Treatment Methods For Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic medical condition in which there is too much sugar in the blood. This is medically referred to as having high blood glucose and can result from several different mechanisms. In Type 1 diabetes, high blood glucose is caused by the inability of the pancreas to produce sufficient levels of insulin, a hormone which regulates glucose. In Type 2 diabetes, high blood glucose is triggered because the body is unable to respond properly to insulin. Other forms include gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy, and prediabetes, which involves higher than normal blood glucose readings that are not yet high enough to be classified as Type 2 diabetes, which is the most common form of diabetes mellitus and affects more than twenty-nine million Americans. Each year, more than one million new cases of Type 2 diabetes are diagnosed.
Some diabetes mellitus patients may not know they have it because it sometimes produces no symptoms. When symptoms are present, they generally include frequent urination, thirst, fatigue, weight loss, and blurry vision. Complications include chronic renal failure, cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, eye problems, heart disease, dental issues, and depression. Diabetes mellitus can be diagnosed with blood tests and controlled with lifestyle modifications and medication. The interventions discussed below can help patients keep their blood sugar under control and reduce the risk of complications from this condition.
Control Blood Pressure
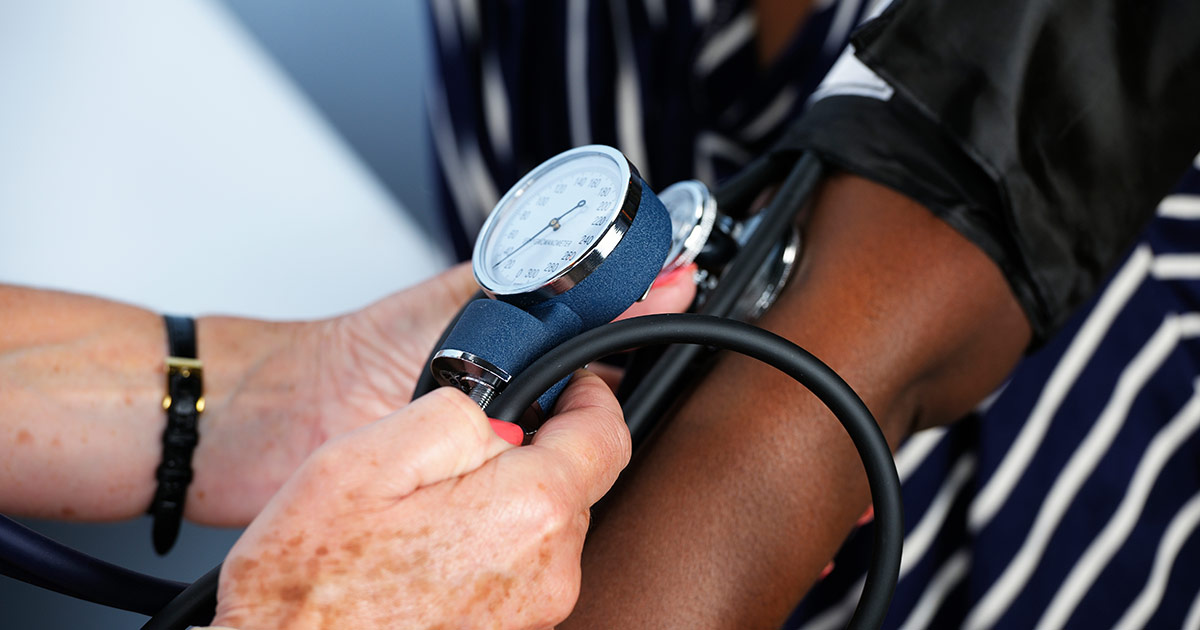
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is one of the most common complications of diabetes mellitus and places patients at an elevated risk of developing heart disease. Blood pressure control is, therefore, a high priority for patients. Blood pressure is measured as a series of two numbers, one when the heart beats (systolic) and the other when it is between beats (diastolic). A normal blood pressure reading is below 120/80, with 120 being the systolic number and 80 being the diastolic number. Blood pressure can be affected by stress, caffeine, and certain medications. A diagnosis of hypertension is made after three consistently high readings taken by a doctor on separate days. Patients usually try to make lifestyle modifications to control their blood pressure first, including limiting salt, losing weight, following stress management techniques, and adopting a diet with fewer processed foods. If these measures do not bring blood pressure readings down, doctors will likely suggest patients begin taking beta blockers, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or other classes of blood pressure lowering medication to normalize their readings. These medications are generally well tolerated and have few side effects.
Keep reading for more on treating diabetes mellitus.
Follow A Balanced Diet
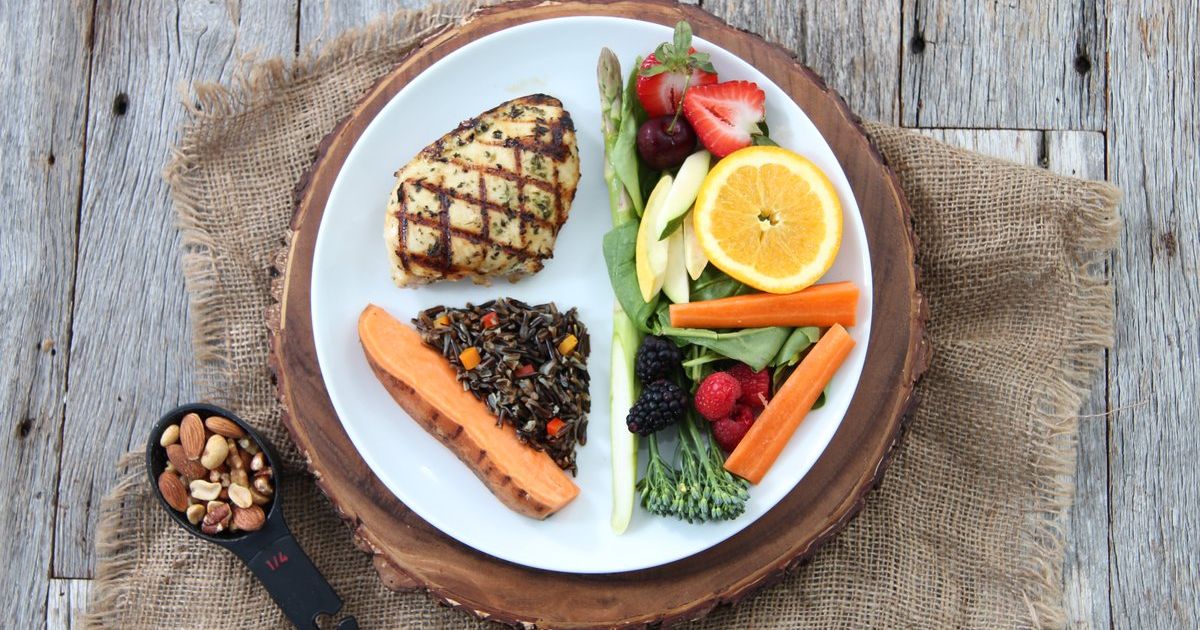

Doctors encourage all patients who have diabetes mellitus to follow a balanced diet. Proper diet can help patients naturally lower their blood glucose and potentially avoid or reduce their need for oral medicines or insulin. The healthiest, most balanced diet for patients to adopt is one rich in fruits, vegetables, and complex carbohydrates and low in refined sugar, saturated fats, and processed foods. Doctors may also ask patients to monitor their carbohydrate intake. Choosing complex carbohydrates such as those found in brown rice, whole wheat bread, oatmeal, and legumes can help keep patients feeling satiated for longer than simple carbohydrates such as white rice and white pasta. Healthy fats such as the kind found in avocados and other vegetables help lower cholesterol levels and are a much better choice than fat from meat. When planning their diet, patients may wish to keep a food diary and take blood sugar readings before and after meals to determine how certain foods affect their levels.
Get to know the next method of treating diabetes mellitus now.
