Silent Saboteurs: Common Ailments That Hide Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases, a group of disorders where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, present a complex medical challenge. These conditions often manifest with symptoms that mimic other ailments, making diagnosis a labyrinthine task for healthcare providers. This article delves into the intricate web of ailments that can mask autoimmune diseases, revealing the hidden layers beneath seemingly benign symptoms. By exploring the top ten ailments that obscure these conditions, we aim to enhance understanding and awareness, aiding in the early detection and treatment of autoimmune disorders. This exploration will illuminate the subtle nuances and interconnected nature of these diseases, offering a comprehensive view of the challenges faced in their diagnosis.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: The Exhaustion Enigma

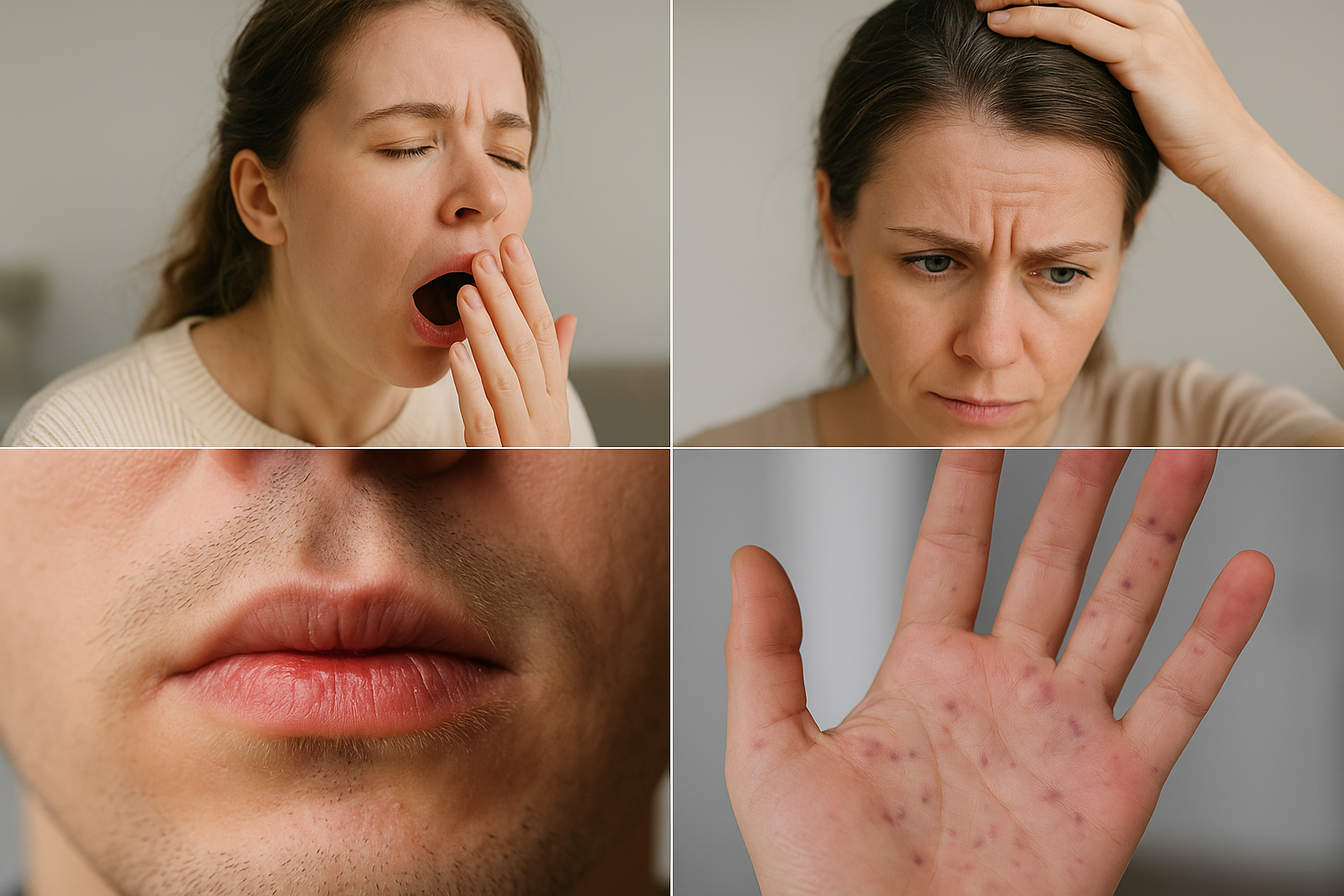
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) is a debilitating disorder characterized by extreme fatigue that cannot be explained by any underlying medical condition. The fatigue worsens with physical or mental activity but doesn't improve with rest. This ailment often masks autoimmune diseases like lupus or multiple sclerosis because of its overlapping symptoms, such as muscle pain, memory issues, and headaches. The challenge lies in the subjective nature of fatigue, making it difficult to quantify and often leading to misdiagnosis. Understanding the intricate link between CFS and autoimmune diseases is crucial for healthcare providers to differentiate between the two and provide accurate treatment.
Fibromyalgia: The Painful Puzzle

Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition known for widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in localized areas. Its symptoms are strikingly similar to those of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, leading to frequent misdiagnosis. The exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, but it's believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. The overlap of symptoms like joint pain and fatigue makes it a prime candidate for masking autoimmune disorders. Effective diagnosis requires a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms and often the exclusion of other conditions, highlighting the need for increased awareness and research into this enigmatic ailment.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The Digestive Dilemma

Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common disorder affecting the large intestine, characterized by cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and diarrhea or constipation. Its symptoms can closely resemble those of autoimmune diseases like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which also affect the gastrointestinal tract. The non-specific nature of IBS symptoms makes it a frequent misdiagnosis for autoimmune conditions, delaying appropriate treatment. Understanding the subtle differences between IBS and autoimmune disorders is essential for proper diagnosis, as it involves recognizing patterns in symptoms and conducting thorough testing to rule out inflammatory conditions.
Depression and Anxiety: The Emotional Overlay

Depression and anxiety are prevalent mental health disorders that often accompany autoimmune diseases, either as a symptom or a consequence. These conditions can mask the underlying autoimmune disorder, as symptoms like fatigue, sleep disturbances, and concentration difficulties overlap. The psychological stress from living with an undiagnosed autoimmune disease can exacerbate mental health issues, creating a vicious cycle. Differentiating between primary mental health disorders and those secondary to autoimmune diseases requires careful assessment by healthcare professionals, emphasizing the need for a holistic approach to diagnosis and treatment that considers both physical and psychological health.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: The Hormonal Haze
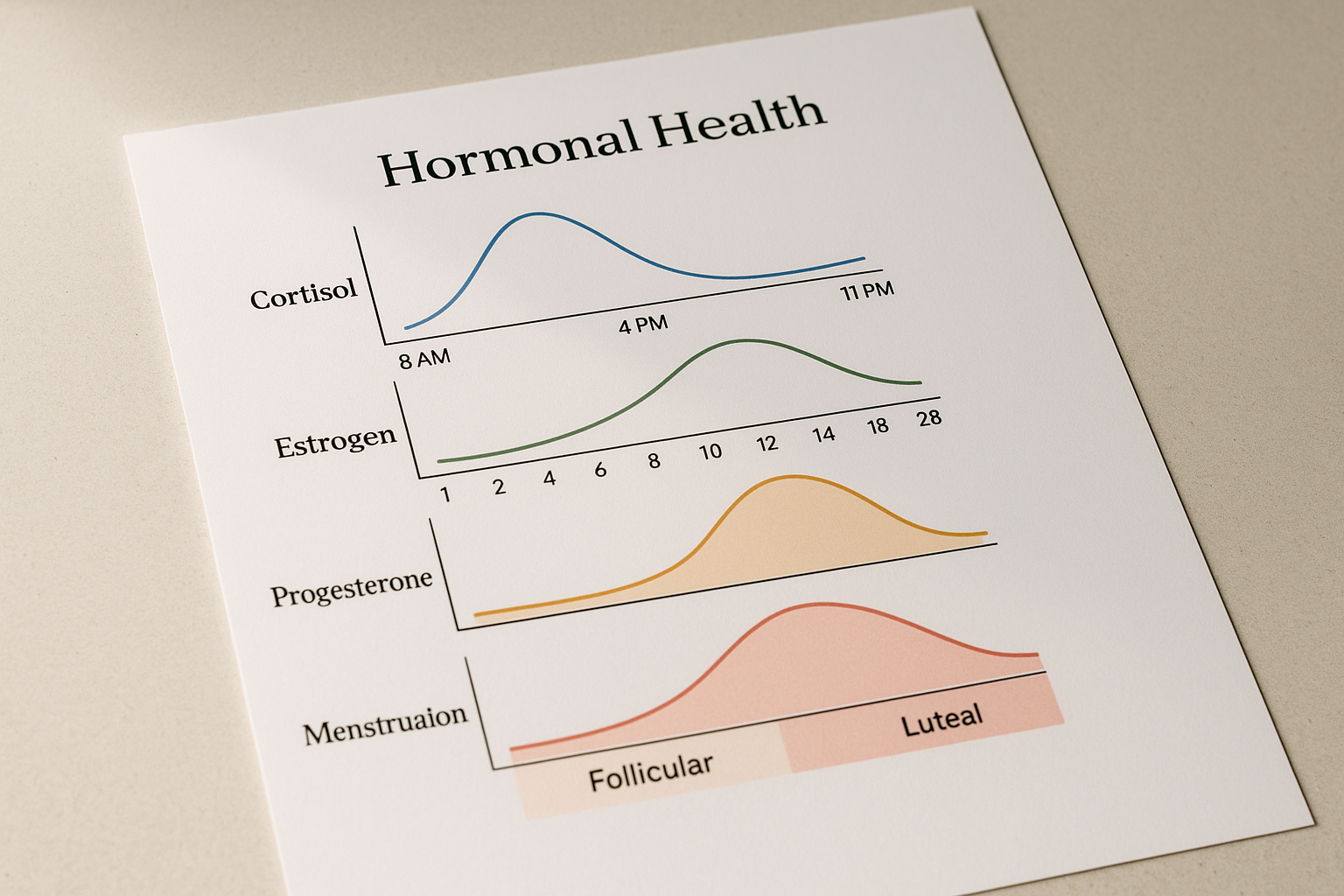
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age, characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. Its symptoms, such as fatigue, weight gain, and skin issues, can mimic those of autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto's thyroiditis or lupus. The hormonal imbalance in PCOS can also affect immune function, further complicating the clinical picture. Accurate diagnosis requires a thorough understanding of the hormonal and metabolic aspects of PCOS and their potential interplay with autoimmune conditions, underscoring the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in managing these complex cases.
Lyme Disease: The Infectious Imitator
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness that can present with a wide range of symptoms, including fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash. These symptoms can overlap with autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, leading to diagnostic confusion. The chronic nature of untreated Lyme disease can mimic autoimmune conditions, with persistent joint pain and neurological symptoms. Distinguishing between Lyme disease and autoimmune disorders requires specific testing for the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium, as well as a detailed patient history to identify potential exposure to tick habitats, highlighting the need for vigilance in regions where Lyme disease is prevalent.
Vitamin D Deficiency: The Silent Saboteur

Vitamin D deficiency is a common condition that can contribute to a range of health issues, including bone pain and muscle weakness. These symptoms can be mistaken for those of autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or multiple sclerosis. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in immune function, and its deficiency can exacerbate autoimmune processes or be a consequence of them. Identifying and correcting vitamin D deficiency is an essential step in the diagnostic process for autoimmune diseases, as it can improve overall health and potentially reduce autoimmune activity, demonstrating the importance of nutritional assessment in managing these conditions.
Hypothyroidism: The Underactive Understudy
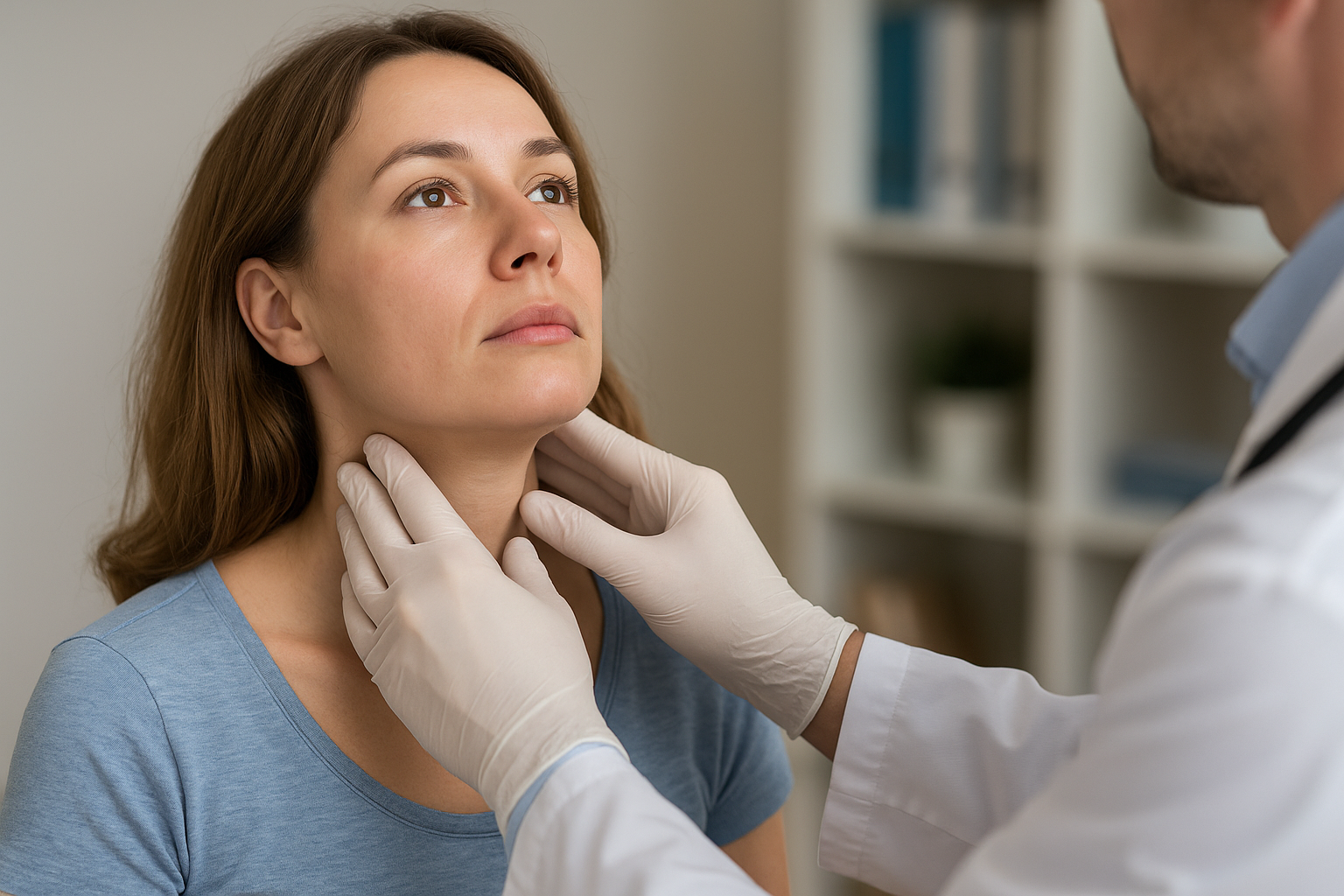
Hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough hormones, can present with symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and depression, which are common in autoimmune diseases like lupus and fibromyalgia. The autoimmune form of hypothyroidism, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, further complicates the picture, as it involves the immune system attacking the thyroid. Differentiating between primary hypothyroidism and autoimmune-related thyroid dysfunction requires comprehensive thyroid function tests and antibody screenings. Understanding the interplay between thyroid health and autoimmune diseases is vital for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, emphasizing the need for a detailed endocrine evaluation in patients with overlapping symptoms.
Sleep Apnea: The Nocturnal Nemesis
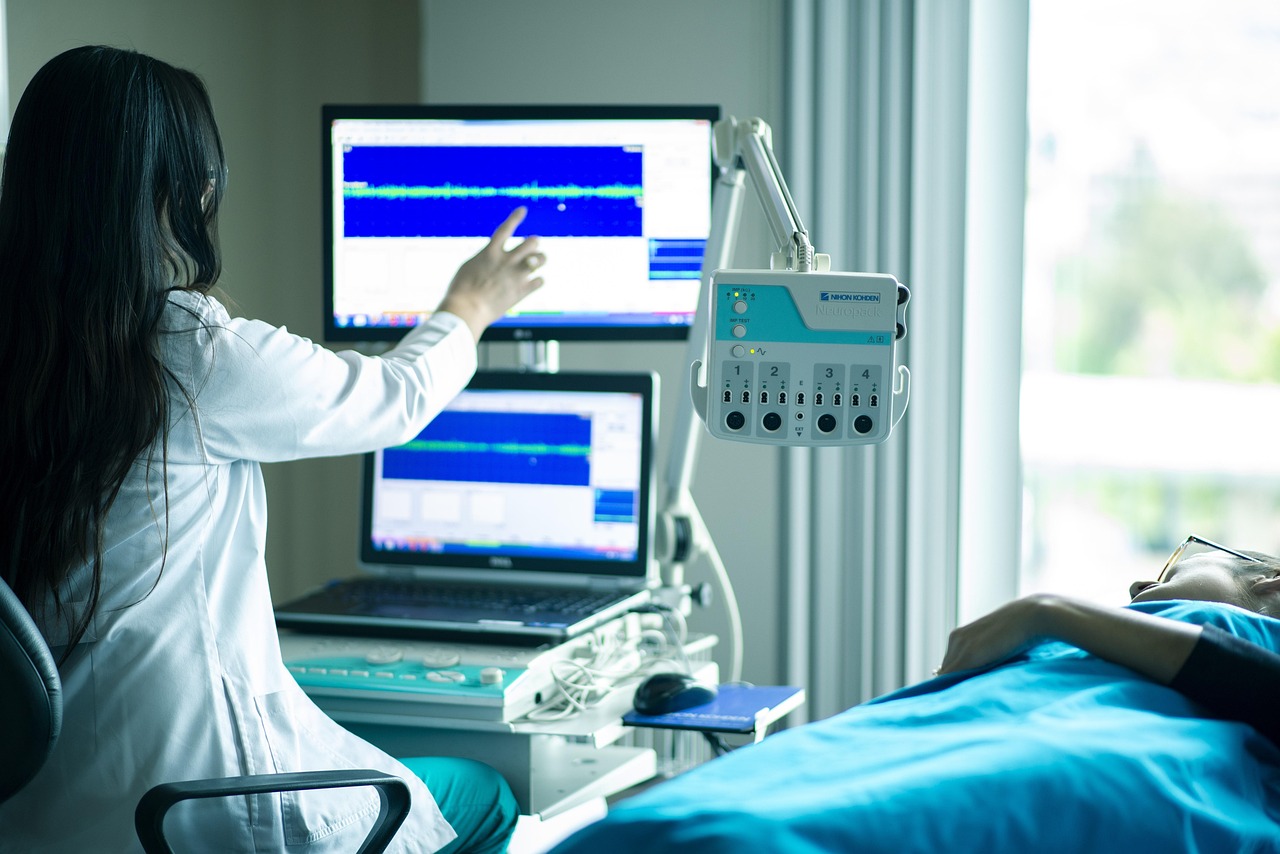

Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue. Its symptoms, such as excessive tiredness and cognitive impairment, can mimic those of autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis or lupus. The chronic sleep deprivation associated with sleep apnea can exacerbate autoimmune symptoms or be misattributed to autoimmune processes. Proper diagnosis involves sleep studies to confirm the presence of apnea and assess its severity. Addressing sleep apnea can significantly improve quality of life and reduce symptom overlap, highlighting the importance of considering sleep disorders in the differential diagnosis of autoimmune diseases.
Celiac Disease: The Gluten Culprit

Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten, leading to damage in the small intestine. Its symptoms, including diarrhea, fatigue, and joint pain, can resemble those of other autoimmune diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. The gastrointestinal and systemic manifestations of celiac disease make it a challenging condition to differentiate, particularly in patients with atypical presentations. Diagnosis requires specific serological tests and a confirmatory biopsy of the small intestine. Understanding the relationship between gluten sensitivity and autoimmune activity is crucial for effective management and highlights the need for dietary assessment in patients with suspected autoimmune diseases.
Navigating the Diagnostic Labyrinth

The complex interplay between autoimmune diseases and the ailments that mask them presents a significant challenge in medical diagnosis. Understanding the subtle nuances and overlapping symptoms of these conditions is essential for healthcare providers to accurately identify and treat autoimmune disorders. This exploration of the top ten ailments that obscure autoimmune diseases underscores the importance of a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis, involving detailed patient history, targeted testing, and consideration of both physical and psychological factors. By unveiling the hidden layers of these conditions, we can improve early detection and enhance treatment outcomes for patients with autoimmune diseases.
