Common Causes And Complications Of Ingrown Nails
Ingrown nails are a commonly occurring condition that happens when the side or corner of the nail grows into the skin. Fingernails and toenails can both be affected, but individuals are more likely to develop ingrown toenails. An ingrown toenail leads to swelling, redness, and pain, and some patients may also develop an infection. The majority of ingrown toenails are centered on the big toe. Home remedies are often enough to treat an ingrown nail, but if patients are experiencing pain severe enough to inhibit their daily activities, or the pain spreads to other parts of the body, they should talk to a doctor about how to relieve their discomfort. Patients may need a course of antibiotics if there's an infection, and their doctor can alleviate other complications as well.
Of course, it's important to understand the causes and complications linked to ingrown nails. Uncover these details now.
Cutting Nails Too Short

Cutting the nails too short can lead to an ingrown toenail. The same is true if individuals don't cut their nail straight across. The risk also becomes higher if an individual's toenails have an unusual curve. It helps individuals to not pick at their nails or peel them with their fingers. When individuals clip their nails, they should trim them straight across rather than curving them to match their toes or fingers. If individuals have a manicure or pedicure done, they should tell the manicurist or pedicurist to clip their nails straight instead of curved. Individuals who have conditions that cause poor circulation in the legs and feet should have their nails clipped regularly by a podiatrist. When individuals cut their nails, they shouldn't cut so deeply that they can no longer see the white part. Individuals should try to stop biting or peeling their nails if they ever engage in those habits. At the same time, individuals should avoid leaving their nails too long as well. A good rule of thumb is to keep the nails about the length of the tip of the fingers or toes.
Read more about the common causes and complications of ingrown nails now.
Injury To The Nail

An injury to the nail can increase an individual's chances of developing an ingrown toenail. One easy way to injure the nails is by clipping them too short. If individuals clip the nail bed, they might notice their nail bleeds a little and that their finger hurts. It's best to put a bandage over the wound while it heals to keep from aggravating it. Other injuries to the nail can occur if the nails are raggedly shaped. If the nail catches on something, it may break or rip partway through the nail bed. Hangnails might also increase the chances of developing an ingrown toenail. A hangnail occurs when the side of the nail or the cuticle begins to peel away, leaving a wound behind. Hangnails can be very irritating and painful. Even when they don't bleed, they often ooze clear fluid. Slamming a nail against something and bending it is another injury that might cause individuals to develop an ingrown nail on the hands or feet.
Get more details about the complications and causes of ingrown nails now.
Shoes That Crowd Toenails

Shoes that crowd the toenails are more likely to cause an ingrown toenail, especially if individuals have long nails. This is part of why experts recommend keeping toenails no longer than the tips of the toes. If individuals have long toenails that press against the front of their shoes, the pressure can force their nail into the side or bottom of the nail bed. High heels and some boots often have narrow toe boxes that can pinch the toes and toenails. It's important to look for shoes that fit well. The toes should be roomy enough that the feet don't feel crowded. If individuals wear improperly fitting shoes, they'll have a higher chance of developing injuries and structural abnormalities like bunions. Individuals with nerve damage in their feet might struggle to sense whether their shoes fit them properly or not. If individuals do have foot problems, they should try to buy their footwear from a store that specializes in shoes for those who have foot issues. The experts there can help customers find the right fit.
Keep reading to learn more about causes and complications of ingrown nails now.
Bone Infection
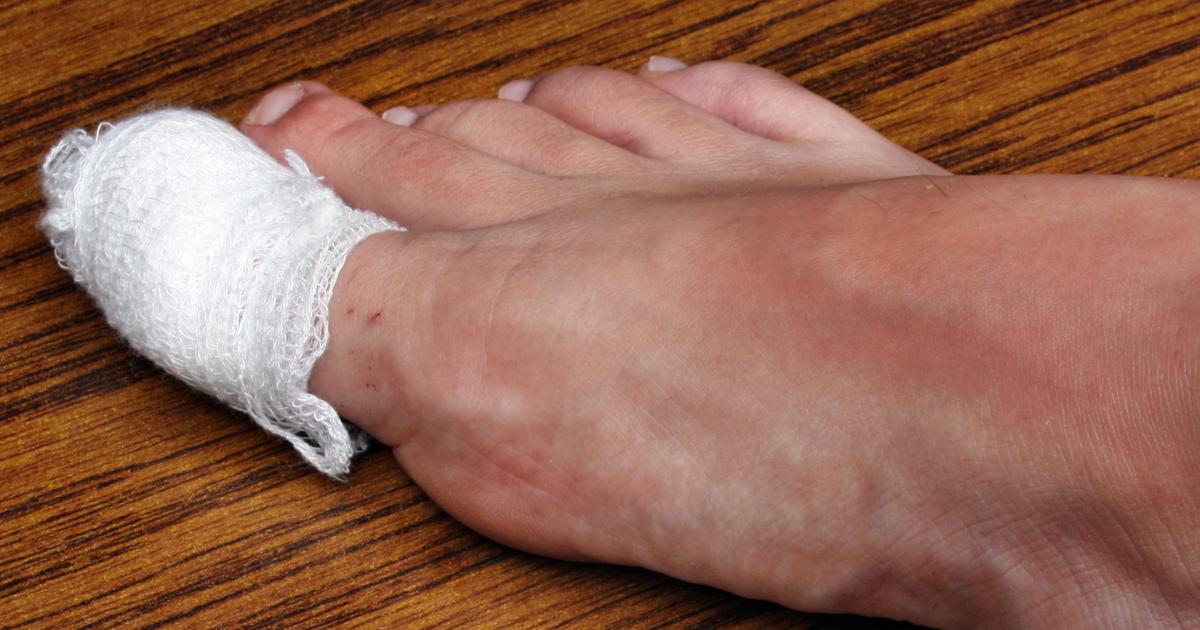
Serious complications from an ingrown toenail are rare. Many individuals have an ingrown toenail at some point during their lives, but not many of them develop a serious enough condition to need medical treatment. However, there have been cases where an ingrown toenail leads to a bone infection, which is also called osteomyelitis. There are several ways for bones to become infected beyond ingrown nails. Sometimes an infection spreads through an individual's bloodstream and into their bone, or another open wound causes the bone to be exposed to infection. Staph bacteria are the most common bacterial causes of bone infections. If individuals have diabetes and nerve damage in their feet, they may be more likely to develop a bone infection because of the inability to tell when they have an ingrown toenail. Only two individuals in every ten thousand will ever develop osteomyelitis. Both children and adults can be affected, and individuals may be at an increased risk if their immune system is compromised.
Discover additional complications of an ingrown nail now.
Gangrene
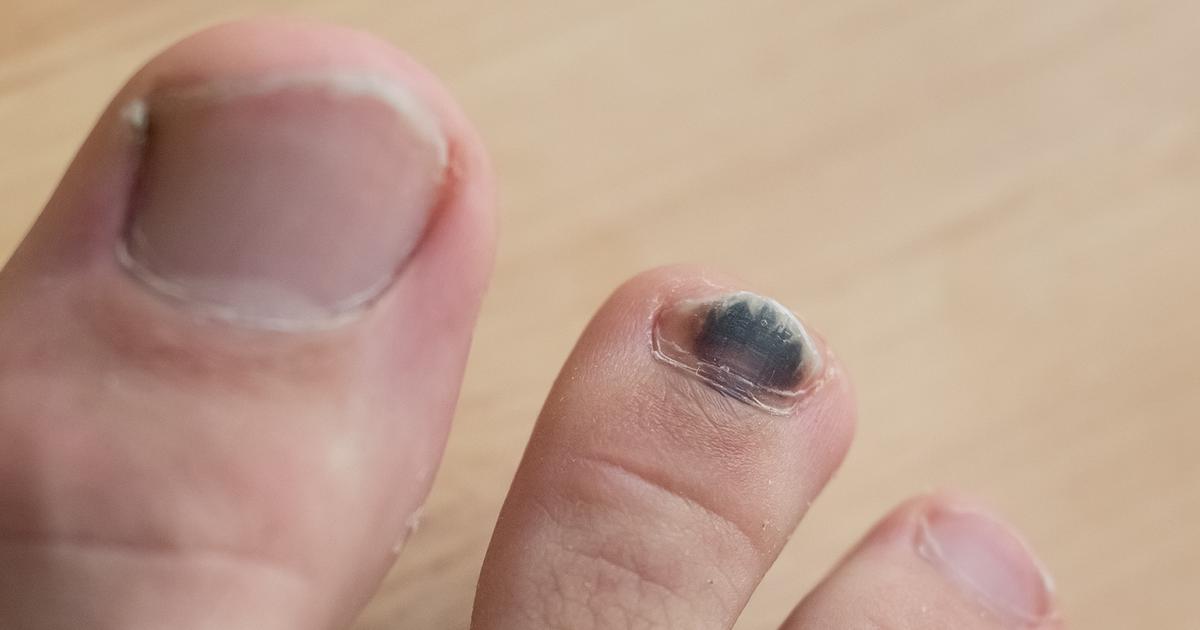
Gangrene is another rare complication of an ingrown nail. In the majority of cases, the injury is treated before it can reach the point of gangrene. However, nerve damage related to diabetes can make it difficult to tell when a wound is serious. Minor foot injuries like ingrown toenails can lead to open sores if they don't heal. If the open sore becomes infected or starts to decay, gangrene is a possibility. Gangrene occurs when blood flow is interrupted to part of the body. Most commonly, gangrene affects the fingers, toes, and limbs. Individuals with underlying conditions that damage the blood vessels and circulatory system are at a higher risk. Gangrene often needs treatment through surgery that removes the dead tissue. Patients are also often prescribed antibiotics to treat infection. Early identification and treatment make for a better prognosis.
