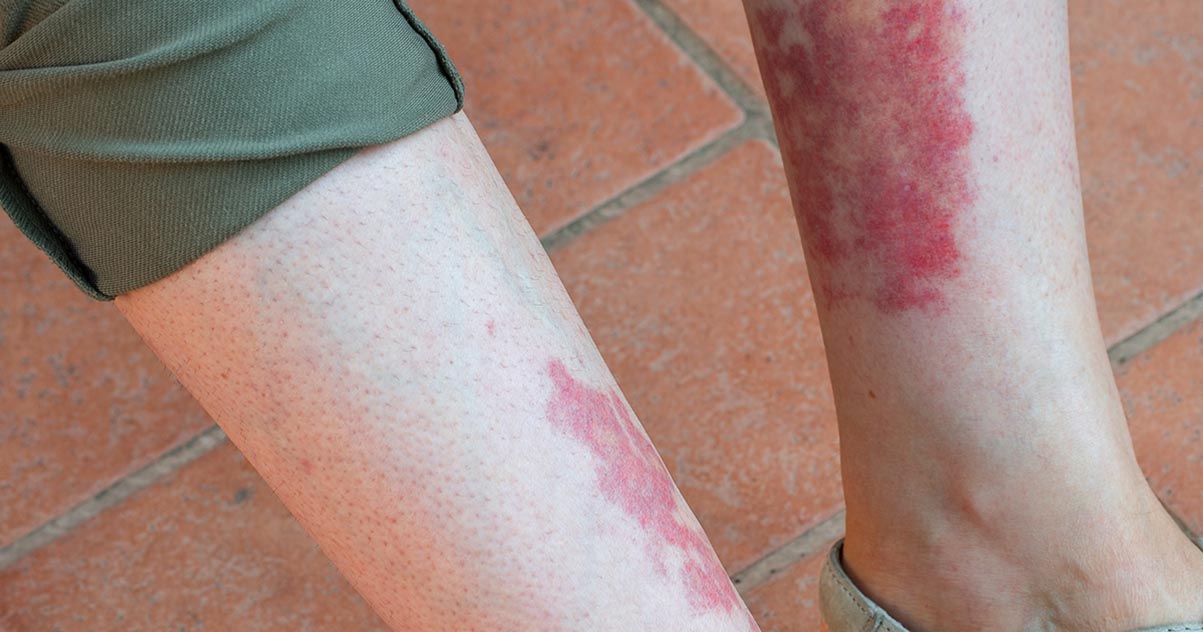
Vasculitis is a medical condition that occurs when the blood vessels become inflamed. It is an autoimmune disease, which means it occurs because the immune system mistakenly attacks the body. This condition doesn't always have a known cause. In some cases, it can develop as a secondary disease after another disease ravages the body. It can also develop as a reaction to a medication or infection. Vasculitis can affect all areas of the blood vessels including capillaries, veins, and arteries. Inflamed blood vessels can become narrow, so it's difficult for blood to move through. Some vessels might become completely closed off or bulge until they burst. A burst blood vessel is called an aneurysm, and it can cause dangerous bleeding in different areas of the body. Burst blood vessels have the potential to cause easy bruising underneath the skin.
Leukemia

Leukemia, which affects blood cells, can cause individuals to be more susceptible to bleeding and bruising. Bruising and bleeding are so common in leukemia patients that one of the common symptoms of leukemia is a rash. Leukemia rashes don't tend to be linked to the cancer, and most cases will either resolve without needing treatment or can be treated through over-the-counter medicines. Some forms of leukemia cause white blood cells to stop functioning the way they should. With healthy white blood cells, the cells die when they become damaged, but in leukemia patients, the cancerous cells continue to grow and spread until they crowd out the healthy ones. This prevents white blood cells from doing their job, which is to fight infection and disease. There are several different symptoms of leukemia besides the bruising and rashes. Patients might develop a fever and flu-like symptoms, and because their immune system is compromised, they might also experience frequent infections. Anemia and bone pain are common symptoms due to the lack of functioning white blood cells.
