What is Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s disease is one of the two main types of irritable bowel disease, along with ulcerative colitis, and is characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. The disease was named after Dr. Burrill B. Crohn, who first discovered the condition in 1932. Crohn’s disease is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system attacks tissues and cells in the body it perceives as foreign. In the case of Crohn’s disease, the body’s immune system attacks its digestive organs, including the intestines. Start reading now for all of the necessary information about what Crohn’s disease is, including symptoms and treatment.
Disease Basics
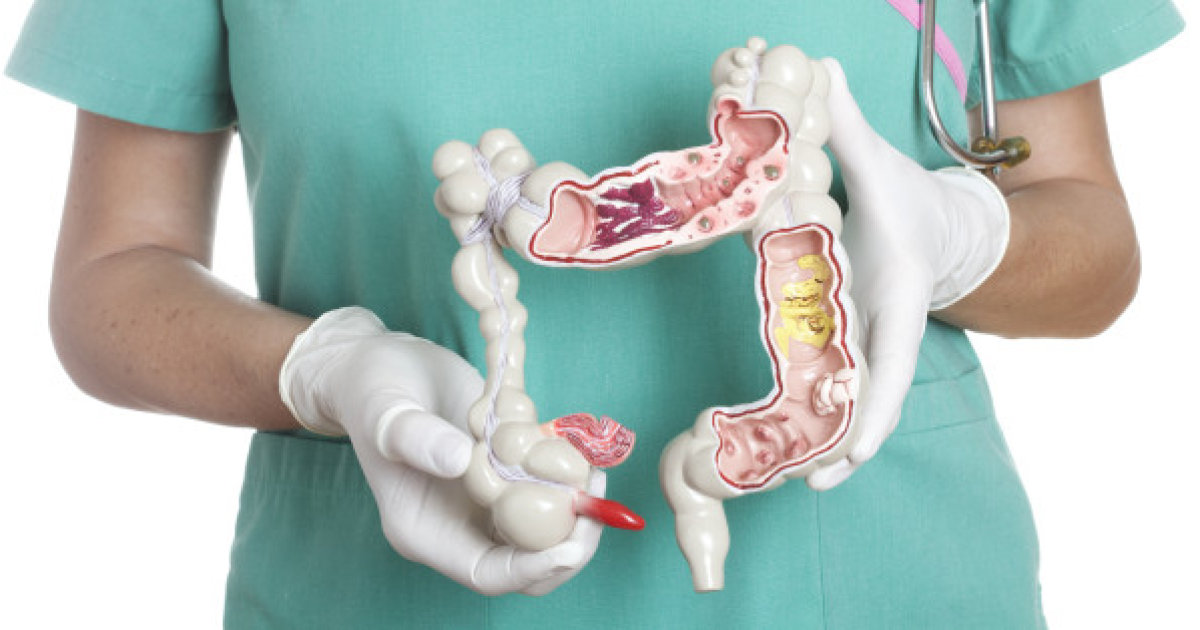
During the early stages of Crohn’s disease, small ulcerations are formed on the inner surface of the bowel walls. Over time, the erosions become deeper and larger, causing scarring and bowel stiffness. The bowel becomes increasingly narrow as the disease progresses and can eventually become obstructed. Crohn’s disease may result in deep ulcers that cause holes in the bowel wall in which bacterial infections can occur and spread to organs surrounding the abdominal cavity. This condition will disrupt the body’s ability to perform healthy functions such as digesting food, eliminating waste, and absorbing the required nutrition.
Continue reading for details on the common symptoms of Crohn’s disease.
Symptoms

In most cases, the areas Crohn’s disease affects are the colon and the final part of the small intestine (the ileum). Symptoms of this condition typically develop gradually, but sometimes symptoms will start without warning. Sometimes patients report periods in which no symptoms are present. Symptoms can range in severity from mild to more extreme depending on the affected individual and each case.
When symptoms of Crohn’s disease are present, they typically include a collection of infected pus, high fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, blood in the stool, mouth sores, abdominal pain and cramping, constipation, loss of appetite, weight loss, night sweats, and fatigue. Patients who have severe cases of Crohn’s disease may also experience symptoms such as joint, eye, skin, liver, and bile duct inflammation. Children with severe Crohn’s disease may also have delayed growth or sexual development.
Continue reading for information on Crohn’s disease risk factors.
