How To Treat Transverse Myelitis
Transverse myelitis is a neurological disorder that causes both sides of part of the spinal cord to become inflamed. In most cases, this causes damage to the myelin, the insulation material that covers the nerve cells. Transverse myelitis causes interruptions between the spinal cord's nerves and the body, so the body doesn't receive messages seamlessly. The symptoms vary depending on the portion of the spinal cord affected.
Transverse myelitis patients often experience pain, paralysis, muscle weakness, sensory issues, or dysfunction of the bowels and bladder. There are several treatment options available, most of which focus on rehabilitative therapy and medications. The majority of individuals with transverse myelitis will have at least a partial recovery, although patients with severe attacks might develop permanent disabilities.
Plasma Exchange Therapy
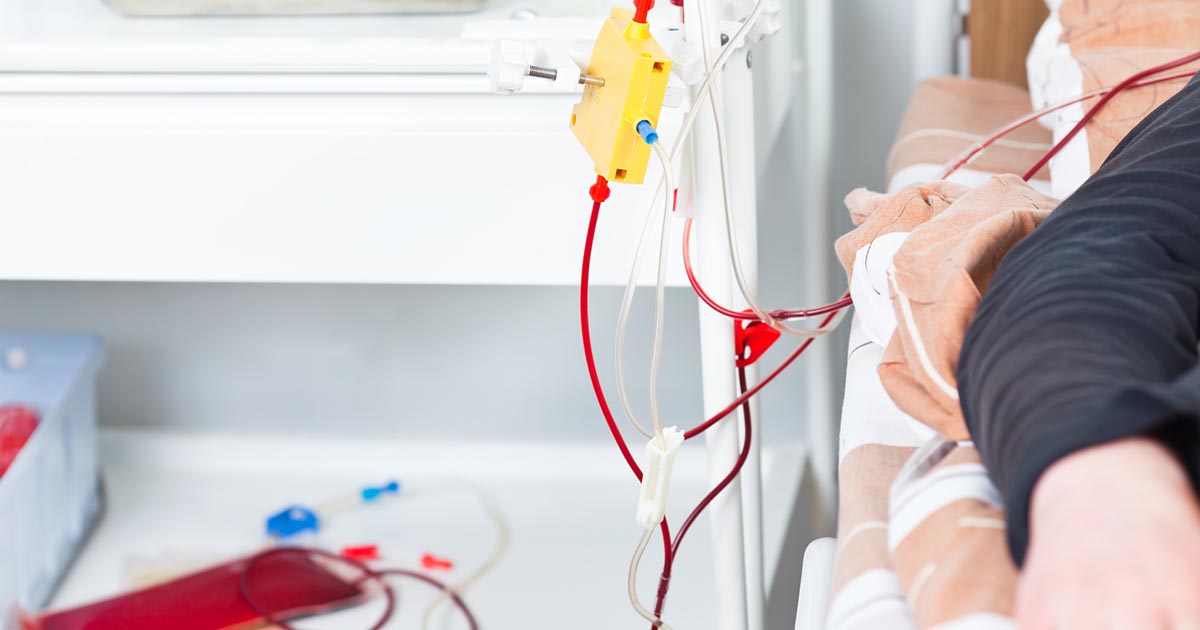
Plasma exchange therapy is a treatment that helps with the acute symptoms of transverse myelitis. While it's not usually the first recommended treatment, it can be very helpful for patients who don't see results with steroids. There haven't been enough studies to explain why plasma exchange therapy helps, but the main theory is exchanging the plasma helps remove inflammatory antibodies produced by the immune system.
Therapeutic plasma exchange, otherwise called plasmapheresis, removes the plasma from a patient's blood and replaces it. Over a period of two to three hours, the patient's blood is removed and the plasma is separated from the red blood cells. A plasma substitute is then added to the red blood cells, and the blood is put back into the patient's body.
Pain Medication
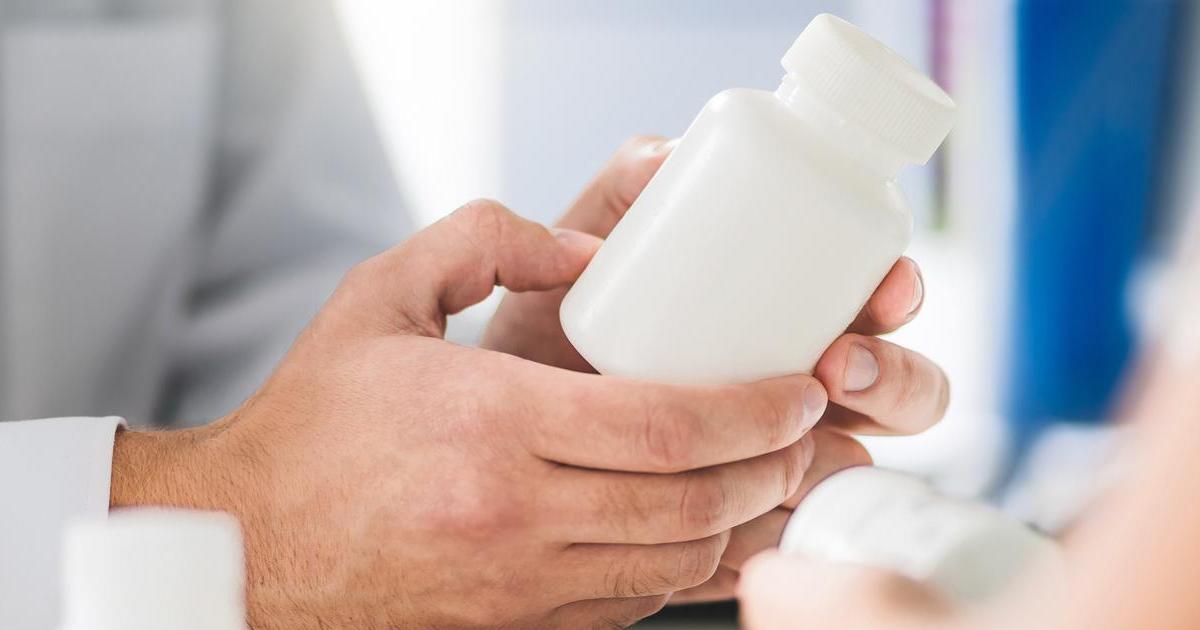

Pain medication is often used to help patients with chronic pain due to transverse myelitis. Some medications to reduce muscle pain may be common pain relievers that don't require a prescription, like ibuprofen and acetaminophen. When the pain is in the nerves, antidepressants like sertraline may be an effective treatment.
Anticonvulsants have also been proven effective. One of the most common symptoms of transverse myelitis is pain. Patients may suddenly start feeling pain in the lower back. There may also be shooting pains down the arms or legs, or pain might surround the abdomen or chest. The pain symptoms will vary depending on what portion of the spinal cord is affected.
Intravenous Corticosteroids
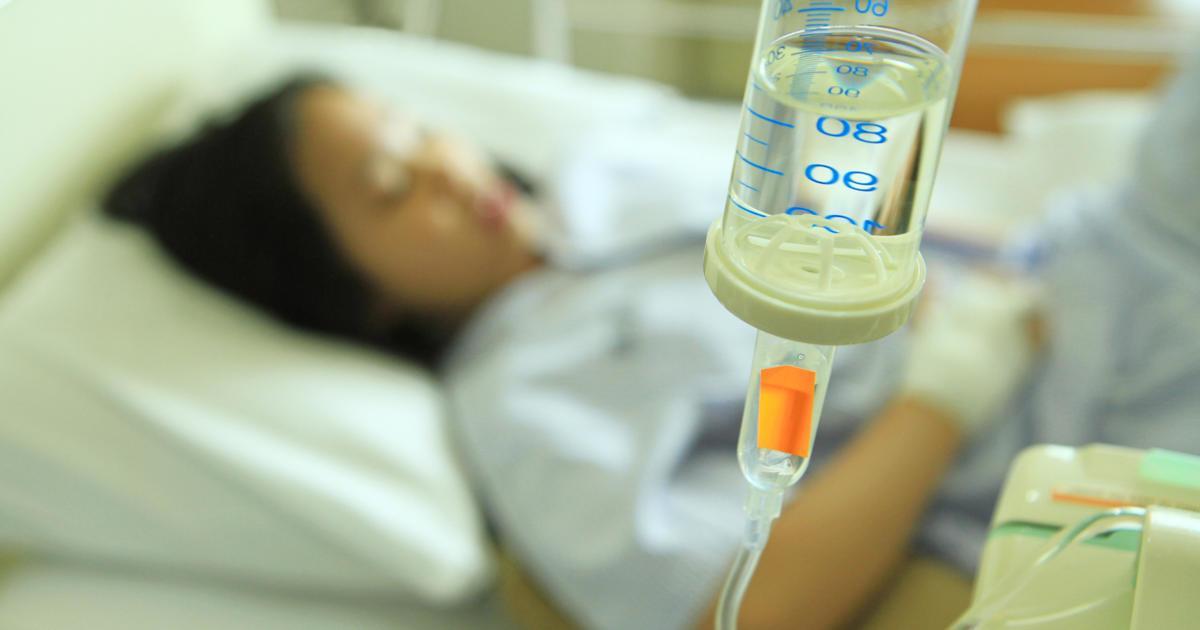
Intravenous corticosteroids are typically the first-line treatment for transverse myelitis. They're administered through a patient's arm over several days. Corticosteroids are artificial drugs that resemble the hormone cortisol. They have the same effect on the body that natural cortisol has when it's secreted by the adrenal gland. Steroids decrease inflammation.
When they're administered intravenously, the drugs target inflammation throughout the body, including the inflammation in the spinal cord. Corticosteroids also reduce the immune system's activity, which can be beneficial, as there is some research indicating there might be an autoimmune component to transverse myelitis, in which the immune system attacks the spinal cord and causes inflammation.
Physical Or Occupational Therapy
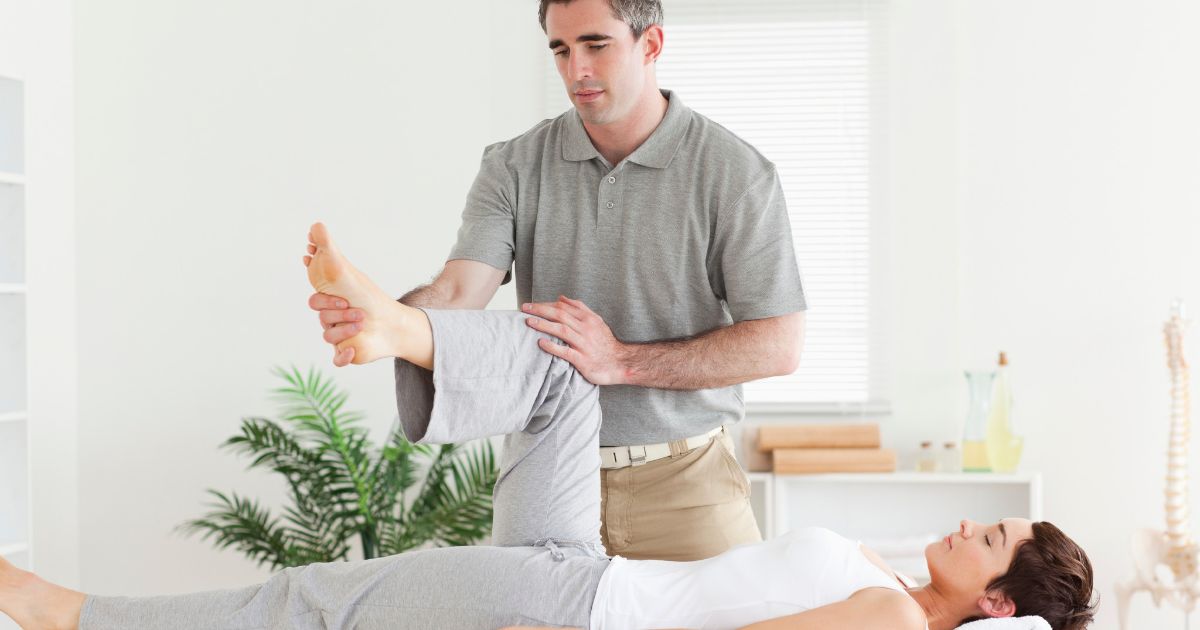

Transverse myelitis patients focusing on long-term recovery may benefit from physical or occupational therapy. Physical therapy helps patients improve their coordination and strength. If the patient has long-term disabilities that require assistive devices, the physical therapist can teach them about using them. Assistive devices might include braces, canes, or a wheelchair. Occupational therapy is a form of therapy that focuses on function in day-to-day life.
Disabled patients will learn new ways to accomplish everyday activities like cleaning, cooking, and bathing. Occupational therapists are experienced working with patients who need help learning the skills required for independence. Many individuals understand the importance of physical therapy, but they might not realize occupational therapy is equally important when learning to manage a disability.
Psychotherapy
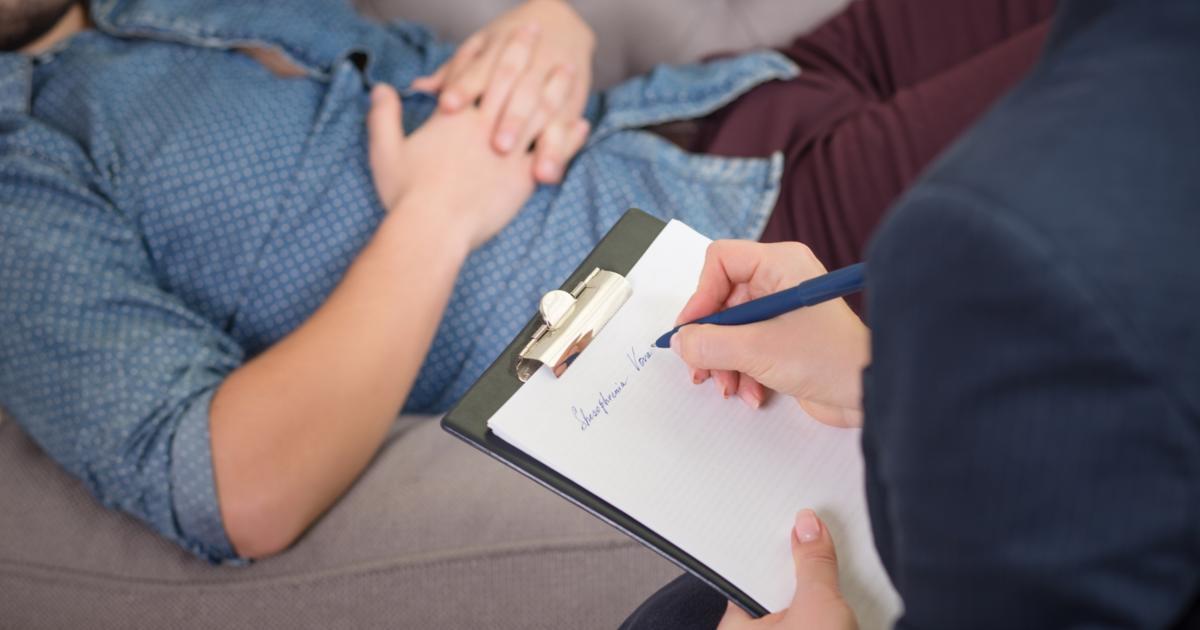

It is quite common for patients dealing with transverse myelitis to develop depression and anxiety, especially when they have long-term complications. Chronic pain and long-term disability both cause significant mental stress. Patients may also have a difficult time adjusting to the changes in their lifestyle or long-term physical limitations. Psychotherapy can be incredibly helpful for patients dealing with mental disorders related to their transverse myelitis. This kind of therapy treats depression, anxiety, and other emotional issues. Mental wellness is an important part of the recovery process, and patients should keep in mind it's just as vital as physical wellness.
