Guide To Hepatopulmonary Syndrome Warning Signs
Hepatopulmonary syndrome is a condition characterized by low blood oxygen levels that are a result of small artery dilation in the lungs of liver disease patients. Due to the enlargement of blood vessels in the lungs, the red blood cells are unable to absorb oxygen properly. Poor oxygen absorption means the lungs and the circulatory system are unable to provide sufficient amounts of oxygen to the rest of the body. Hepatopulmonary syndrome could be a result of impaired clearance by the liver of chemicals that relax the blood vessels called vasodilators. It could also be the result of increased production of vasodilators, or it could be due to a decreased production of vasoconstrictors, chemicals that contract the blood vessels. The only treatment known to be effective for hepatopulmonary syndrome is a liver transplant.
Get familiar with the major warning signs of hepatopulmonary syndrome now.
Progressive Shortness Of Breath
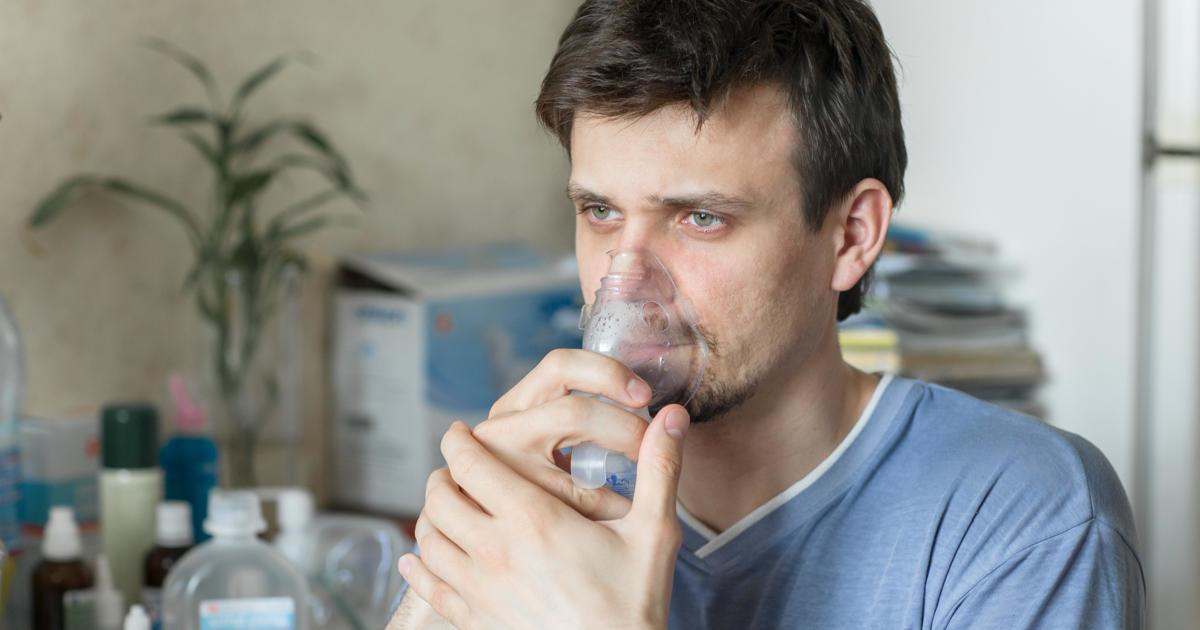

Progressive shortness of breath (dyspnea) is the most common sign found in individuals who have hepatopulmonary syndrome. Even in the patients who have a relatively stable liver function, dyspnea will still progressively worsen over time. The reason why dyspnea occurs is the dilation of blood vessels in the lungs allows for more blood to flow through them. This blood flow increases to the point where the lungs can no longer sufficiently oxygenate it all. The blood also flows through the lungs at a faster speed than normal, which gives the red blood cells less time to absorb oxygen. The lungs compensate for this by attempting to inhale enough oxygen to meet the needs of the blood flowing through them. A fast respiration rate can make an individual feel as if they cannot catch their breath or are out of breath. Many hepatopulmonary syndrome patients present with platypnea or breathlessness that occurs when they are in the upright position and improves upon lying down. Platypnea occurs because of the effect gravity has on the blood flowing through the lungs. When lying down, there is a better distribution of blood throughout the lungs than when sitting or standing upright.
Continue reading to reveal more symptoms of hepatopulmonary syndrome now.
Liver Disease Symptoms
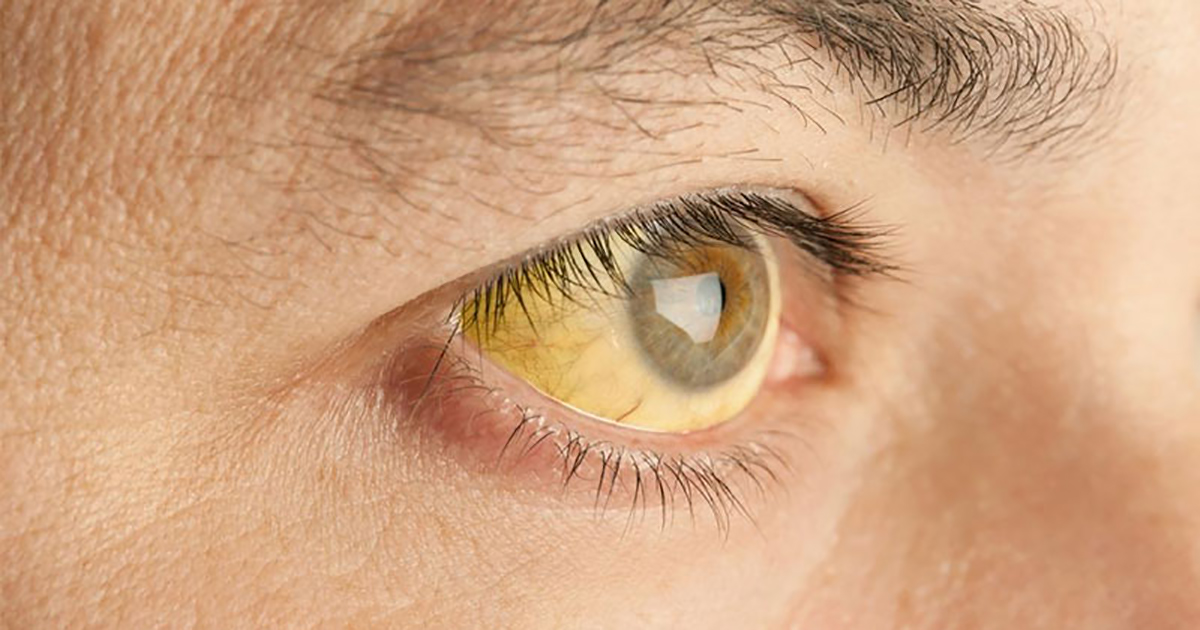
Hepatopulmonary syndrome is a complication of liver disease. Liver disease can occur as a result of genetic factors, infection of certain viruses, or lifestyle choices that cause damage to the liver. Because this condition occurs alongside liver disease, symptoms of a diseased liver will manifest before hepatopulmonary syndrome symptoms do. Jaundice is a common sign of liver disease that makes the white of the eyes and the skin appear yellow. When a diseased liver has progressed to cirrhosis or scarring of the liver, abdominal pain and swelling will become increasingly pronounced. Dark urine, pale stool, or blood in the stool can also be indicative of liver disease. As liver function declines, the patient will experience chronic fatigue and weakness. Due to built up toxicity in the body, nausea and vomiting often occur in individuals with a compromised and diseased liver. They may also have itchy skin, bruise easily, and exhibit a marked loss of appetite. Hepatopulmonary syndrome most often presents with one or more liver disease symptoms in addition to the symptoms associated with decreased blood oxygen levels.
Learn more about what can indicate the presence of hepatopulmonary syndrome now.
