The Most Common Symptoms of Inflammatory Disease
Inflammation is one of the body’s natural defenses against infections from bacteria, viruses, and other invaders. Inflammation is usually a process in which the body produces and deploys white blood cells to flush out and destroy any foreign bodies in the bloodstream. However, there are certain conditions or situations in which the body can trigger inflammatory responses without any invaders being present. These conditions are known as inflammatory diseases and affect millions of individuals around the world. Learn more now about the common signs and symptoms indicating that an individual may be dealing with an inflammatory disease.
Swelling
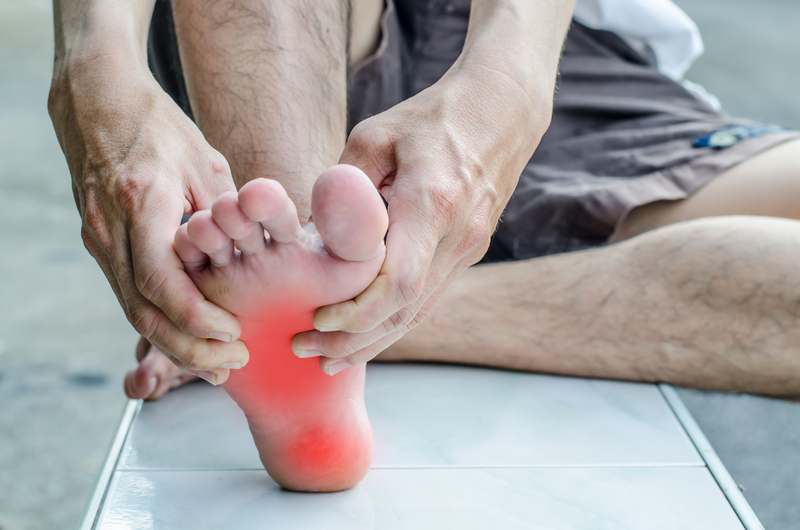
One of the most common symptoms of inflammation is the swelling of body parts, usually seen in the extremities, such as the legs, arms, feet, and hands. As the body produces an overabundance of white blood cells, the fluids associated with these cells will need to pool somewhere, usually within the extremities. In some cases, if the joints become swollen, they can also become warm to the touch, such as what some patients experience with arthritis. To reduce symptoms consider using an anti-inflammatory cream. Due to gravity, the most common body parts to swell due to inflammatory diseases are the feet. If a patient experiences frequent swelling of their feet, they should consult with their doctor and schedule a screening for inflammatory diseases.
Back Or Neck Pain
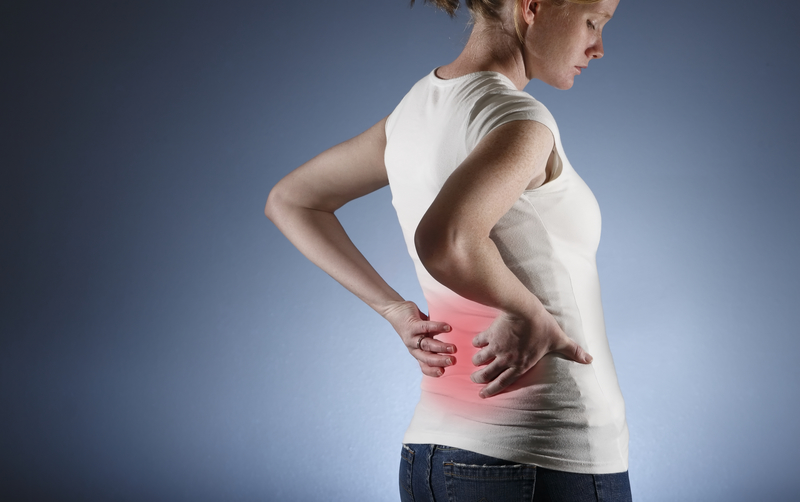

The swelling caused by inflammatory diseases is not just limited to the hands and feet. Sometimes fluids can build up in other areas such as the lower back, the neck, or the shoulders. One of the most common complaints doctors hear about is neck and shoulder pain. While this is most often assumed to be lifestyle or stress-related tension, certain inflammatory diseases can cause chronic neck and back pain, such as arthritis. In some instances, swelling in the neck, back, or shoulders can lead to joint pain and stiffness, and even the loss of joint function. To prevent and treat pain use Penetrex and a lower back belt. If an individual has tried all the remedies that they can find but still have a sore back or neck, they should ask their doctor about inflammatory diseases and if they are possibly afflicted with it.
