What Causes Eosinophilia?
Eosinophilia is a somewhat common condition that occurs when there are more eosinophils in an individual's system than there should be. Eosinophils are a kind of white blood cell designed to fight diseases. When this condition develops within the body, it's typically an indicator the patient is suffering from cancer, a parasitic infection, or an allergic reaction. The high amounts of eosinophils could exist within the blood or tissues surrounding the inflammation or infection the patient is suffering from.
The tissue version of eosinophilia is commonly detected by taking a look at certain fluids in the body such as mucus. The blood version of eosinophilia is oftentimes detected through a blood test. Once this condition has been detected, it's important for patients to consult their doctor for treatment.
Churg-Strauss Syndrome

One possible cause of a rise in the eosinophils in an individual's system is because of Churg-Strauss syndrome, a disorder that occurs when certain blood vessels become inflamed. In many cases, the inflammation will cause issues with blood flow throughout the body, which lead to serious complications in the affected tissues and organs. The primary sign of Churg-Strauss syndrome is asthma.
Other symptoms include gastrointestinal bleeding, hay fever, and pain within the hands and feet. There are three stages of Churg-Strauss syndrome. While the first stage centers around allergic reactions, the second stage is considered the eosinophilic stage, which means patients will experience a high count of eosinophils in the blood and certain tissues throughout the body. Symptoms of this stage include fatigue, night sweats, fever, and joint pain.
Atopic Dermatitis
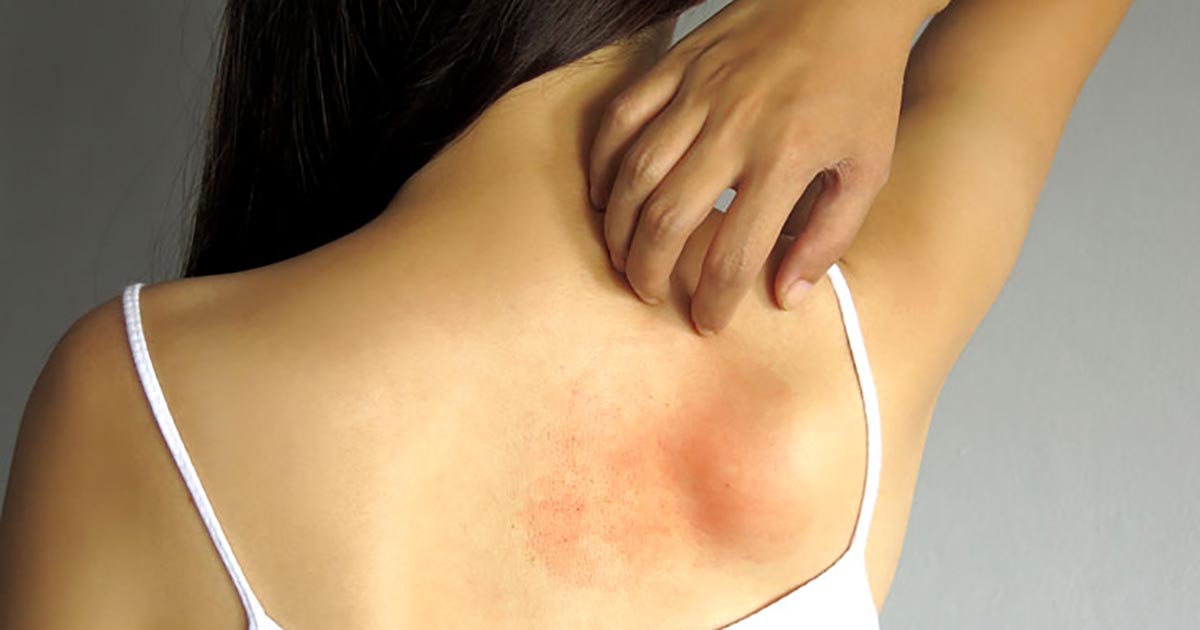
Atopic dermatitis is a very common skin condition that causes the skin to become red and itchy. While this condition typically affects younger children, it can occur at any age. This is a long-lasting disease that will likely flare up from time to time. While there's currently no cure for atopic dermatitis, a variety of treatments can help reduce the itching and prevent future outbreaks. The signs of atopic dermatitis will vary from patient to patient, though some of the more common ones include thickened and cracked skin, red or brown patches on the skin, dry skin, severe itching at night, and the presence of small bumps on the skin. It is possible patients will also develop eosinophilia while dealing with atopic dermatitis.
Some of the complications pertaining to this disease include sleep problems, skin infections, and hay fever. Patients can prevent this condition from occurring and causing eosinophilia by taking only short showers and baths, by moisturizing the skin twice every day, and by using gentle or mild soap. Various medications and therapies can be used to attempt to control the condition and reduce the number of flareups that occur.
