Mitochondrial Boosters: Recharge Your Cells for Next-Level Energy
Deep within every cell of your body lies a microscopic engine—your mitochondria. These tiny powerhouses convert the food you eat into the energy that fuels everything you do, from thinking clearly to moving with ease. But stress, aging, and modern habits can slow them down, leaving you drained and foggy. The good news? You can reignite your internal energy source with a few science-backed shifts. This article reveals 12 smart, practical ways to recharge your mitochondria and reclaim your vitality—from what’s on your plate to how you move, rest, and recover. These aren’t just biohacks; they’re foundational tools for a sharper brain, stronger body, and brighter mood. Whether you’re chasing peak performance or just want to feel like yourself again, it starts at the cellular level. Let’s power up from the inside out.
1. Nutrition: Fueling Your Mitochondria

A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for mitochondrial health. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, and dark leafy greens, help combat oxidative stress, a major factor in mitochondrial dysfunction. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, support mitochondrial membranes and improve energy production. Additionally, coenzyme Q10, a vital component of the electron transport chain, can be sourced from organ meats and oily fish, or taken as a supplement. Ensuring adequate intake of B vitamins, particularly B2, B3, and B6, is also important, as they play a critical role in the energy conversion process. By prioritizing these nutrients, you can provide your mitochondria with the fuel they need to function optimally.
2. Exercise: The Mitochondrial Boost

Regular physical activity is a powerful stimulator of mitochondrial biogenesis, the process by which new mitochondria are formed. Aerobic exercises, such as running, cycling, and swimming, increase the demand for energy, prompting cells to produce more mitochondria to meet this need. Resistance training, on the other hand, enhances mitochondrial density and efficiency, especially in muscle cells. Exercise also improves insulin sensitivity, which aids in the efficient delivery of glucose to cells, further supporting mitochondrial function. A balanced exercise regimen that includes both aerobic and strength-training components can significantly enhance your mitochondrial health and overall energy levels.
3. Sleep: Restoring Cellular Energy

Quality sleep is essential for mitochondrial repair and regeneration. During deep sleep stages, the body undergoes critical maintenance processes, including the removal of damaged mitochondria and the synthesis of new ones. Sleep deprivation, on the other hand, leads to increased oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which can impair mitochondrial function. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a restful environment, and minimizing blue light exposure before bedtime are effective strategies for improving sleep quality. By prioritizing restorative sleep, you provide your mitochondria with the opportunity to recharge and rejuvenate, setting the stage for optimal energy production.
4. Stress Management: Calming the Cellular Storm

Chronic stress is a significant contributor to mitochondrial dysfunction, as it elevates cortisol levels and increases oxidative stress. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, have been shown to reduce stress and promote mitochondrial health. These practices help lower cortisol levels and enhance the body's antioxidant defenses, protecting mitochondria from damage. Engaging in regular stress-reducing activities not only supports mitochondrial function but also improves mental clarity and emotional well-being. By managing stress effectively, you create a more harmonious environment for your cells to thrive.
5. Intermittent Fasting: A Cellular Reset

Intermittent fasting, which involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting, has been shown to enhance mitochondrial function and promote longevity. Fasting triggers autophagy, a cellular cleansing process that removes damaged mitochondria and stimulates the production of new ones. This process improves mitochondrial efficiency and resilience, leading to increased energy levels and better overall health. Popular intermittent fasting protocols include the 16/8 method, where you fast for 16 hours and eat within an 8-hour window, and the 5:2 method, which involves two non-consecutive days of reduced calorie intake each week. By incorporating intermittent fasting into your routine, you can give your mitochondria a much-needed reset.
6. Cold Exposure: Invigorating Your Cells

Cold exposure, through practices such as cold showers, ice baths, or cryotherapy, can stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis and enhance their function. The cold activates brown adipose tissue, a type of fat that generates heat by burning calories, which in turn increases mitochondrial activity. This process not only boosts energy production but also enhances metabolic rate and improves insulin sensitivity. Regular exposure to cold temperatures can also increase the production of norepinephrine, a hormone that supports mitochondrial health. By embracing the cold, you can invigorate your cells and enhance your body's ability to generate energy efficiently.
7. Red and Near-Infrared Light Therapy: Cellular Rejuvenation
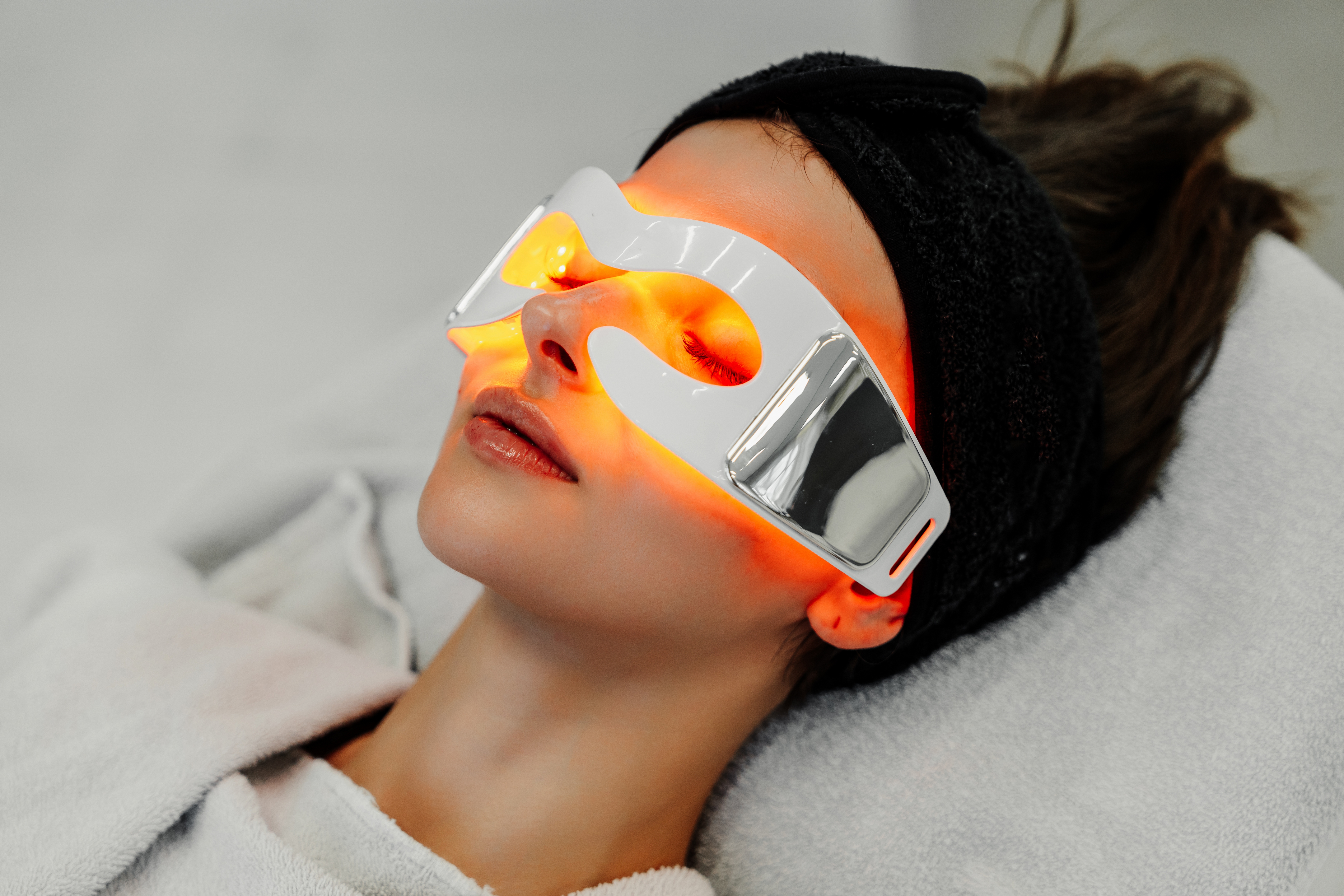
Red and near-infrared light therapy, also known as photobiomodulation, involves exposing the body to specific wavelengths of light that penetrate the skin and reach the mitochondria. This exposure stimulates the production of ATP, the energy currency of the cell, and enhances mitochondrial function. Research has shown that this therapy can reduce inflammation, promote tissue repair, and improve overall cellular health. Devices that emit red and near-infrared light are available for home use, making it accessible for those looking to enhance their mitochondrial function. By incorporating this form of light therapy into your routine, you can support cellular rejuvenation and boost your energy levels.
8. Hydration: The Cellular Lubricant

Adequate hydration is vital for maintaining optimal mitochondrial function, as water is essential for the transport of nutrients and the removal of waste products within cells. Dehydration can lead to decreased energy production and increased oxidative stress, both of which impair mitochondrial efficiency. Consuming water-rich foods, such as fruits and vegetables, and drinking sufficient amounts of water throughout the day can help maintain proper hydration levels. Additionally, electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, are important for cellular hydration and should be replenished regularly. By prioritizing hydration, you provide your mitochondria with the environment they need to function effectively.
9. Avoiding Environmental Toxins: Protecting Your Mitochondria

Exposure to environmental toxins, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and air pollutants, can damage mitochondria and impair their function. These toxins increase oxidative stress and disrupt cellular processes, leading to decreased energy production and increased risk of chronic diseases. To protect your mitochondria, it is important to minimize exposure to these harmful substances by choosing organic produce, using natural cleaning products, and reducing air pollution exposure. Additionally, supporting the body's detoxification pathways through a diet rich in cruciferous vegetables and adequate hydration can help eliminate toxins. By reducing your toxic load, you create a healthier environment for your mitochondria to thrive.
10. Supplementation: Targeted Nutritional Support
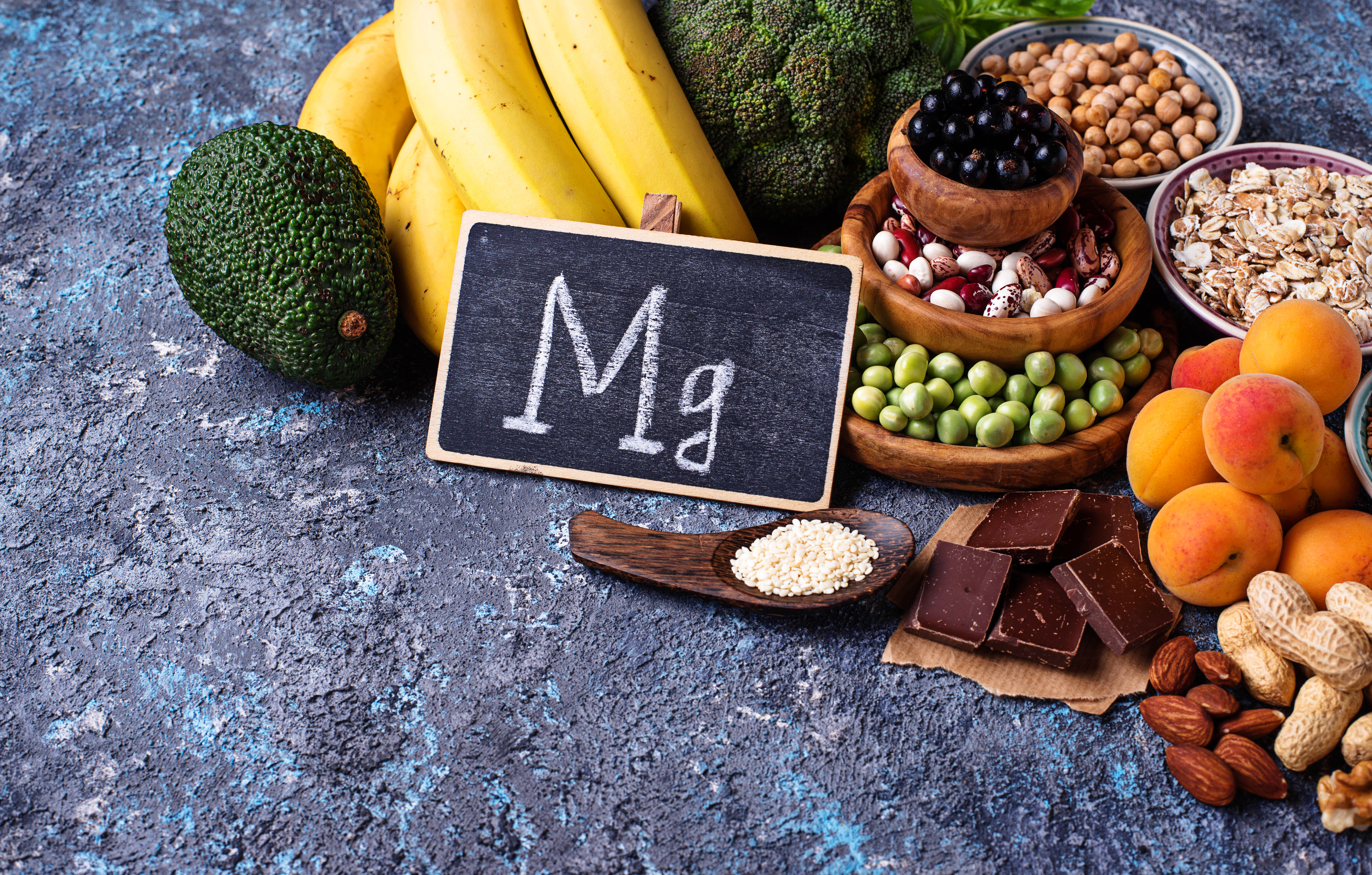
Certain supplements can provide targeted support for mitochondrial health, enhancing their function and energy production. Coenzyme Q10, as mentioned earlier, is a key player in the electron transport chain and can be supplemented to boost mitochondrial efficiency. Alpha-lipoic acid, a powerful antioxidant, helps protect mitochondria from oxidative damage and supports energy metabolism. Acetyl-L-carnitine facilitates the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production, while magnesium is essential for ATP synthesis. Before starting any supplementation, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate options for your individual needs. By providing your mitochondria with targeted nutritional support, you can enhance their function and boost your energy levels.
11. Mindful Breathing: Oxygenating Your Cells

Mindful breathing techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing and alternate nostril breathing, can enhance oxygen delivery to cells and improve mitochondrial function. Oxygen is a critical component of the energy production process, and efficient oxygen delivery supports optimal mitochondrial activity. Mindful breathing practices increase lung capacity, improve circulation, and reduce stress, all of which contribute to better oxygenation of cells. Incorporating these techniques into your daily routine can enhance your overall energy levels and promote a sense of calm and well-being. By focusing on your breath, you provide your cells with the oxygen they need to produce energy efficiently.
12. Social Connections: Energizing Through Community

Strong social connections and a sense of community have been shown to positively impact mitochondrial health and overall well-being. Engaging in meaningful relationships and social activities can reduce stress, enhance emotional resilience, and promote a sense of belonging, all of which support mitochondrial function. Social interactions stimulate the release of oxytocin, a hormone that reduces stress and inflammation, protecting mitochondria from damage. By nurturing your social connections and participating in community activities, you can create a supportive environment for your cells to thrive. Building and maintaining strong relationships is not only beneficial for your mental health but also for your cellular vitality.
Power Up Where It Matters Most

True energy doesn’t come from caffeine or willpower—it starts in your cells. By weaving these 12 mitochondria-boosting strategies into your daily routine, you’re not just managing fatigue—you’re upgrading your entire system from the inside out. Every nutrient-dense meal, every walk, every moment of deep rest feeds the engines that keep you sharp, strong, and alive. These aren’t just health habits—they’re fuel for the life you want to live. Whether you’re chasing big goals or simply craving more clarity and stamina, it all begins with cellular power. So start small. Stay consistent. And remember: when your mitochondria thrive, so do you.
