How Is Asthma Diagnosed?
Asthma is a medical condition that makes breathing difficult. During asthma flareups and attacks, the patient's airways become narrowed, swollen, and also produce excess mucus. In addition to making breathing difficult, the condition can trigger shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing. Some individuals with asthma experience symptoms as a minor nuisance, though some deal with symptoms severe enough to be life-threatening and interfere with day-to-day activities. Though asthma doesn't have a cure, the symptoms are controllable. Patients will need to work with their doctor on an ongoing basis to make sure the symptoms continue to be controlled through medication. The symptoms can vary widely from person to person.
There are several ways that asthma can be diagnosed. The severity of symptoms and the type of asthma will affect the diagnostic methods used. Learn more about diagnosing asthma now.
Use Of A Peak Flow Meter
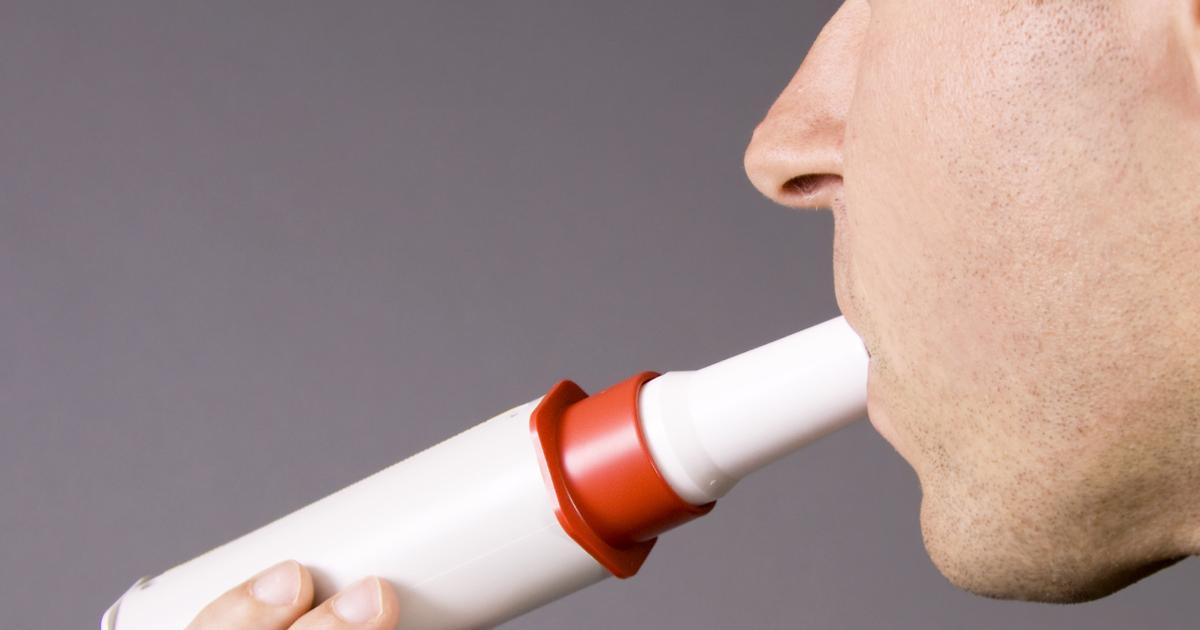
Peak flow meters are portable and hand-held devices that measure an individual's capacity to push air from their lungs. They are available in two ranges. The first, called a low-range meter, is designed for use by small children. Meanwhile, a standard-range is used for adults, teenagers, and older children. Because adults have larger and more developed airways than small children, they need a wider range of measurements. In addition to being used for the original diagnosis of asthma, peak flow meters are often helpful after patients receive their diagnosis. If individuals have been recently diagnosed or take daily medicine to control their asthma, the use of a peak flow meter helps with their day-to-day management. Peak flow meters can be used for asthma management in individuals aged five years and older. In addition, some individuals who have chronic bronchitis or emphysema might benefit from using a peak flow meter.
Read more about various asthma diagnostic methods now.
Spirometry
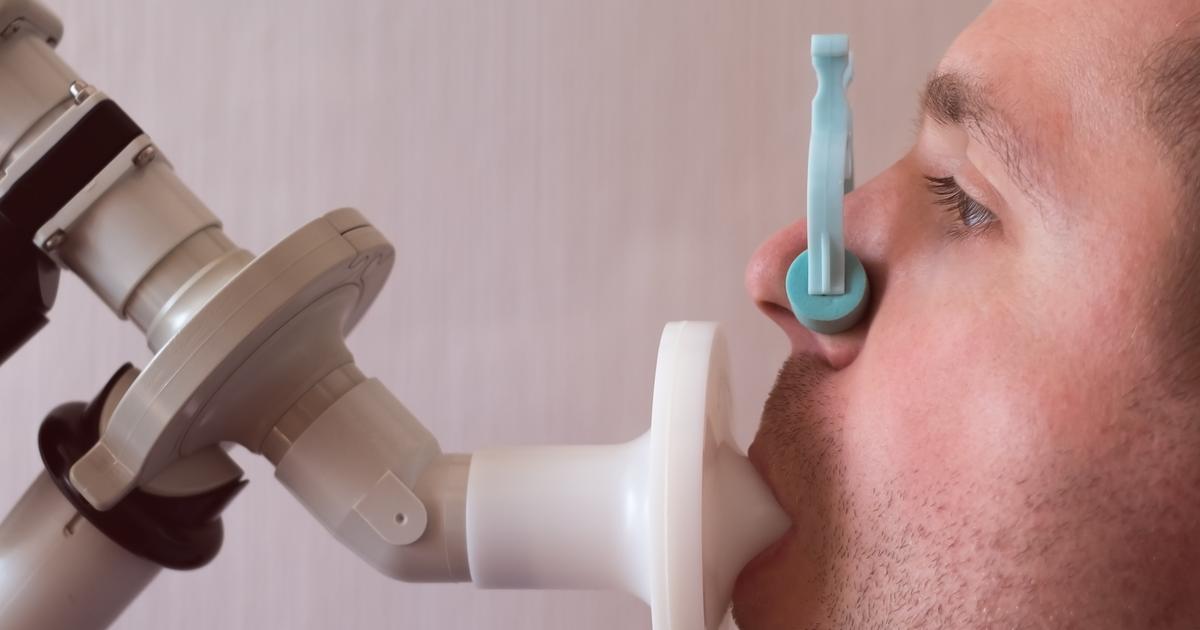
Spirometry is a common test used in doctor's offices to assess how well a patient's lungs work. It measures the amount of air individuals inhale, the amount of air they exhale, and how fast they exhale. In addition to diagnosing asthma, spirometry can diagnose chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other breathing conditions. Doctors might periodically use spirometry to monitor the condition of a patient's lungs and make sure their asthma treatment is working correctly. For patients who have already been diagnosed with asthma, spirometry might be used to monitor treatment or to make sure their lung function is adequate before surgery. Spirometry is generally considered a safe diagnostic test, though patients might feel dizzy or short of breath momentarily after the test is performed. Patients do have to undergo some exertion, so the test isn't used for those who have heart conditions or who have recently experienced a heart attack. Before taking the test, patients should wear loose clothing and avoid eating large meals.
Keep reading to learn more about how asthma is diagnosed now.
