How Is Pityriasis Rubra Pilaris Treated?
Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a group of illnesses that cause the skin to be constantly inflamed and scaled. Depending on the specific condition, a patient's entire body may be affected, or they may only experience symptoms on certain portions of the body. Some manifestations of pityriasis rubra pilaris also involve thickened skin on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, abnormalities in nail growth, and hair thinning. Individual manifestations of pityriasis rubra pilaris are differentiated based on the areas affected, other present conditions, and the age of the patient at symptom onset. Both adults and children can experience this condition. It's important to note that since pityriasis rubra pilaris is a group of related illnesses, a treatment that works for one type may not work for another.
Topical Corticosteroids
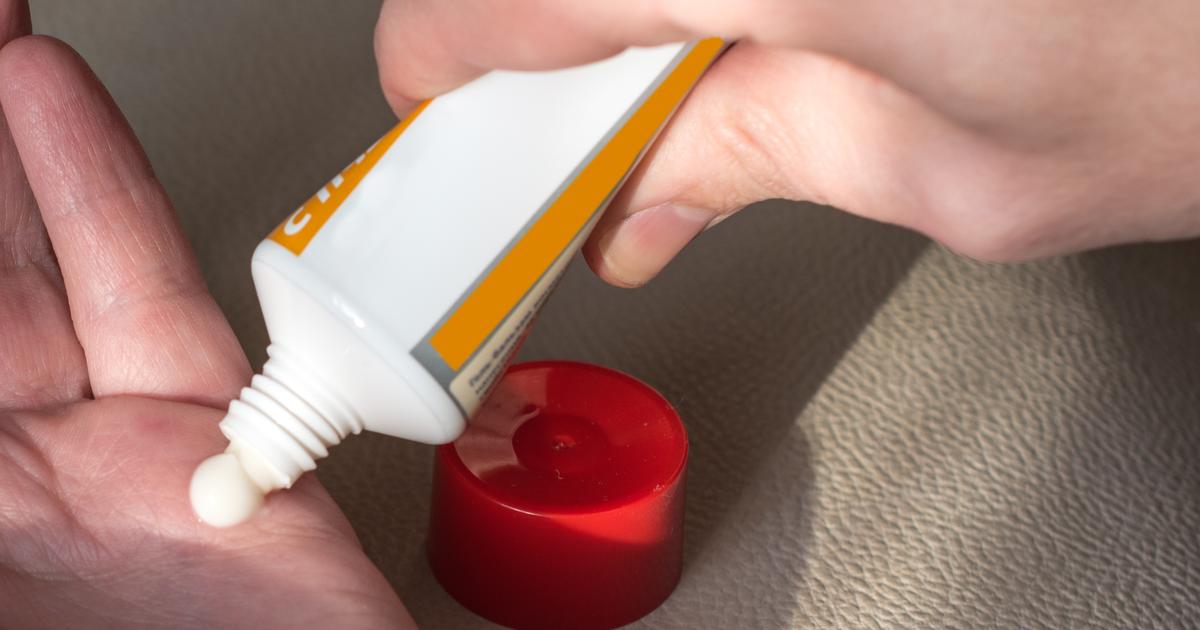

One of the most common methods of treating pityriasis rubra pilaris is through topical corticosteroids. The body naturally produces hormones called corticosteroids in the adrenal glands. Corticosteroid medication is a synthetic version of the body's natural corticosteroid hormones. As such, the medication has the same effects as natural corticosteroids. Topical corticosteroids are medications applied directly to the skin, rather than ingested orally or administered intravenously.
The medication uses powerful anti-inflammatory properties to counteract skin inflammation. In addition, the medication suppresses the immune system's response. Inflammation occurs when the immune system floods the skin with histamines because it believes the body is under attack. While some corticosteroids treat the entire body, topical medications affect only the patch of skin they are applied to.
Oral Retinoids
While a topical treatment option is a favored way to reduce symptom discomfort, many patients also benefit from additional oral medication. Additional medicines are particularly important for individuals with large areas of affected skin. The first medicines used are generally oral retinoids, which are commonly prescribed when topical medication alone can't fully control the condition.
The medication slows the rapid growth of skin cells, which helps reduce the amount of scaling and skin thickening in patients. In addition, the medication reduces swelling and redness throughout the body, rather than focusing on just one patch of skin. An oral retinoid is often prescribed with other inflammatory skin conditions and scaling skin conditions. Most commonly, the treatment is used for psoriasis patients.
