Why Do My Knees Hurt? The Top 12 Culprits To Watch For
Knee pain is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide, often disrupting daily activities and diminishing quality of life. Despite being a prevalent issue, the reasons behind knee pain can be elusive, leading to frustration and prolonged discomfort. Understanding what keeps your knees crying out in pain is crucial for effective management and relief. This article delves into 12 distinct factors that contribute to knee pain, offering insights into how each element plays a role in this complex condition. From anatomical vulnerabilities to lifestyle choices, each section will dissect a specific cause, providing a comprehensive overview of the myriad influences on knee health. By the end of this exploration, readers will have a clearer understanding of knee pain's multifaceted nature and practical strategies to address it.
1. Anatomical Vulnerabilities – The Knee's Complex Structure
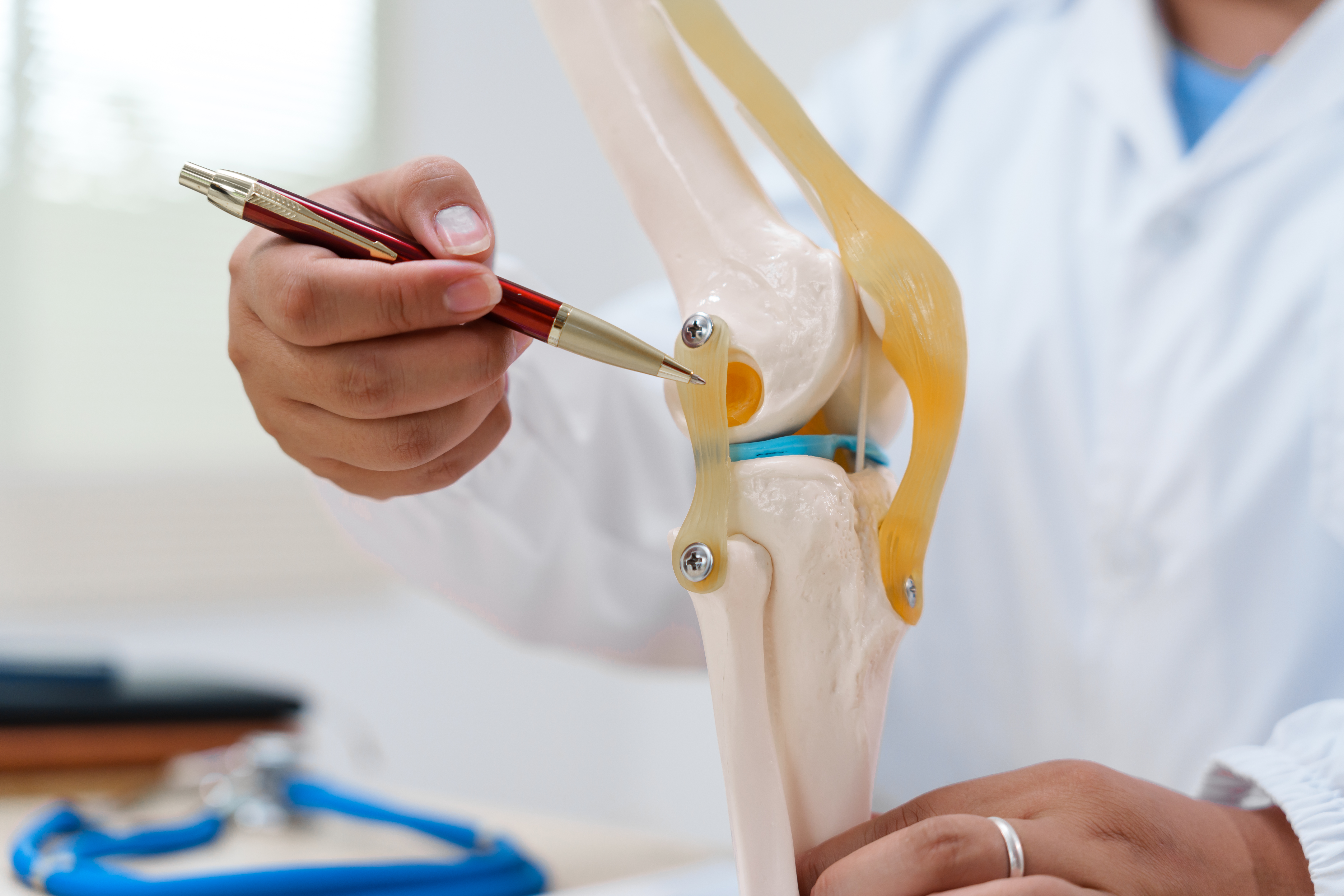
The knee joint is a marvel of biological engineering, designed to support the body's weight while allowing for a wide range of motion. However, its complexity also makes it susceptible to various problems. The knee comprises bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons, each component playing a vital role in its function. When any part of this intricate system is compromised, pain can ensue. For instance, the meniscus, a C-shaped cartilage, acts as a cushion between the thigh and shin bones. Tears in the meniscus are common, especially in athletes, leading to pain and swelling. Moreover, ligaments such as the ACL and PCL provide stability, and injuries to these can result in significant discomfort and mobility issues. Understanding the knee's anatomy is crucial for diagnosing and treating the underlying causes of pain effectively.
2. Osteoarthritis – The Wear and Tear Culprit
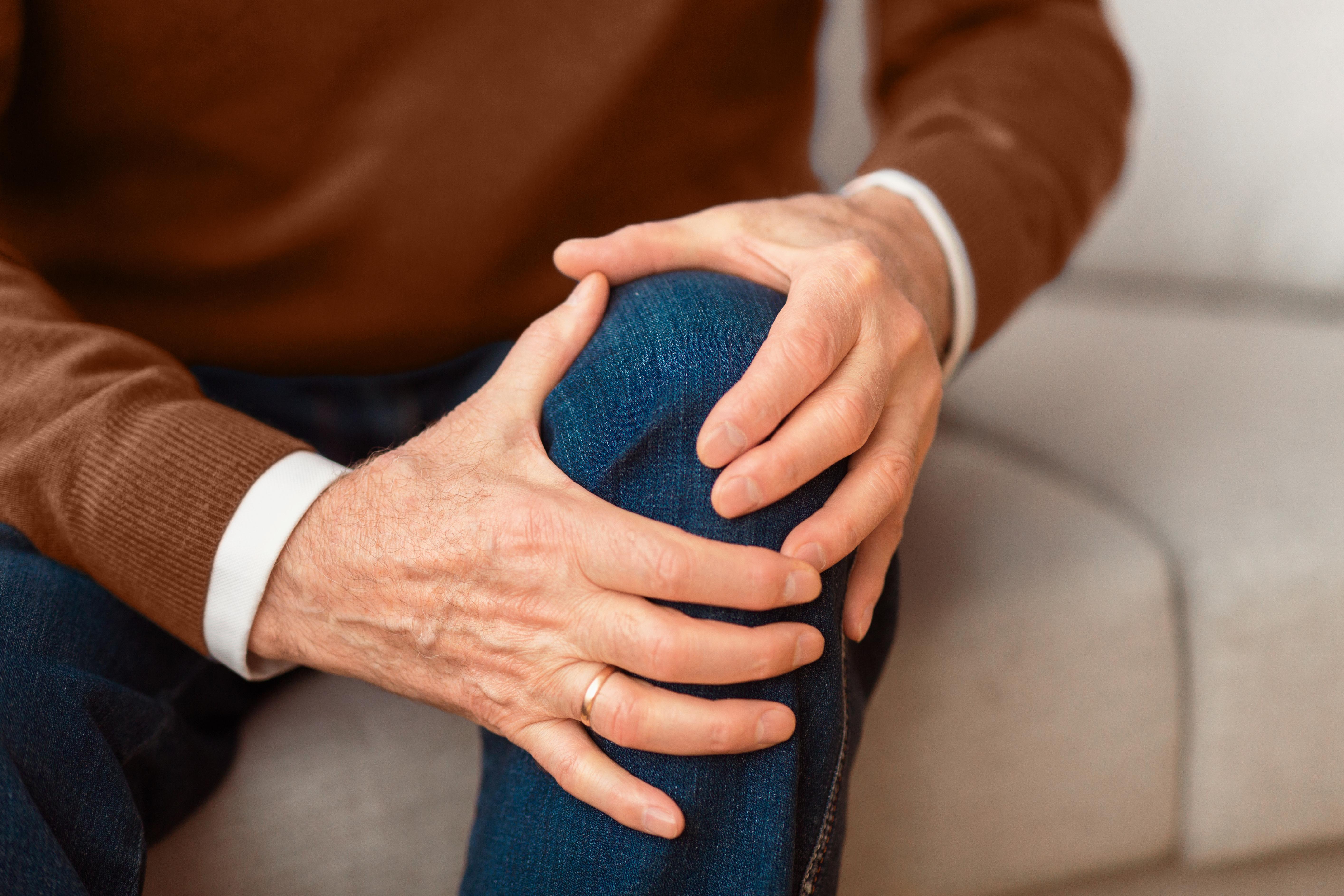

Osteoarthritis is one of the most common causes of knee pain, particularly in older adults. It is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. As the cartilage wears away, bones begin to rub against each other, causing inflammation and discomfort. Risk factors for osteoarthritis include age, obesity, previous knee injuries, and genetic predisposition. Managing osteoarthritis involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and exercise, alongside medical interventions like pain relievers and physical therapy. In severe cases, surgical options like knee replacement may be considered. Understanding osteoarthritis's impact on the knee is essential for developing effective treatment plans and improving patient outcomes.
3. Rheumatoid Arthritis – An Autoimmune Assault
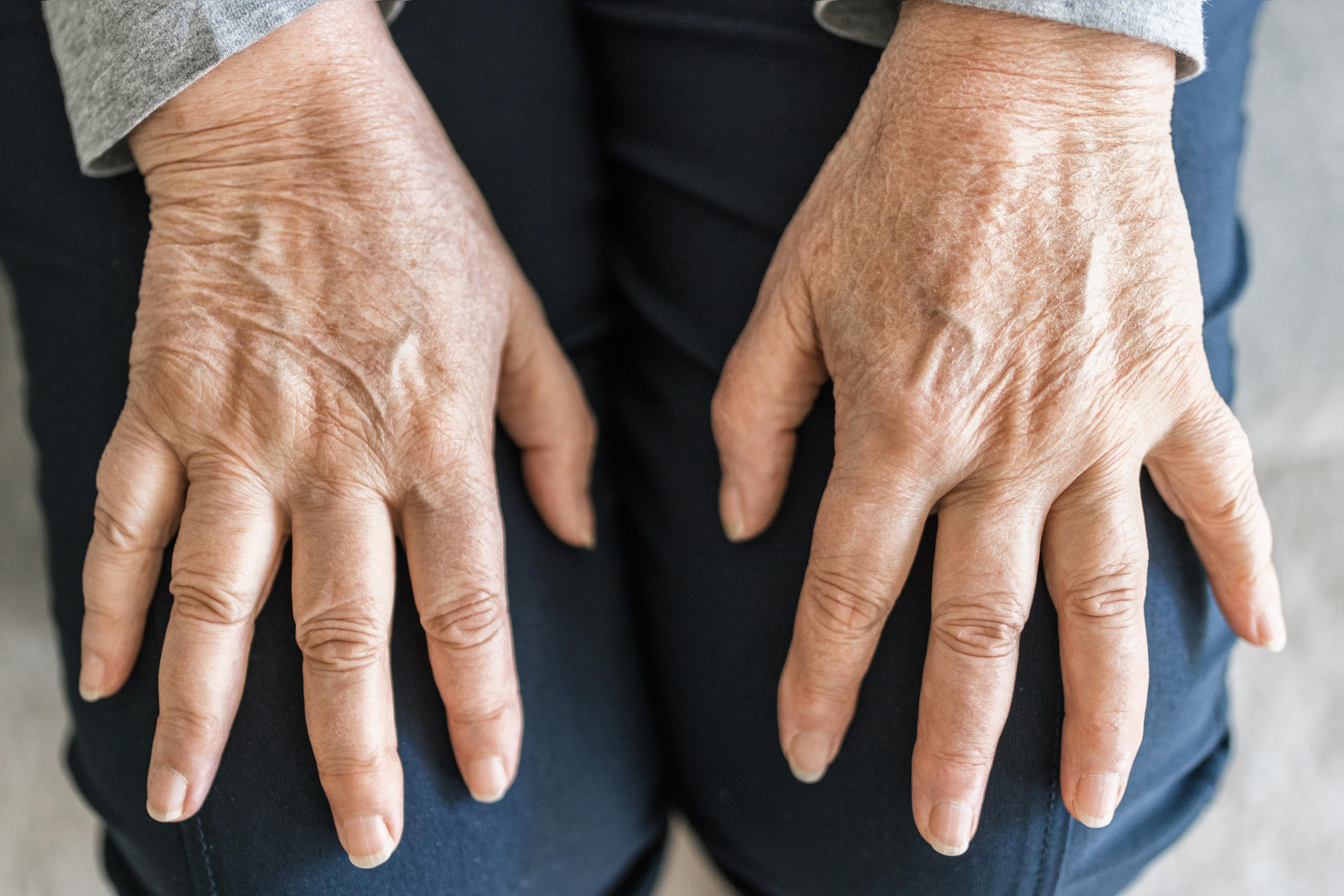
Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the joint lining, causing inflammation and pain. RA can affect any joint, but the knees are often involved, leading to significant discomfort and disability. The exact cause of RA is unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Symptoms include swelling, redness, and warmth in the joints, along with stiffness and pain. Treatment for RA focuses on reducing inflammation and slowing disease progression through medications such as DMARDs and biologics. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing RA effectively and preventing joint damage.
4. Bursitis – The Inflammation of Cushions
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint, reducing friction between bones, tendons, and muscles. When these sacs become inflamed, a condition known as bursitis occurs, leading to pain and swelling around the knee. Bursitis can result from repetitive motion, prolonged kneeling, or direct trauma to the knee. It is commonly seen in athletes and individuals whose occupations require frequent kneeling, such as carpenters and gardeners. Treatment for bursitis includes rest, ice application, and anti-inflammatory medications. In some cases, aspiration of the bursa fluid or corticosteroid injections may be necessary. Understanding bursitis's role in knee pain helps in identifying appropriate preventive and therapeutic measures.
5. Tendinitis – The Overuse Injury
Tendinitis refers to the inflammation of tendons, the thick cords that attach muscle to bone. In the knee, patellar tendinitis, often called "jumper's knee," is a common overuse injury seen in athletes involved in sports requiring frequent jumping, such as basketball and volleyball. The repetitive stress on the tendon can lead to micro-tears, resulting in pain and swelling below the kneecap. Managing tendinitis involves reducing activity levels, applying ice, and engaging in physical therapy to strengthen the affected area. Preventive strategies include proper warm-up exercises and using appropriate techniques during sports activities. Recognizing tendinitis as a cause of knee pain is vital for implementing effective treatment and prevention strategies.
6. Ligament Injuries – Stability Compromised

Ligament injuries, particularly to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), are common causes of knee pain and instability. These injuries often occur during activities that involve sudden stops, jumps, or changes in direction. ACL tears are prevalent in sports like soccer, football, and skiing, causing immediate pain, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the knee. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the injury and the patient's activity level, ranging from physical therapy and bracing to surgical reconstruction. Understanding the impact of ligament injuries on knee health is essential for developing effective rehabilitation programs and preventing future injuries.
7. Meniscus Tears – The Cartilage Conundrum

The meniscus is a crucial component of the knee joint, providing cushioning and stability. Tears in the meniscus are a common source of knee pain, especially in athletes and older adults. These tears can result from acute trauma, such as a sudden twist or turn, or from degenerative changes over time. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and a popping sensation during movement. Treatment options depend on the tear's location and severity and may include rest, physical therapy, or surgical intervention. Understanding the role of the meniscus in knee function is vital for diagnosing and treating tears effectively, ensuring optimal recovery and preventing long-term complications.
8. Gout – The Metabolic Menace

Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling. While gout can affect any joint, the knees are commonly involved, causing intense discomfort. Risk factors for gout include a diet high in purines, obesity, and certain medical conditions like hypertension and kidney disease. Managing gout involves lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and weight loss, alongside medications to reduce uric acid levels and control inflammation. Recognizing gout as a potential cause of knee pain is crucial for implementing effective treatment strategies and preventing recurrent attacks.
9. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome – The Runner's Dilemma

Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), often referred to as "runner's knee," is a common cause of knee pain, particularly in athletes. It occurs when the patella, or kneecap, does not move properly within its groove, leading to pain and discomfort around the front of the knee. Factors contributing to PFPS include muscle imbalances, overuse, and improper alignment of the knee joint. Treatment focuses on strengthening and stretching exercises to improve muscle balance and knee alignment, as well as modifying activities to reduce stress on the knee. Understanding PFPS is essential for athletes and active individuals to prevent and manage this condition effectively.
10. Obesity – The Weighty Burden

Obesity is a significant risk factor for knee pain, as the excess weight places additional stress on the knee joints, accelerating wear and tear. This increased load can lead to conditions like osteoarthritis and exacerbate existing knee problems. Weight loss is a crucial component of managing knee pain in obese individuals, as even modest weight reduction can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve joint function. A combination of dietary changes, exercise, and behavioral modifications is often recommended for effective weight management. Recognizing the impact of obesity on knee health is vital for addressing this modifiable risk factor and improving overall well-being.
11. Sedentary Lifestyle – The Inactivity Issue

A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to knee pain by weakening the muscles that support the knee joint, leading to imbalances and instability. Prolonged periods of inactivity can also result in stiffness and reduced range of motion, exacerbating knee discomfort. Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines is essential for maintaining knee health, as exercise strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and enhances joint function. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial for individuals with knee pain. Understanding the role of physical activity in knee health is crucial for preventing and managing pain effectively.
12. Footwear – The Foundation Factor

The type of footwear worn can significantly impact knee health, as improper shoes can alter gait and increase stress on the knees. High heels, for example, shift the body's weight forward, placing additional strain on the knees. Similarly, worn-out or unsupportive shoes can lead to improper alignment and contribute to knee pain. Selecting appropriate footwear with adequate support and cushioning is essential for maintaining knee health, particularly for individuals who spend long hours on their feet. Recognizing the influence of footwear on knee pain is crucial for making informed choices and preventing discomfort.
A Clear Path to Stronger, Pain-Free Knees

Addressing knee pain requires a comprehensive understanding of its various causes and contributing factors. This article has explored 12 distinct elements that can lead to knee discomfort, from anatomical vulnerabilities and medical conditions to lifestyle choices and external influences. By recognizing these factors, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and alleviate knee pain, improving their quality of life. A holistic approach that combines medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and preventive measures is essential for maintaining knee health and preventing future issues. Empowered with knowledge and practical strategies, readers can embark on a journey toward pain-free, healthy knees.
