Side Effects Of Pannus Growth
A pannus is a type of tissue containing blood vessels. The tissue grows erratically and covers an otherwise normal body structure. Pannus growths can occur at many sites throughout the body, and typical sites for pannus formation include the cornea, joint surfaces, abdomen, and artificial heart valves. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis commonly develop pannus growths on the joints of their hands and fingers. If a pannus growth reaches an advanced size, it may sometimes resemble a tumor. Patients of any age can develop a pannus growth. Doctors begin with a health history and physical examination when diagnosing this condition. Imaging studies such as CT scans may be used to help distinguish pannus growths from other conditions. Depending on the location of a pannus growth, patients may need specialist evaluation. For example, patients with a pannus growth on the cornea may need to be assessed by an ophthalmologist, and patients with these growths on the joints may need to be evaluated for rheumatoid arthritis by a rheumatologist. Occasionally, pannus growths can be surgically drained or removed; the appropriateness of this treatment depends on the location and size of the pannus growth. Other treatment options for pannus growths focus on slowing the growth rate of the tissue and on pain relief.
Pannus growths can lead to the development of many side effects, such as those outlined below.
Irreversible Tendon Damage

If a pannus growth forms over a joint, as is the case with many arthritis patients, it can adversely affect cartilage and tendons. Over time, its presence may cause irreversible tendon damage, which can lead to difficulty with walking and fine motor tasks such as writing or grasping objects. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis should be monitored frequently, and doctors may prescribe corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and pannus spread. Typically, these drugs can only be used for a short length of time due to the risk of serious side effects. Potential side effects from corticosteroid use include weight gain, high blood pressure, elevated blood glucose, thinning bones, and swelling in the lower legs. The drugs may also cause elevated eye pressure (glaucoma).
Learn more about the side effects of a pannus growth now.
Bone Deterioration
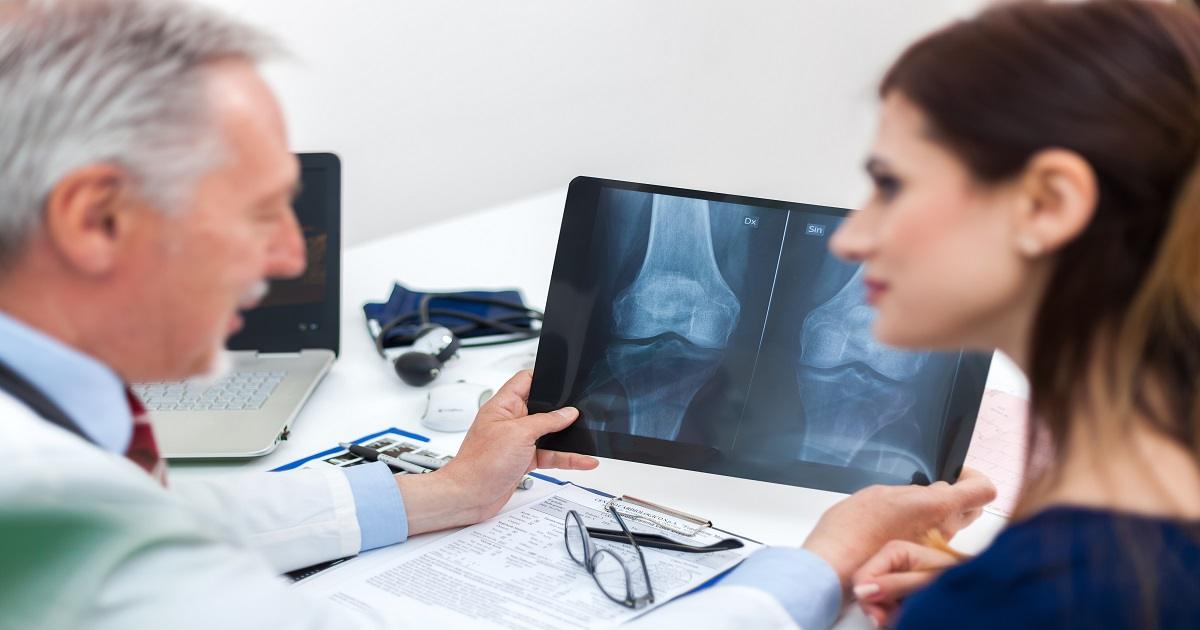
Bone deterioration due to pannus growths is most commonly seen in arthritis patients. The corticosteroids that are often necessary to slow pannus growths can lead to weakened, thin bones that may be more prone to fracture. As pannus tissue growths advance in size, they can destroy the protective joint capsule as well as tendons, and they also invade both the bones and the bone marrow, resulting in considerable damage and pain. Patients who experience bone deterioration may need to use aids such as canes or walkers, and they may also need joint replacement surgeries, such as knee or hip replacements. Bone-strengthening medication may be appropriate for some patients, and these can help reduce the risk of a fracture. Patients experiencing bone deterioration should be very careful while exercising as strenuous exercise may not be safe for them. These patients should consult their healthcare team to find out about the extent of the deterioration, and they may need specialized bone scans. Doctors may recommend certain exercise routines and methods to make daily tasks easier to increase quality of life. Patients may also benefit from physical and occupational therapy.
Continue reading for more information regarding the side effects of pannus growths now.
