Little-Known Signs Your Thyroid Is Out of Whack
Your thyroid may be small, but when it's out of sync, it can throw your entire body off balance. This tiny, butterfly-shaped gland in your neck helps regulate everything from metabolism and mood to energy levels, weight, skin, sleep, and even heart rhythm. Yet when it underperforms or overworks, the signs aren’t always obvious—they’re often subtle, scattered, and easy to misattribute to stress, aging, or lifestyle. That’s why understanding the red flags matters. We've expanded our guide —a deeper dive into the overlooked symptoms that could be pointing to hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or autoimmune thyroid disorders. Whether you’re feeling constantly tired, battling unexplained weight changes, or just sensing that something’s “off,” tuning into these signals can help you catch dysfunction early and take back control of your health. Because when your thyroid’s out of balance, your body feels it—loud and clear.
1. Unexplained Weight Changes: A Common Indicator

One of the most noticeable signs of thyroid dysfunction is unexplained weight changes. The thyroid gland's hormones play a pivotal role in regulating metabolism, which in turn affects how the body uses energy. When the thyroid is underactive (hypothyroidism), the metabolism slows down, leading to weight gain, even if dietary habits remain unchanged. Conversely, an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) speeds up metabolism, often resulting in weight loss despite maintaining or even increasing caloric intake. Weight changes due to thyroid issues are not just about aesthetics but are indicative of underlying metabolic disturbances. In hypothyroidism, the body's energy expenditure decreases, causing calories to be stored as fat. This can lead to gradual weight gain, which might be resistant to diet and exercise. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism increases the body's energy consumption, leading to a caloric deficit and subsequent weight loss. This weight fluctuation can be distressing and may affect one's self-esteem and overall health. It's important to note that while weight changes can be a sign of thyroid dysfunction, they are not definitive proof of a thyroid issue. Other factors, such as diet, exercise, and lifestyle, also play a role in weight management. However, if weight changes occur without any apparent reason, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to investigate the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Early detection and treatment can help manage weight and restore metabolic balance.
2. Fatigue and Energy Levels: The Thyroid's Impact

Fatigue is another common symptom associated with thyroid dysfunction, often leaving individuals feeling drained and lacking energy. The thyroid hormones are integral to maintaining energy levels, as they influence how the body converts food into energy. When the thyroid is not functioning properly, it can lead to feelings of exhaustion and a lack of motivation, even after a full night's sleep. In hypothyroidism, the body's metabolism slows down, leading to decreased energy production. This can result in persistent fatigue, making it difficult to complete daily tasks or engage in physical activities. Individuals with hypothyroidism often report feeling sluggish and mentally foggy, as the lack of energy affects both physical and cognitive functions. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism can cause a different type of fatigue, characterized by restlessness and an inability to relax. The body's systems are in overdrive, leading to exhaustion from constant activity. Understanding the link between thyroid function and energy levels is crucial for identifying potential thyroid issues. If fatigue persists despite adequate rest and a healthy lifestyle, it may be worth exploring the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the root cause of fatigue can lead to improved energy levels and overall quality of life.
3. Mood Swings and Mental Health: The Emotional Toll

The thyroid gland's influence extends beyond physical health, impacting emotional well-being and mental health. Mood swings, anxiety, and depression can all be linked to thyroid dysfunction, as the hormones produced by the thyroid play a role in regulating mood and cognitive function. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to significant changes in emotional health, affecting how individuals feel and interact with the world around them. Hypothyroidism is often associated with symptoms of depression, as the decreased production of thyroid hormones can lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in activities once enjoyed. The slowed metabolism can also contribute to cognitive difficulties, such as memory problems and difficulty concentrating. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism is more commonly linked to anxiety, irritability, and mood swings. The overproduction of thyroid hormones can lead to a heightened state of alertness, making it difficult to relax and increasing the likelihood of emotional outbursts. Recognizing the connection between thyroid function and mental health is essential for addressing emotional symptoms that may be linked to thyroid dysfunction. If mood swings or changes in mental health occur without an apparent cause, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid issues. Proper diagnosis and treatment can help restore emotional balance and improve overall well-being.
4. Temperature Sensitivity: Feeling Hot or Cold

Temperature sensitivity is another subtle signal that the thyroid may be out of balance. The thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating body temperature, and an imbalance can lead to increased sensitivity to heat or cold. Individuals with thyroid dysfunction may find themselves feeling unusually hot or cold, even in comfortable environments, as their body's ability to regulate temperature is compromised. In hypothyroidism, the slowed metabolism can lead to a decreased ability to generate heat, resulting in a feeling of coldness. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may find themselves reaching for extra layers of clothing or blankets, even when others are comfortable. This sensitivity to cold can be particularly noticeable in the extremities, such as hands and feet, which may feel cold to the touch. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can cause an increased sensitivity to heat. The overactive metabolism generates excess heat, leading to feelings of warmth and sweating, even in cool environments. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may find themselves feeling hot and uncomfortable, seeking out cooler environments or clothing to alleviate the sensation. Temperature sensitivity can be a useful indicator of thyroid dysfunction, as it reflects the body's ability to maintain homeostasis. If you notice changes in how you perceive temperature, it may be worth exploring the possibility of thyroid issues with a healthcare professional. Understanding and addressing the root cause of temperature sensitivity can lead to improved comfort and quality of life.
5. Hair and Skin Changes: The External Clues

Changes in hair and skin can provide external clues to thyroid dysfunction, as the thyroid hormones play a role in maintaining healthy hair and skin. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to noticeable changes in hair texture, thickness, and skin condition, offering visible signs that the thyroid may be out of balance. In hypothyroidism, the slowed metabolism can lead to dry, brittle hair and hair loss. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may notice thinning hair or increased shedding, as the lack of thyroid hormones affects the hair growth cycle. The skin may also become dry, rough, and pale, as the decreased circulation and metabolism affect the skin's ability to retain moisture. In contrast, hyperthyroidism can lead to thinning hair and fragile skin, as the overactive metabolism affects the body's ability to maintain healthy hair and skin. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may experience hair that is fine and prone to breakage, as well as skin that is thin and easily irritated. The increased circulation and metabolism can also lead to flushed skin and excessive sweating. Recognizing changes in hair and skin can provide valuable insights into thyroid function, as these external symptoms often reflect internal hormonal imbalances. If you notice changes in your hair or skin that are not explained by other factors, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved hair and skin health, as well as overall well-being.
6. Digestive Disturbances: The Gut-Thyroid Connection

The thyroid gland's influence extends to the digestive system, with thyroid dysfunction potentially leading to a variety of digestive disturbances. The thyroid hormones play a role in regulating the speed and efficiency of digestion, and an imbalance can lead to changes in bowel habits, appetite, and overall digestive health. In hypothyroidism, the slowed metabolism can lead to constipation and sluggish digestion. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may experience infrequent bowel movements, bloating, and discomfort, as the decreased production of thyroid hormones affects the muscles of the digestive tract. The slowed digestion can also lead to a decreased appetite, as the body requires less energy and nutrients. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can lead to diarrhea and increased bowel movements, as the overactive metabolism speeds up digestion. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may experience frequent bowel movements, abdominal cramping, and an increased appetite, as the body requires more energy and nutrients to support the heightened metabolism. Understanding the gut-thyroid connection is essential for identifying potential thyroid issues, as digestive disturbances can be an early indicator of thyroid dysfunction. If you experience changes in digestion or appetite that are not explained by other factors, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved digestive health and overall well-being.
7. Menstrual Irregularities: Hormonal Harmony Disrupted

The thyroid gland plays a significant role in regulating the menstrual cycle, and thyroid dysfunction can lead to menstrual irregularities. The thyroid hormones influence the production and balance of reproductive hormones, and an imbalance can lead to changes in menstrual frequency, duration, and flow. In hypothyroidism, the decreased production of thyroid hormones can lead to heavy, prolonged, or irregular menstrual periods. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may experience menstrual cycles that are longer or more frequent than usual, as the hormonal imbalance affects the body's ability to regulate the menstrual cycle. The decreased metabolism can also lead to symptoms such as fatigue and weight gain, which can further affect menstrual health. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can lead to lighter or infrequent menstrual periods, as the overactive metabolism affects the production and balance of reproductive hormones. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may experience shorter or less frequent menstrual cycles, as the body requires more energy and nutrients to support the heightened metabolism. Recognizing menstrual irregularities as a potential sign of thyroid dysfunction is important for maintaining reproductive health. If you experience changes in your menstrual cycle that are not explained by other factors, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved menstrual health and overall well-being.
8. Muscle and Joint Pain: The Physical Manifestation

Muscle and joint pain can be a physical manifestation of thyroid dysfunction, as the thyroid hormones play a role in maintaining muscle and joint health. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to discomfort, stiffness, and pain, affecting the body's ability to move and function optimally. In hypothyroidism, the slowed metabolism can lead to muscle weakness, stiffness, and cramps, as the decreased production of thyroid hormones affects the muscles' ability to contract and relax. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may experience joint pain and stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity, as the lack of thyroid hormones affects the body's ability to repair and maintain joint tissues. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can lead to muscle weakness and fatigue, as the overactive metabolism affects the muscles' ability to support the body's increased energy demands. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may experience muscle tremors, cramps, and joint pain, as the heightened metabolism affects the body's ability to maintain muscle and joint health. Recognizing muscle and joint pain as a potential sign of thyroid dysfunction is important for maintaining physical health and mobility. If you experience unexplained muscle or joint pain, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved muscle and joint health, as well as overall well-being.
9. Cardiovascular Symptoms: The Heart-Thyroid Link

The thyroid gland's influence extends to the cardiovascular system, with thyroid dysfunction potentially leading to a variety of heart-related symptoms. The thyroid hormones play a role in regulating heart rate, blood pressure, and overall cardiovascular health, and an imbalance can lead to changes in heart function and circulation. In hypothyroidism, the slowed metabolism can lead to a decreased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and elevated cholesterol levels, as the decreased production of thyroid hormones affects the heart's ability to pump blood efficiently. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort, as the lack of thyroid hormones affects the body's ability to maintain cardiovascular health. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can lead to an increased heart rate, palpitations, and elevated blood pressure, as the overactive metabolism affects the heart's ability to support the body's increased energy demands. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as anxiety, rapid heartbeat, and dizziness, as the heightened metabolism affects the body's ability to maintain cardiovascular health. Recognizing cardiovascular symptoms as a potential sign of thyroid dysfunction is important for maintaining heart health and preventing complications. If you experience changes in heart function or circulation that are not explained by other factors, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
10. Sleep Disturbances: The Restless Nights

Sleep disturbances can be a sign of thyroid dysfunction, as the thyroid hormones play a role in regulating sleep patterns and overall sleep quality. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or feeling rested upon waking, affecting overall health and well-being. In hypothyroidism, the slowed metabolism can lead to excessive sleepiness and difficulty staying awake during the day, as the decreased production of thyroid hormones affects the body's ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and a lack of motivation, as the lack of thyroid hormones affects the body's ability to maintain restful sleep. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can lead to difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings, and restless sleep, as the overactive metabolism affects the body's ability to relax and unwind. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as anxiety, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating, as the heightened metabolism affects the body's ability to maintain restful sleep. Recognizing sleep disturbances as a potential sign of thyroid dysfunction is important for maintaining overall health and well-being. If you experience changes in sleep patterns or quality that are not explained by other factors, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
11. Cognitive Changes: The Brain Fog

Cognitive changes, often referred to as "brain fog," can be a sign of thyroid dysfunction, as the thyroid hormones play a role in maintaining cognitive function and mental clarity. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and a lack of mental sharpness, affecting overall cognitive health. In hypothyroidism, the slowed metabolism can lead to cognitive difficulties, such as forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating, and a lack of mental clarity, as the decreased production of thyroid hormones affects the brain's ability to process information efficiently. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as confusion, difficulty making decisions, and a lack of motivation, as the lack of thyroid hormones affects the brain's ability to function optimally. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can lead to cognitive changes such as anxiety, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating, as the overactive metabolism affects the brain's ability to focus and process information efficiently. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as racing thoughts, difficulty making decisions, and a lack of mental clarity, as the heightened metabolism affects the brain's ability to function optimally. Recognizing cognitive changes as a potential sign of thyroid dysfunction is important for maintaining cognitive health and mental clarity. If you experience changes in cognitive function or mental clarity that are not explained by other factors, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved cognitive function and overall well-being.
12. Swelling and Enlargement: The Visible Signs
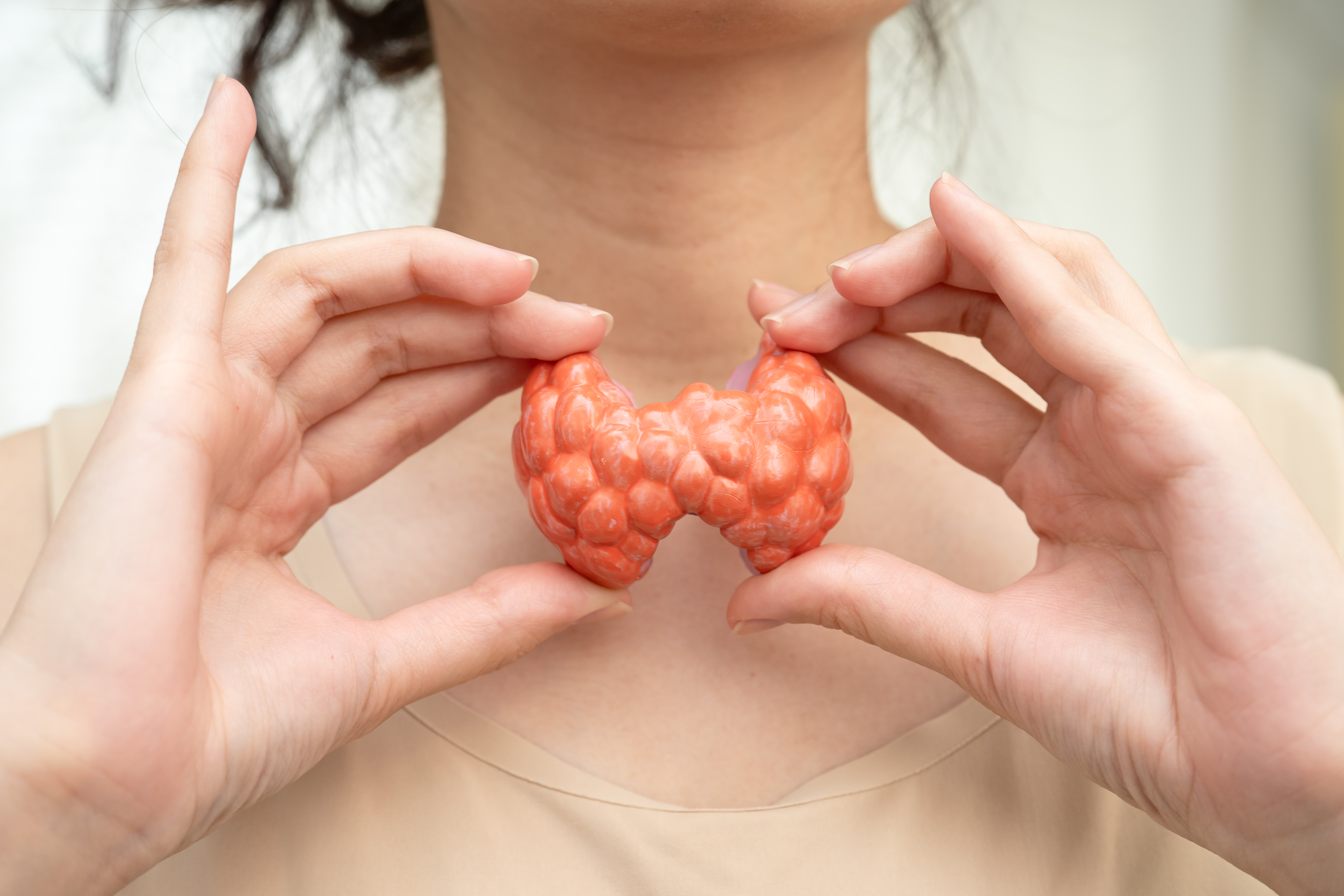

Swelling and enlargement of the thyroid gland, known as a goiter, can be a visible sign of thyroid dysfunction. The thyroid gland may become enlarged due to an imbalance in hormone production, leading to noticeable swelling in the neck area. In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland may become enlarged as it attempts to produce more hormones to compensate for the decreased production of thyroid hormones. This can lead to a visible swelling in the neck, known as a goiter, which may cause discomfort or difficulty swallowing. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may also experience symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold sensitivity, as the lack of thyroid hormones affects the body's ability to function optimally. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can also lead to an enlarged thyroid gland, as the overactive metabolism affects the gland's ability to regulate hormone production. This can lead to a visible swelling in the neck, known as a goiter, which may cause discomfort or difficulty swallowing. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may also experience symptoms such as weight loss, anxiety, and heat sensitivity, as the heightened metabolism affects the body's ability to function optimally. Recognizing swelling and enlargement of the thyroid gland as a potential sign of thyroid dysfunction is important for maintaining thyroid health and preventing complications. If you notice changes in the size or shape of your thyroid gland, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved thyroid health and overall well-being.
13. Cholesterol Levels: The Lipid Connection

Cholesterol levels can be affected by thyroid dysfunction, as the thyroid hormones play a role in regulating lipid metabolism and overall cardiovascular health. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to changes in cholesterol levels, affecting overall cardiovascular health. In hypothyroidism, the slowed metabolism can lead to elevated cholesterol levels, as the decreased production of thyroid hormones affects the body's ability to break down and eliminate cholesterol. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold sensitivity, as the lack of thyroid hormones affects the body's ability to maintain cardiovascular health. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can lead to decreased cholesterol levels, as the overactive metabolism affects the body's ability to break down and eliminate cholesterol. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as weight loss, anxiety, and heat sensitivity, as the heightened metabolism affects the body's ability to maintain cardiovascular health. Recognizing changes in cholesterol levels as a potential sign of thyroid dysfunction is important for maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing complications. If you experience changes in cholesterol levels that are not explained by other factors, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
14. Fertility Issues: The Reproductive Impact

Fertility issues can be a sign of thyroid dysfunction, as the thyroid hormones play a role in regulating reproductive health and hormone balance. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to changes in fertility, affecting overall reproductive health. In hypothyroidism, the decreased production of thyroid hormones can lead to changes in menstrual cycles, ovulation, and hormone balance, affecting fertility. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold sensitivity, as the lack of thyroid hormones affects the body's ability to maintain reproductive health. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can lead to changes in menstrual cycles, ovulation, and hormone balance, affecting fertility. Individuals with an overactive thyroid may experience symptoms such as weight loss, anxiety, and heat sensitivity, as the heightened metabolism affects the body's ability to maintain reproductive health. Recognizing fertility issues as a potential sign of thyroid dysfunction is important for maintaining reproductive health and preventing complications. If you experience changes in fertility that are not explained by other factors, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to explore the possibility of thyroid dysfunction. Addressing the underlying cause can lead to improved reproductive health and overall well-being.
15. Hoarseness or Voice Changes: The Hidden Vocal Clue
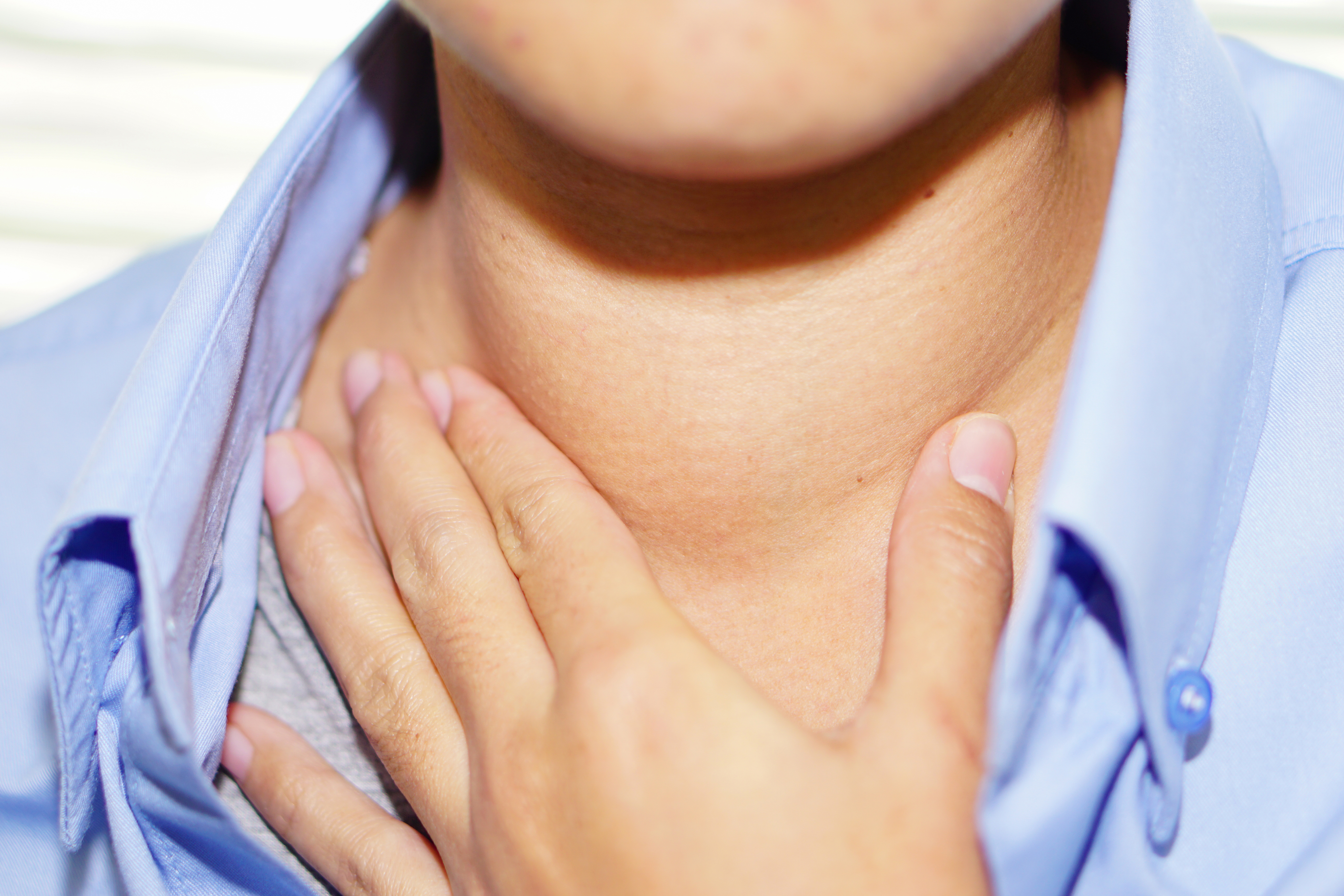
If your voice has become hoarse or unusually raspy—especially without a cold or known irritation—it could be your thyroid signaling trouble. An enlarged thyroid (goiter) or underlying inflammation from autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s can press on the vocal cords or surrounding nerves, subtly changing your voice. Some individuals also report frequent throat clearing or a sensation of tightness in the neck. Because voice shifts are easy to dismiss or attribute to strain, they often go overlooked. But if they persist, especially alongside fatigue or neck fullness, it’s worth investigating your thyroid function.
16. Eyebrow Thinning: Especially the Outer Third

While hair loss in general can signal thyroid imbalance, one particularly telling sign is thinning or loss of the outer third of your eyebrows. This seemingly minor change is strongly associated with hypothyroidism and often appears before other symptoms become disruptive. Thyroid hormones support hair follicle health and regulate the hair growth cycle. When levels drop, certain areas—especially eyebrows—are among the first to show visible signs. If your brow tails are fading despite no changes in grooming or stress, your thyroid may be part of the story. Subtle, yes—but incredibly telling.
17. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Nerve-Related Signal

Tingling, numbness, or weakness in the hands—particularly in the thumb, index, or middle fingers—can be more than a repetitive strain issue. Carpal tunnel syndrome is surprisingly common in those with untreated hypothyroidism. The reason? Thyroid hormone deficiency can lead to fluid retention and swelling in connective tissues, which puts pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. If you're developing nerve pain without repetitive stress, or your symptoms worsen at night, a thyroid check may be in order. Treating the underlying thyroid imbalance often alleviates the nerve compression.
18. Puffy Face or Swollen Eyes: The Inflammatory Signal

A subtly swollen face or persistent puffiness around the eyes might be your thyroid waving a red flag. In hypothyroidism, slowed circulation and increased fluid retention can lead to visible swelling in the face, lips, or eyelids. For hyperthyroid individuals, particularly those with Graves’ disease, inflammation behind the eyes can cause bulging (exophthalmos) or discomfort. These physical cues are easy to overlook or attribute to poor sleep, allergies, or salty meals—but they can be some of the most visible markers of thyroid imbalance. If puffiness becomes persistent or noticeable in photos, it’s time to look deeper.
19. Slow Reflexes or Coordination Issues: The Neuromuscular Clue

Your thyroid doesn’t just influence metabolism—it also affects how quickly your nerves communicate with muscles. In hypothyroidism, slowed nerve conduction can lead to noticeably sluggish reflexes, poor coordination, or clumsiness. You might drop things more often, feel stiff when getting up, or take longer to respond physically. These neuromuscular changes are subtle but significant, especially when paired with fatigue or brain fog. A doctor testing your reflexes might notice a delay in the relaxation phase—an often-overlooked but classic sign of thyroid dysfunction. Don’t chalk it up to aging or being off your game—your thyroid may be the real culprit.
20. Unexplained Auditory Changes: Tinnitus and Muffled Hearing

If you're experiencing a persistent ringing in your ears (tinnitus) or a feeling of muffled hearing, your thyroid may be the surprising culprit. Thyroid hormones are essential for the health of the intricate structures within the inner ear that are responsible for hearing. When hormone levels are out of balance, it can disrupt nerve function and fluid pressure, leading to these subtle auditory changes. While often attributed to loud noises or aging, persistent auditory issues—especially when accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue—can be a quiet signal that your thyroid needs attention.
21. Increased or Decreased Sweating

Beyond general temperature sensitivity, thyroid dysfunction can cause a noticeable change in your body's sweating patterns. In hyperthyroidism, the body's overactive metabolism generates excess heat, causing you to sweat more frequently and profusely, even in cool environments. Conversely, hypothyroidism's sluggish metabolism can lead to a reduced ability to regulate temperature, causing a decrease in sweating. This can result in the skin feeling dry and clammy. These changes in sweating are a direct result of your thyroid's impact on your body's internal thermostat.
22. Unusually Brittle or Dry Nails

While hair and skin changes are common, a very specific red flag for thyroid dysfunction is unusually brittle, dry, or peeling nails. Thyroid hormones regulate cell turnover, and when they are out of balance, the body's ability to produce healthy nail cells is compromised. You might notice your nails are splitting or breaking more easily, or that ridges have appeared on the surface. This isn't just a sign of poor diet; it's a visible cue that your thyroid is failing to support the rapid cell growth needed for strong, healthy nails.
23. Heightened or Reduced Sense of Taste and Smell

An often-overlooked symptom of thyroid imbalance is a change in your senses, specifically your ability to taste and smell. Thyroid hormones are crucial for the proper function of nerve receptors, including those in the tongue and nose. When levels are low (hypothyroidism), some individuals report a dulled sense of taste and smell. Food might taste bland or flavors might seem muted. This loss of sensory acuity is not to be dismissed; it’s your thyroid’s way of signaling a broader systemic slowdown, and addressing it can help bring your senses back to life.
24. Changes in Blood Sugar and Insulin Sensitivity

Thyroid hormones and blood sugar are intricately linked. Hyperthyroidism can cause your body to become more insulin resistant, leading to higher blood sugar levels. Conversely, hypothyroidism can impact the liver's ability to regulate glucose. If you are experiencing unexpected fluctuations in blood sugar, even without changes to your diet or activity, your thyroid could be a factor. This connection is especially important for individuals with diabetes or a family history of it, as it highlights a metabolic link that goes beyond diet and exercise.
25. Low Libido: The Unspoken Hormonal Toll

An often-unspoken symptom of thyroid dysfunction is a significant drop in libido. Thyroid hormones are crucial for regulating certain hormones, including testosterone in both men and women. In cases of hypothyroidism, the general fatigue and hormonal slowdown can directly impact your desire. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can cause anxiety and exhaustion that make intimacy difficult. This is a subtle but important signal that the hormonal balance of your body is compromised. Addressing the underlying thyroid issue often helps restore hormone levels, which can lead to a natural return of overall vitality.
26. Unexplained Anemia

If you have been diagnosed with anemia but the cause is not a simple iron deficiency, your thyroid may be the culprit. Thyroid hormones are essential for red blood cell production in the bone marrow. When your thyroid is underactive, this process can be slowed down, leading to a type of anemia that doesn't respond to iron supplementation. The fatigue associated with anemia can also be misattributed to other factors, but its connection to thyroid health is well-documented. If your energy levels are low and you have a new anemia diagnosis, it may be time to get a full thyroid panel.
27. Dysphagia: A Lump in Your Throat

Difficulty swallowing, or dysphagia, can be a direct physical manifestation of a thyroid that is out of balance. While you may have a goiter, which is a visible swelling, a less obvious symptom is the sensation of a lump in your throat or discomfort when swallowing. This can be caused by an enlarged thyroid gland pressing on the esophagus. Though often benign, any difficulty swallowing should be evaluated by a doctor immediately to rule out more serious issues and assess whether a goiter is the cause. This physical clue is your thyroid’s way of directly signaling a problem.
28. Blood Pressure Out of Whack

While the article mentions cardiovascular symptoms, a specific and often overlooked sign is a change in your blood pressure readings. Hypothyroidism can lead to an increase in blood pressure, specifically the diastolic pressure (the bottom number), as a result of a slowed heart rate and reduced elasticity of blood vessels. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism can cause an increase in systolic pressure (the top number). If your blood pressure is consistently outside of its normal range, it is a strong signal that your cardiovascular system is being impacted, and your thyroid may be to blame.
29. Unexplained Muscle Atrophy or Weakness

Beyond general muscle and joint pain, a significant red flag for thyroid dysfunction is unexplained muscle atrophy or weakness. In severe cases of hypothyroidism, a lack of thyroid hormones can slow down the repair and maintenance of muscle tissue, leading to a gradual loss of muscle mass. For those with hyperthyroidism, the body's accelerated metabolism can cause muscles to break down at an increased rate, resulting in overall weakness and a difficulty with strength-based activities. If you are losing muscle mass without explanation, it is a sign that your metabolic engine may be running too slow or too fast.
30. Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination

If you find yourself constantly thirsty and needing to urinate more often than usual, it could be a sign of a hyperactive thyroid. The body's metabolism is in overdrive, which can lead to increased fluid intake and output. Conversely, hypothyroidism can cause a decreased sense of thirst and less frequent urination. These changes, though often dismissed, are a clear indication that your body is struggling to maintain fluid balance and that your thyroid is impacting your metabolic functions.
31. Weakened Immune System

An underactive thyroid can directly compromise your immune system, leaving you more vulnerable to common infections. Thyroid hormones are essential for the proper functioning of your immune cells. When they are in short supply, your body’s ability to defend itself against viruses and bacteria is diminished. You might find yourself catching colds and other infections more frequently or taking longer to recover. This weakened state is a subtle but important red flag that your thyroid is not providing the hormonal support your immune system needs.
32. Chronic Low Body Temperature

If you consistently feel cold and have a body temperature that is below the normal range, it could be a sign of hypothyroidism. The thyroid gland is a key regulator of your body’s internal thermostat. When your thyroid is underactive, your metabolism slows down, leading to a decreased ability to generate heat. This can result in a chronic feeling of coldness, particularly in your hands and feet, which is often a first sign of a deeper issue with your thyroid function.
33. Vision Changes

Beyond the puffy eyes associated with Graves’ disease, thyroid imbalance can cause a variety of vision changes. In hyperthyroidism, the inflamed tissues behind the eyes can push the eyeballs forward, leading to a sensation of pressure, double vision, or even blurred vision. Hypothyroidism can also affect vision by causing dry eyes or a general lack of sharpness. If you are experiencing changes in your vision that are not explained by other factors, it may be a sign that your thyroid is impacting the delicate functions of your eyes.
34. Unexplained Hoarseness or a "Frog in Your Throat"

If your voice has become hoarse or you have a persistent sensation of a lump or a "frog in your throat," it could be your thyroid signaling a problem. An enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) can press on the trachea (windpipe) or the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which controls your vocal cords. While a hoarse voice can be easily dismissed as a cold or strain, a persistent change, especially when accompanied by other symptoms, is a physical clue that your thyroid may be impacting its surrounding structures.
When Your Thyroid Speaks, Listen Closely

The key is to stop dismissing what feels different and start connecting the dots. Whether you’re navigating symptoms that don’t add up or simply want to feel like yourself again, checking your thyroid may be the missing piece. Because when your thyroid is out of balance, every system in your body pays the price—and when it’s back on track, everything runs smoother. So don’t ignore the signs. Your thyroid’s talking. It’s time to listen.
