Guide To The Side Effects Of Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen belongs to a class of medicines called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It can be purchased over-the-counter or in higher strengths with a prescription. Ibuprofen is utilized to alleviate pain caused by a headache, menstrual cramps, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, dental pain, and muscle aches. Ibuprofen is also an effective fever-reducer that can also help alleviate pains and aches that occur with the flu or common cold. Inflammation in an individual's body occurs upon the production of certain substances that begin inflammatory processes in the affected tissue. Ibuprofen works by using a mechanism to inhibit the production of such pro-inflammatory substances in the body. The effect of ibuprofen helps bring down swelling, decrease pain, and reduce body temperature.
Like other medications, however, ibuprofen does come with some potential side effects. Get familiar with these now.
Abdominal Pain
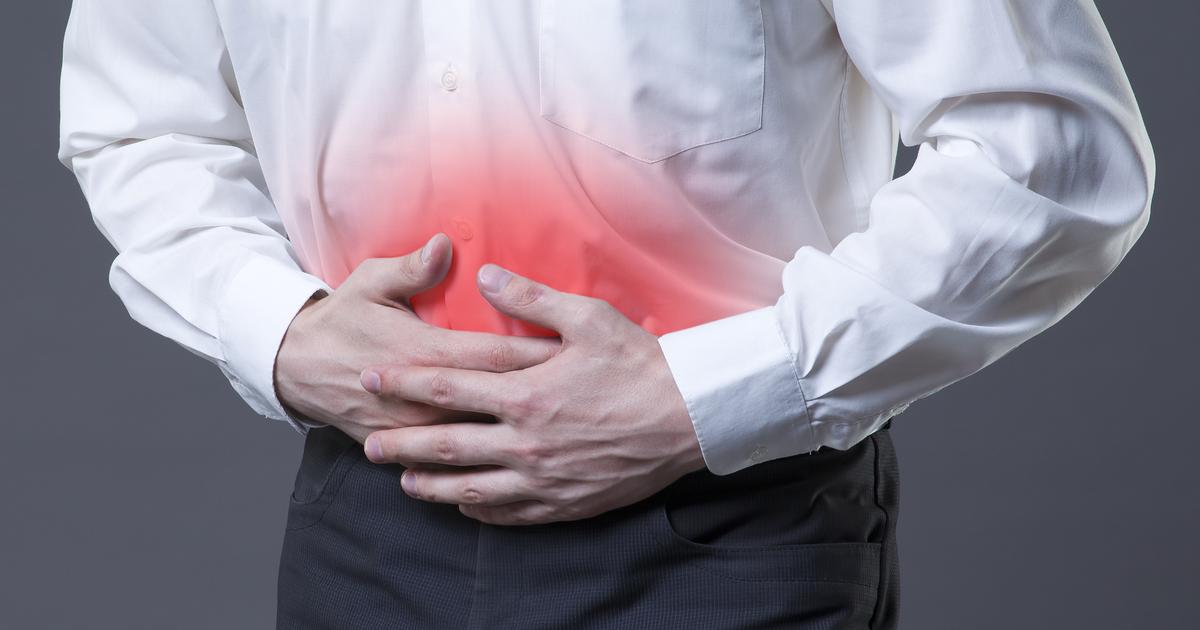
A small portion of individuals who take ibuprofen may experience abdominal pain. Abdominal pain is the result of the depletion of the three main mechanisms the stomach and intestinal tissues use for protection against stomach acid and other gastric juices. The stomach lining mucus layer is broken down by ibuprofen, and there is a decrease in chemical bicarbonate responsible for neutralizing acids in the stomach and intestines. Abdominal pain manifests when food that has been consumed or digestive components produced by the liver, pancreas, and stomach actually cause cellular damage to the underlying and unprotected tissues of the stomach and intestine. Pain in the abdomen is common with damage to the linings of the stomach and intestines because they contain a large concentration of sensory nerves responsible for transmitting pain. Should ibuprofen cause an ulcer or lesion to form in the lining of the stomach or intestine, the abdominal pain can last for up to several weeks.
Read more about the side effects linked to ibuprofen now.
Nausea And Vomiting

Some individuals who take ibuprofen may experience nausea and vomiting due to cellular damage to the digestive tract. When cellular damage is detected in the gastrointestinal tract, the brainstem receives signals with this information from the individual's mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors. As a result of this process, the affected individual's solitary tract nucleus, motor vagus nucleus, and the central pattern generator are triggered. Once these structures have been activated, a chain reaction occurs that results in the individual feeling the urge to vomit. The individual's saliva production increases and the movement of food through their digestive tract slows down. Should an ulcer form in the stomach or intestine as a result of ibuprofen use, blood from the lesion can also trigger these mechanisms and cause nausea and vomiting.
Get more details on ibuprofen side effects now.
