10 Silent Signals of a Stroke You Need To Spot Early
Strokes are often perceived as sudden, dramatic events, yet they frequently begin with subtle, silent signals that are easy to overlook. These early symptoms are crucial to recognize, as they can significantly impact the outcome if immediate medical attention is sought. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die. The faster a stroke is identified and treated, the better the chances of recovery. This article delves into early symptoms of stroke that everyone should be aware of, emphasizing the importance of prompt recognition and response. By understanding these early warning signs, individuals can potentially avert severe consequences, aiding in faster intervention and improved recovery outcomes.
1. Sudden Numbness or Weakness
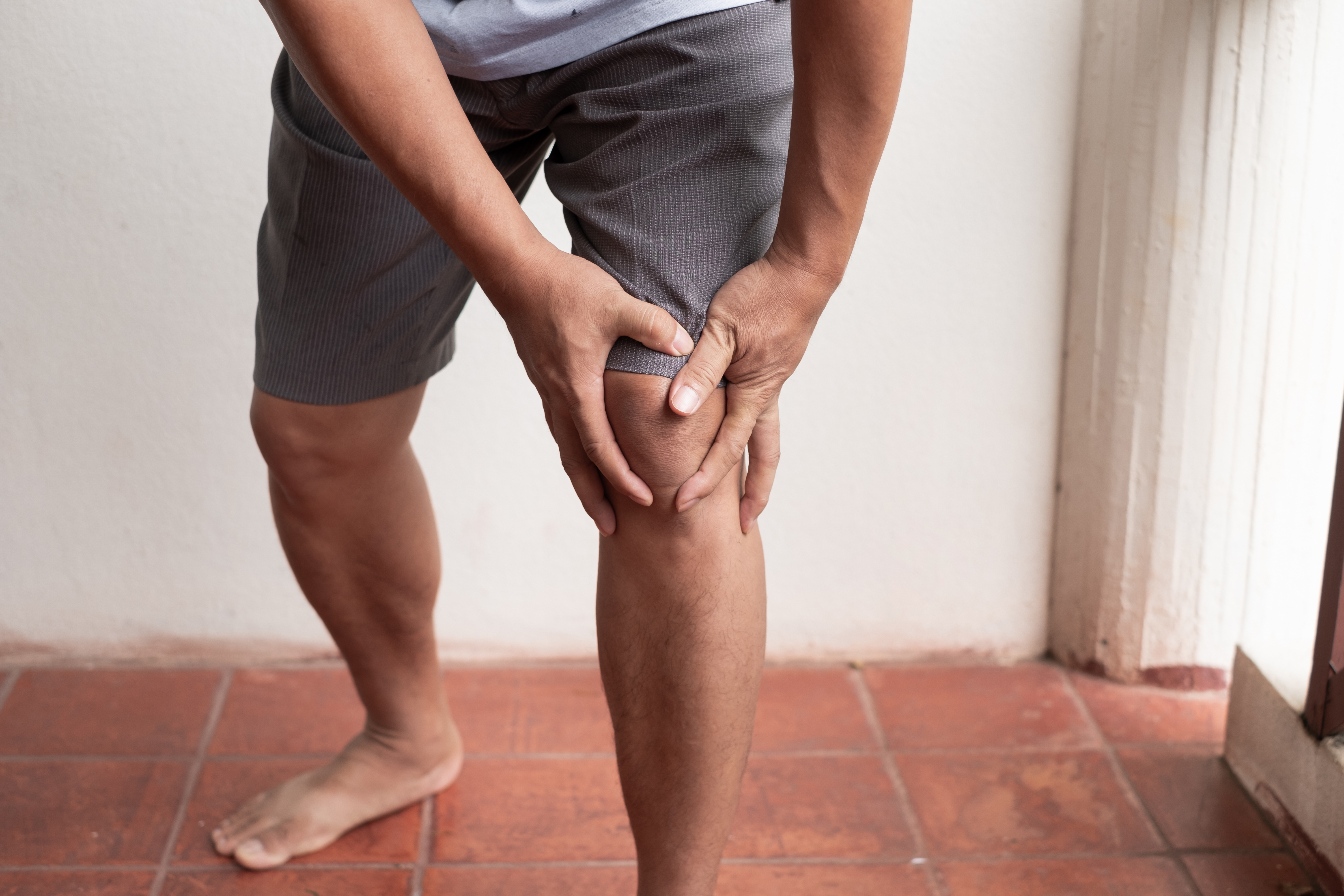
One of the most common early signs of a stroke is sudden numbness or weakness, particularly on one side of the body. This symptom can manifest in the face, arm, or leg, and is often accompanied by a feeling of heaviness or an inability to move the affected limb. The sudden onset of this symptom is key, as it distinguishes a stroke from other conditions that might cause similar sensations. The underlying cause is typically a disruption in the blood flow to specific parts of the brain that control muscle movement and sensation. Recognizing this symptom early can lead to quicker medical intervention, potentially reducing the severity of the stroke's impact. It's crucial to act swiftly if you or someone you know experiences these sensations, as time is of the essence in minimizing long-term damage.
2. Confusion and Difficulty Speaking

Another early indicator of a stroke is sudden confusion or difficulty speaking. This can range from trouble finding the right words to complete inability to speak or understand speech. The brain's language centers, primarily located in the left hemisphere, are highly susceptible to damage from interrupted blood flow. As a result, even a minor stroke can cause significant communication difficulties. Individuals may also experience problems with reading and writing, further complicating their ability to communicate effectively. This symptom can be particularly distressing, both for the individual experiencing it and for those around them. Understanding that these changes in communication are potential signs of a stroke can prompt quicker action, ensuring that medical professionals can intervene and potentially reverse or mitigate the damage.
