When Your Kidneys Sound The Alarm: What To Know About Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is a complex condition that affects the kidneys, specifically the glomeruli, which are tiny filtering units within the kidneys. The importance of understanding this condition lies in its potential to lead to serious kidney damage if not detected and managed early. The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste products from the blood, balancing bodily fluids, and regulating blood pressure. When glomeruli are inflamed, these functions can be severely impaired. This introduction sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of the early warning signs of glomerulonephritis, as well as broader insights into maintaining kidney health. As we delve into this topic, it becomes evident that awareness and early intervention are key to preventing long-term kidney damage and preserving overall health.
Understanding the Anatomy and Function of the Kidneys
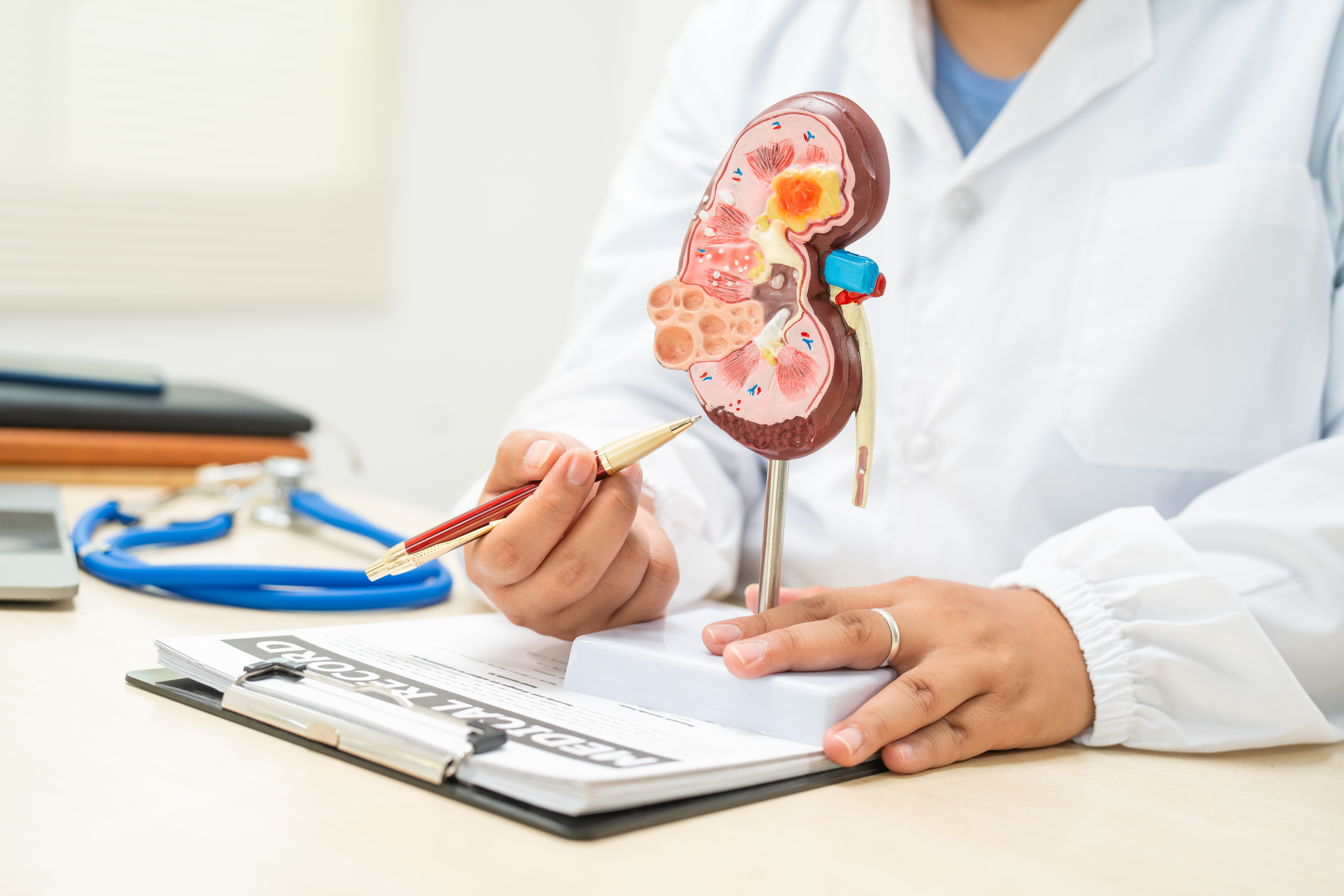
The kidneys are remarkable organs that perform several vital functions essential for maintaining homeostasis. Each kidney contains around a million nephrons, the functional units responsible for filtering blood. Within each nephron, the glomerulus acts as a sieve, allowing water and small molecules to pass through while retaining larger molecules like proteins and blood cells. This filtration process is crucial for removing waste and excess substances from the bloodstream. Additionally, the kidneys regulate electrolyte balance, blood pressure, and red blood cell production. Understanding this intricate anatomy and physiology is fundamental to recognizing how conditions like glomerulonephritis disrupt normal kidney function, leading to potential health complications.
What is Glomerulonephritis? An In-Depth Look
Glomerulonephritis is characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli, which can be acute or chronic. Acute glomerulonephritis often follows infections such as streptococcal throat infections, whereas chronic glomerulonephritis may develop over years without obvious symptoms. The inflammation can result from immune system malfunctions, where antibodies mistakenly attack the glomeruli. This condition can lead to proteinuria (excessive protein in urine), hematuria (blood in urine), and, ultimately, reduced kidney function. Understanding the types and causes of glomerulonephritis is essential for identifying early warning signs and implementing timely interventions to prevent progressive kidney damage and associated health issues.
