Serious Side Effects Of Vasodilators
A vasodilator is a type of medication that dilates or opens up blood vessels. Vasodilators work through a mechanism that causes changes in the muscles inside of the venous and arterial walls. This mechanism allows an individual's blood to flow more effortless through the blood vessels so the heart does not have to work so hard. There are three types of this medication: venous dilators, arterial dilators, and mixed dilators. Vasodilators are prescribed to individuals who have high blood pressure, pulmonary hypertension, preeclampsia, angina, or heart failure that require treatment. Vasodilators are not the preferred or first method of treating these diseases and conditions because they are known to be very potent. Vasodilators are used in cases where a patient's condition or disease is not able to be controlled through other means.
Vasodilators may produce serious side effects in affected individuals. Get the details on these now.
Heart Palpitations
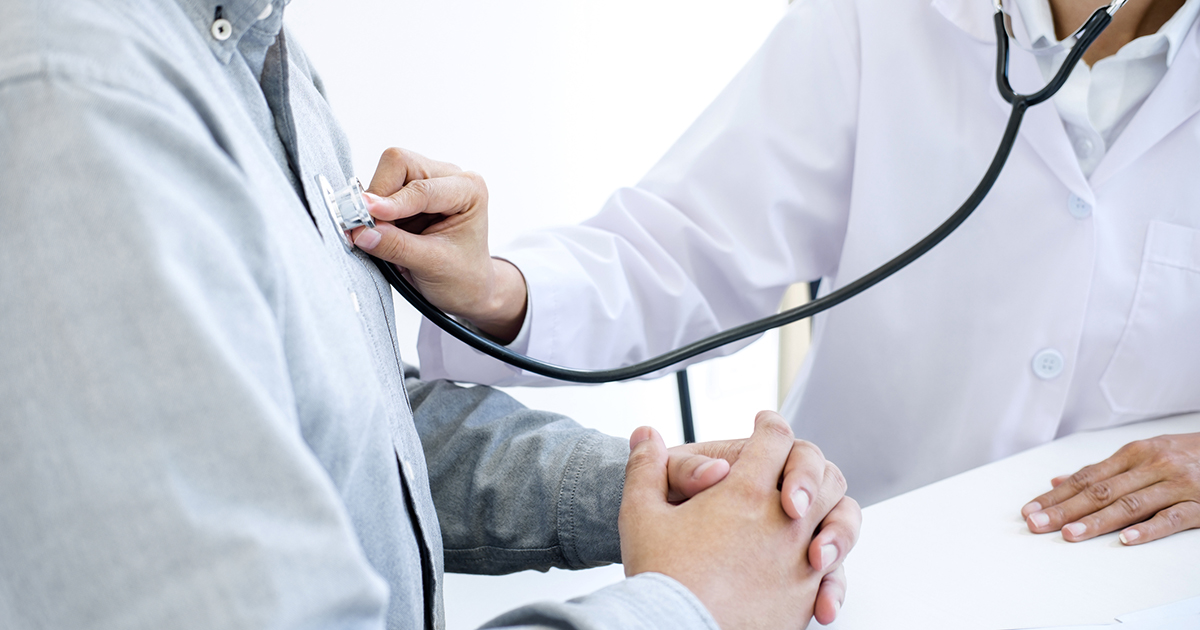

A pounding or fluttering heartbeat is medically referred to as heart palpitations, and these can occur in individuals who take vasodilators. Heart palpitations describe when an individual can feel that their heart is beating too fast, skipping beats, fluttering, pounding, or pumping too hard. Heart palpitations can manifest in several regions the torso, including the neck, chest, or throat. Palpitations may occur in individuals who take vasodilators due to the mechanism they use to help lower blood pressure. Vasodilators exert their action on the muscle tissue inside of the blood vessel walls to cause them to expand and allow a greater volume of blood to flow through. When blood vessels near the heart, neck, and chest become larger due to this medication, they are closer to other structures inside the body. Sensory nerves are included in the list of structures and tissues closer to where blood is pumping through the dilated arteries. When the nerves around any particular area in the neck, chest, or throat become activated by this pulsing because the vessels are dilated, they transmit this sensory information to the brain. The brain interprets this as heart palpitations in the affected area.
Read more about the side effects linked to vasodilators now.
Fluid Retention
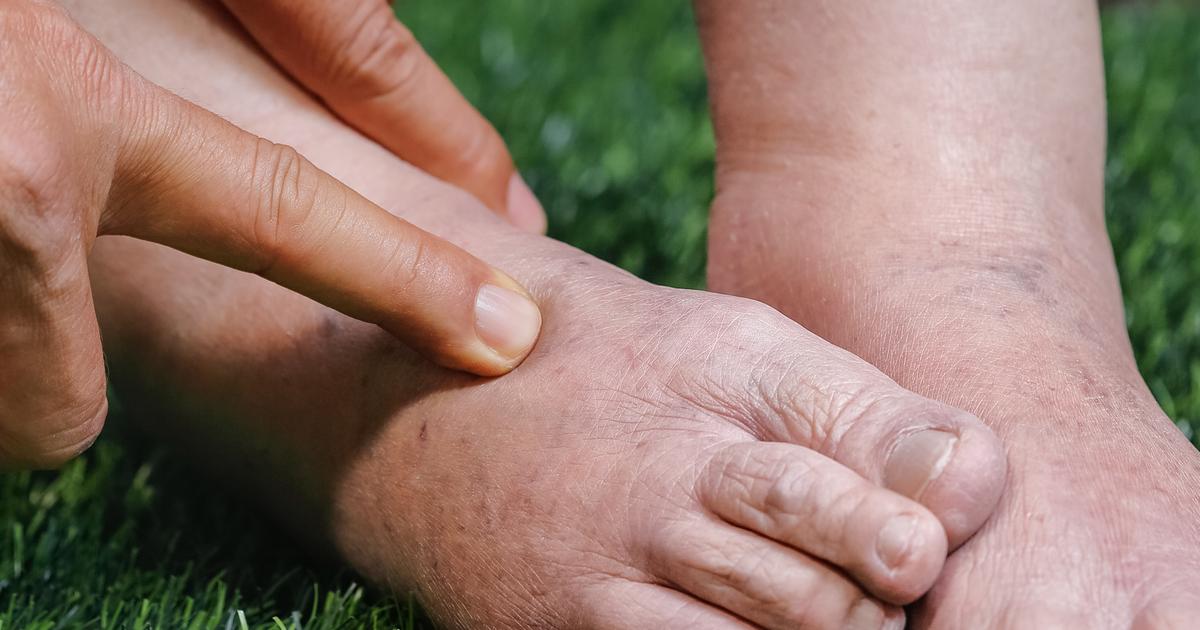
Individuals who take vasodilators may experience fluid retention, which refers to when the body accumulates excessive fluids in the body tissues outside of circulation as a result of some underlying mechanism. Vasodilators are medications that induce the dilation of blood vessels around the body. However, vasodilators do not only act upon the arteries, but they also have this effect on veins. When the veins dilate too much, the valves inside of the veins are unable to do their job as well to push blood against the force of gravity. The result is an excessive pooling of blood in the lower extremities because the blood becomes backed up. Backed up blood in the veins causes the pressure inside of the veins to become higher than the pressure outside of the veins in the surrounding tissues. When the pressure gradient is too high in the veins, they begin to leak fluid into the tissues that surround them as a compensatory measure. In addition, the walls of the veins become more penetrable when their walls are stretched out. This mechanism causes fluid retention in some patients who take vasodilators.
Uncover more side effects of vasodilators now.
