Guide To Treating Pituitary Tumors
A pituitary tumor occurs when an abnormal mass of tissue grows in the pituitary gland. These tumors can affect the hormone regulation of the pituitary gland. They may cause it to produce too many or too few hormones. The majority of pituitary tumors are not cancerous. These growths are called adenomas. They will stay inside the pituitary gland or the tissues around the pituitary gland, instead of spreading to other areas.
There are several pituitary tumor treatments out there, including medications for pituitary tumors. Surgery for pituitary tumors is another option. Natural remedies for pituitary tumors are only supportive treatments. One example may be acupuncture for pituitary tumors. Ultimately, the best treatment for pituitary tumors depends on how the tumor is impacting the patient's daily life, and if the tumor is cancerous. Thus, understanding the options to treat pituitary tumors is vital.
Craniotomy
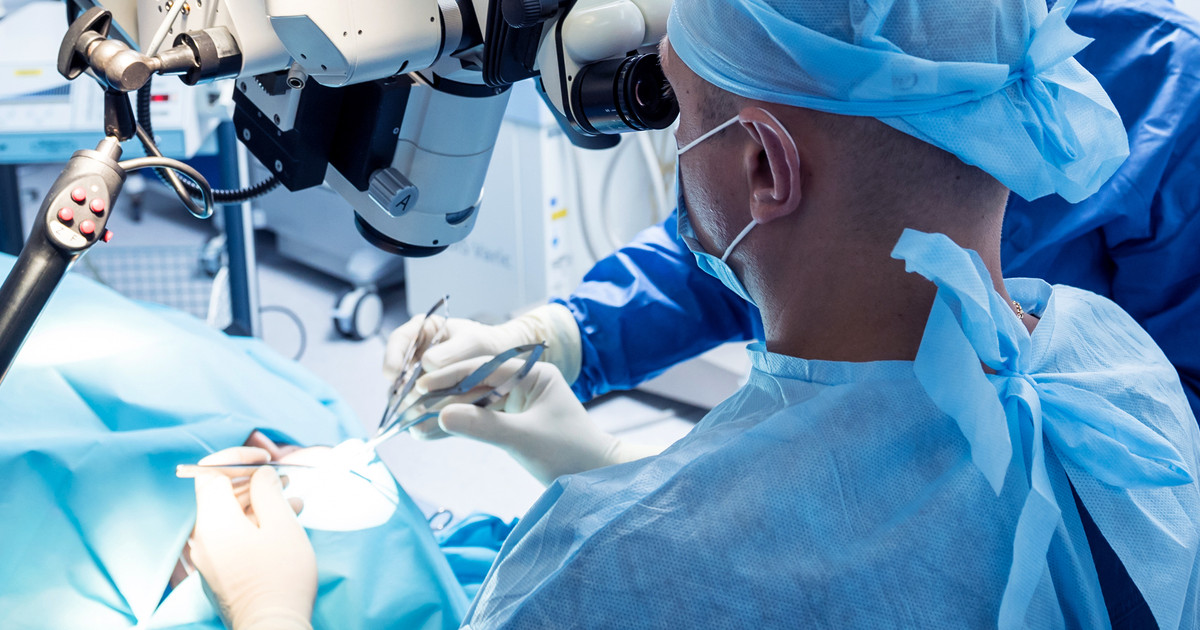
A craniotomy is a surgical procedure that is typically used to remove a tumor from the pituitary gland. It may also be used to treat abscesses, aneurysms, brain tumors, and traumatic brain injuries. A craniotomy may also be used to treat hemorrhage. A trained neurosurgeon performs this type of procedure. Patients who undergo the procedure are typically given a general anesthetic.
A surgeon will remove a portion of the patient's skull to expose the pituitary gland when treating a tumor. They are then able to excise the pituitary tumor. Surgeons may do so in its entirety or remove as much as possible without causing brain damage. Before the surgery, the surgeon will shave part of the patient's scalp to make the incision. They will drill a hole precisely above the pituitary tumor and then remove a flap of bone. After the surgeon has removed the tumor, they will replace the flap with wires, screws, or plates.
Continue reading to reveal additional options for treating a pituitary tumor now.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery

Most doctors will recommend treating the effects of the pituitary tumor with medication. However, stereotactic radiosurgery is recommended if medication cannot control the tumor or if the tumor is likely to grow. This is radiation therapy that does not require invasive surgical procedures. It is sometimes preferred to traditional therapy because it requires fewer doses for the same level of efficacy.
This procedure allows for one to five doses of focused radiation to be administered to a pituitary tumor. It is a popular option for tumors that cannot be removed completely through surgery. It may also be used on tumors that tend to recur after surgery. Different methods can be used to administer stereotactic radiosurgery. One is by using a linear accelerator. The radiation can also be given using a surgical tool called a gamma knife.
Get more information on how to treat pituitary tumors now.
Dopamine Agonists
Pituitary tumors can adversely affect the levels of dopamine in the brain. Dopamine is one of the most complex neurotransmitters in the brain. It is responsible for many different functions. Changes in dopamine levels can alter your memory, mood, behavior, and physical movements. Dopamine agonists can imitate dopamine and replace what is lost when a patient's levels are low. Older versions of this medication tend to have cardiovascular side effects. However, the more recent ones have fewer of these side effects. They can also target more specific dopamine receptors.
It is important to follow the exact dosage instructions for any dopamine agonists. They can sometimes cause severe withdrawal symptoms, including organ failure and problems with pain. Patients must also avoid driving until they are aware of how the medication affects them. This type of medication can cause sleepiness and dizziness. If the dose is too high, patients may experience serious mental health problems and compulsive behavior as well.
Learn more about treating pituitary tumors now.
Somatostatin Analogs
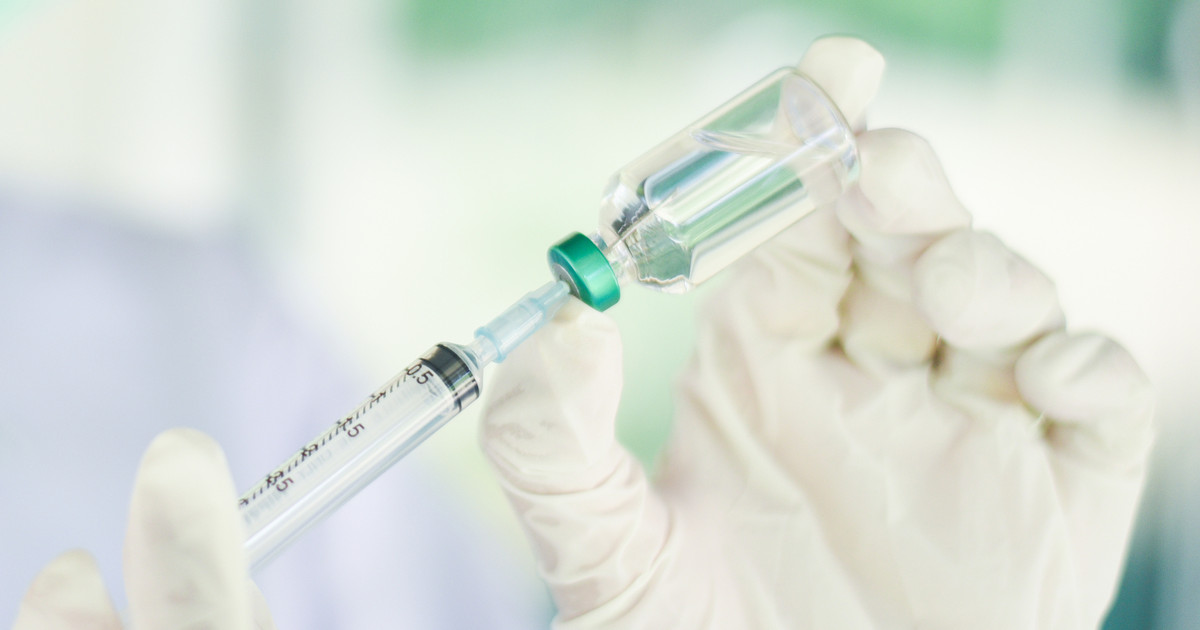
Pituitary tumors can sometimes cause the body to make too many hormones rather than too few. Some pituitary tumors can trigger a set of symptoms referred to as carcinoid syndrome. Somatostatin analogs are sometimes used to treat this syndrome. The bowel, pancreas, stomach, and hypothalamus naturally make somatostatin. It can stop or slow the body's production of insulin and some gut hormones. This substance is also necessary to empty the bowel and stomach.
Somatostatin analogs are artificial versions of this substance. When patients take them, they help slow the body's production of serotonin and growth hormone. This controls diarrhea, skin flushing, and other carcinoid syndrome symptoms. In addition, it can sometimes help shrink the original tumor. Somatostatin analogs are usually administered as an injection, with one injection occurring every four weeks. A nurse usually administers the injection, though some doctors may show patients how to administer their own.
Discover more pituitary tumor treatment options now.
External Beam Radiation
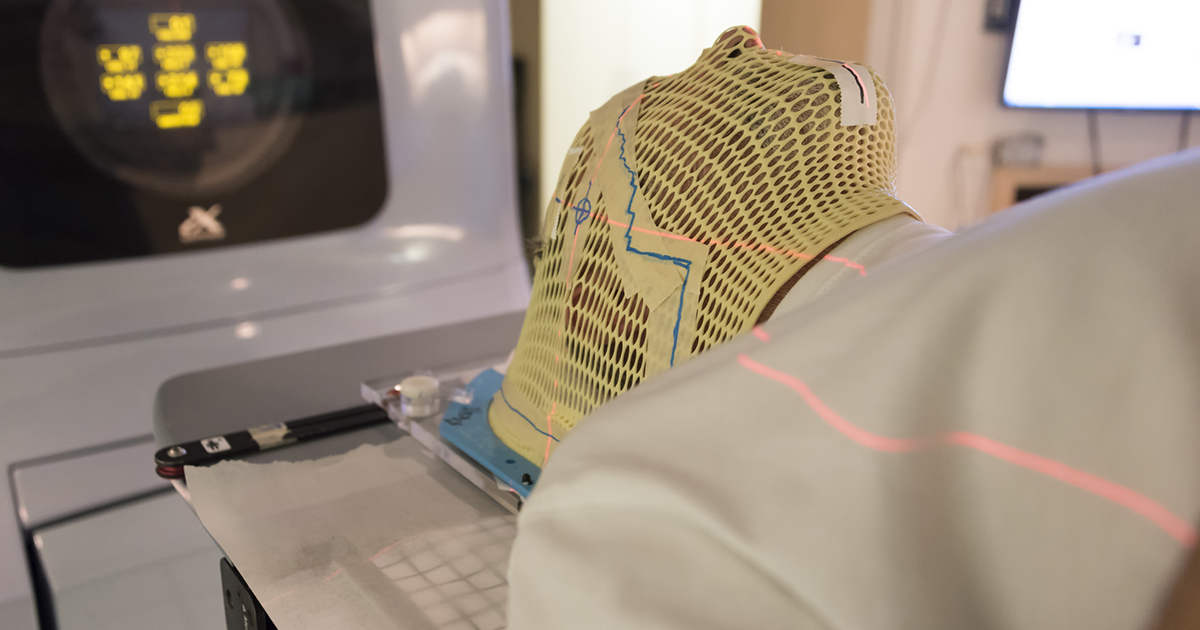

External beam radiation is the most common form of radiation therapy for cancerous tumors. Thus, it may be used when a pituitary tumor is cancerous. The goal is to use radiation doses to shrink tumors and destroy cancer cells. External beam radiation is done using a linear accelerator, which is a special type of X-ray machine. Linear accelerators can deliver radiation at any necessary angle. They can also customize the beams to the shape of the tumor.
The machine never has to touch the patient. Instead, it moves around their body and aims radiation beams at the tumors. Focused external beam radiation may offer more focused and targeted treatment than traditional radiation therapy. The practice can also reduce the damage done to the organs and healthy tissue surrounding the tumor. This makes it popular for pituitary tumors, since they are quite close to the brain.
