Glaucoma Treatment Options
Glaucoma is a common eye condition that can cause loss of vision or blindness if left untreated. In fact, it is one of the leading causes of blindness in older adults. Glaucoma develops from fluid buildup within the eye because of problems with drainage, which usually leads to pressure in the eye and damage to the optic nerve. Early detection and treatment of glaucoma is key to minimizing damage.
The most common type of glaucoma is open-angle, which occurs gradually and is usually asymptomatic in the early stages. The other major type is closed-angle glaucoma, which can cause an acute attack or develop slowly over time. An acute attack is considered an emergency and requires immediate medical attention to prevent blindness. Symptoms include severe eye pain and blurred vision. Risk factors of glaucoma include age, eye injuries or conditions, or certain illnesses like diabetes. Lost vision can’t be restored, but a variety of treatments are available to preserve a patient's remaining sight.
Eyedrop Medications
Eyedrops are usually the first treatment recommended to control intraocular pressure (IOP), since they can be very effective at controlling it for many patients. These medications include prostaglandins, beta blockers, and alpha-adrenergic agonists. This treatment lowers eye pressure by increasing drainage of fluid or decreasing the formation of fluid in the eye. During application, some of the eyedrops are absorbed into the bloodstream. Side effects of eye drops include blurred vision, stinging, redness, itching, and changes in eye color.
Glaucoma eye drops are categorized by their active ingredient and are typically available in generic forms. One of the most recommended types is prostaglandins because they only require one application per day. Most others require two to four, and some patients have difficulty keeping up with the daily schedule. Prostaglandins work by relaxing the eye muscles for better flow of fluids. Taking medications regularly and following dosage amounts is crucial to controlling eye pressure. Specific techniques can maximize the amount of drug absorbed in the eye and lessen the portion that goes into the bloodstream. Doctors can advise their patients about the most effective method of administering the drops.
Keep reading for more glaucoma treatment options.
Oral Medications
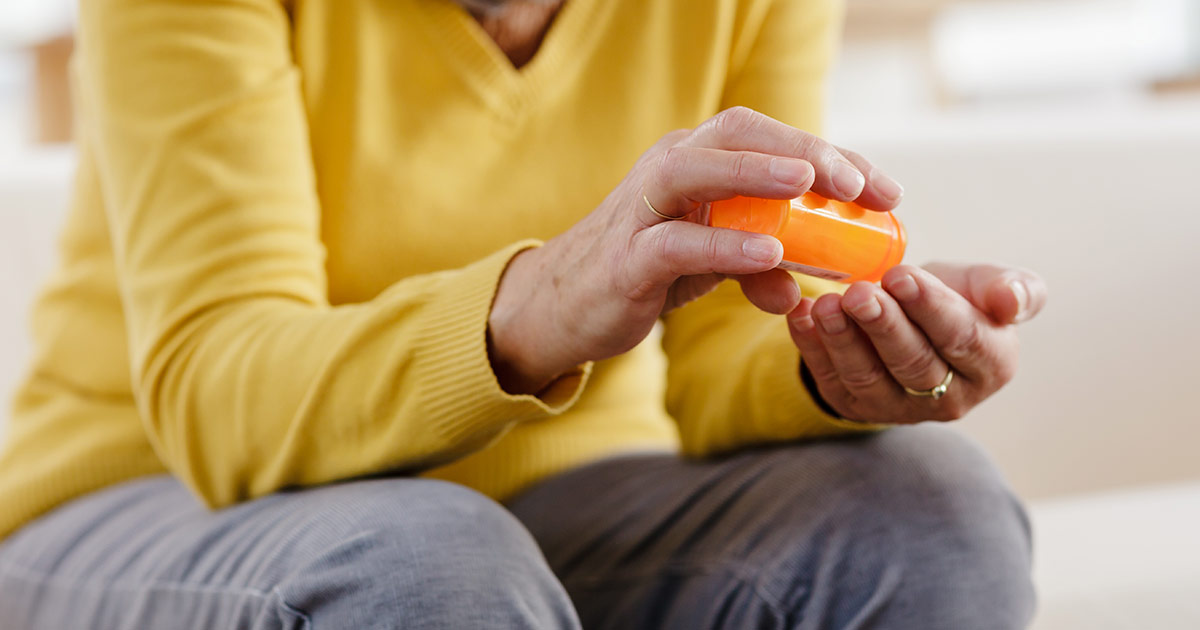

Oral medications are sometimes prescribed in addition to eyedrops to help reduce eye pressure to a normal level. These medications have the same effect as eyedrops as they decrease fluid production and increase drainage. They’re typically added to the regimen if eyedrop medications aren’t able to reduce eye pressure to the desired level. The oral medication usually recommended is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, which helps slow production of fluid in the eyes. Acetazolamide and methazolamide are two examples of this type of medication. There are more systemic side effects when taking pills in comparison to eyedrops, and they include stomach upset, fatigue, depression, a tingling sensation in the extremities, frequent urination, and kidney stones. Oral medications for glaucoma may cause potentially dangerous interactions with other drugs, so it's important for patients to keep their doctor informed of all current medications. In addition, it's imperative to take recommended medicine regularly and consistently because it controls eye pressure and preserves vision.
Discover the next option for treating glaucoma now.
