Common Symptoms Of Mastocytosis
Mastocytosis is a condition where an affected individual has an accumulation of mast cells in their organs that may include the liver, skin, spleen, small intestine, and bone marrow. Mastocytosis that only affects the skin is called cutaneous mastocytosis, and mastocytosis that affects more than one organ is called systemic mastocytosis. Systemic mastocytosis is more common among adults, whereas cutaneous mastocytosis is more commonly found in children. This condition is caused by a spontaneous gene mutation in the KIT gene that has usually not been inherited from a family member. However, rare cases of mastocytosis may be the result of an inherited genetic mutation. Diagnosis is determined through the use of skin biopsy, bone marrow biopsy, blood test, urine tests, bone scan, genetic testing, and or gastrointestinal evaluations. Treatment for mastocytosis is highly dependent on which parts of the individual's body are having symptoms.
Get familiar with the major symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Itching
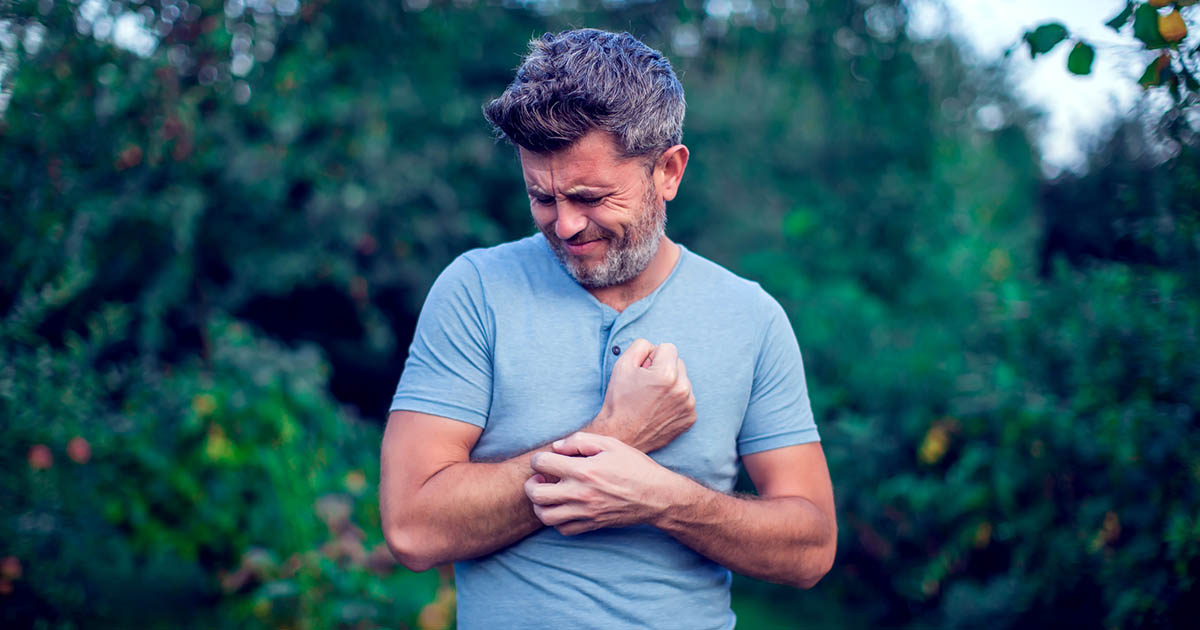

Individuals affected by mastocytosis may have excessive itching of the skin. Pruritis, itchy skin that stimulates the affected individual to itch, is caused by the production of a cytokine called Interleukin-31 or IL-31. Th2 cells, macrophages, dendric cells, and mast cells are all responsible for the production of IL-31. The overproduction and accumulation of mast cells cause the overproduction of IL-31. Increased numbers of IL-31 result in sensory nerve cell activation in the skin and surrounding tissues. The nerve cells become hyperactive when the IL-31 receptors on them become activated by signals precipitated from high levels of IL-31. Once activated, the sensory nerves send signals to the brain that cause the individual to feel an itchy sensation in their skin. Specific areas of mast cell concentration commonly appear in the form of lesions that can be very itchy. Skin contact with certain substances and ingestion of certain foods and drugs can cause an affected individual to experience a worse sensation of itchiness.
Keep reading to learn more about the symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Cramps In The Belly
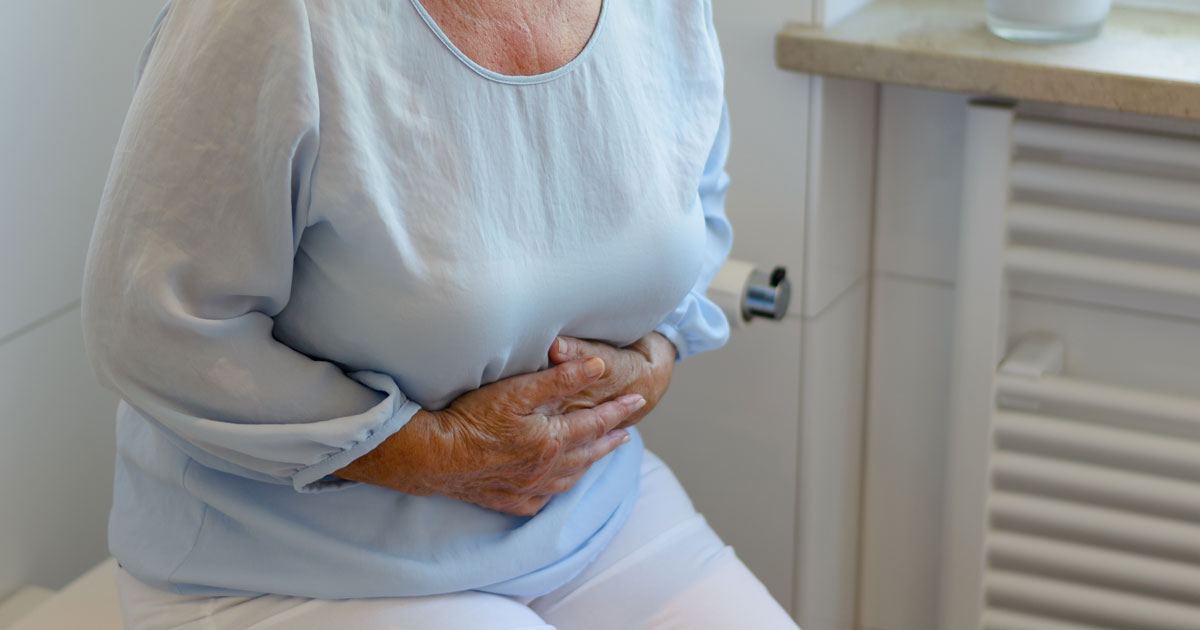
An individual experiencing cramps in the belly along with other characteristic symptoms may be affected by mastocytosis. Gastrointestinal manifestations, like cramps in the belly, are the most common symptoms seen in cases of mastocytosis, second only to pruritis. The abdominal cramping that occurs in affected individuals can be caused by the infiltration of mast cells into the mucosal tissues of the digestive tract. This infiltration results in damage to the cells that make up these tissues, which results in malabsorption. Malabsorption causes diarrhea and provides a rich source of undigested food for the gut flora to consume and thrive on. Bacterial overgrowth in the intestine as a result of mast cell damage precipitated malabsorption may occur in some cases. Infiltration of mast cells into the affected individual's liver can cause them to be unable to digest fats, causing abdominal cramps associated with steatorrhea.
Uncover more information regarding the warning signs of mastocytosis now.
