How To Overcome PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder)
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, or PTSD, is a mental health condition characterized by either witnessing or experiencing a terrifying life event. Common symptoms include nightmares, severe anxiety, flashbacks, and obsessive or uncontrollable thoughts. These symptoms may occur immediately after the event, or they may not develop until years later. There are four types of PTSD, including intrusive memories, avoidance, adverse changes in mood and thought, and emotional reactions and physical changes. Events commonly associated with PTSD are military or combat exposure, sexual violence, physical assault, childhood abuse or environmental factors such as weather-related events or a fire.
10. Therapy Treatment
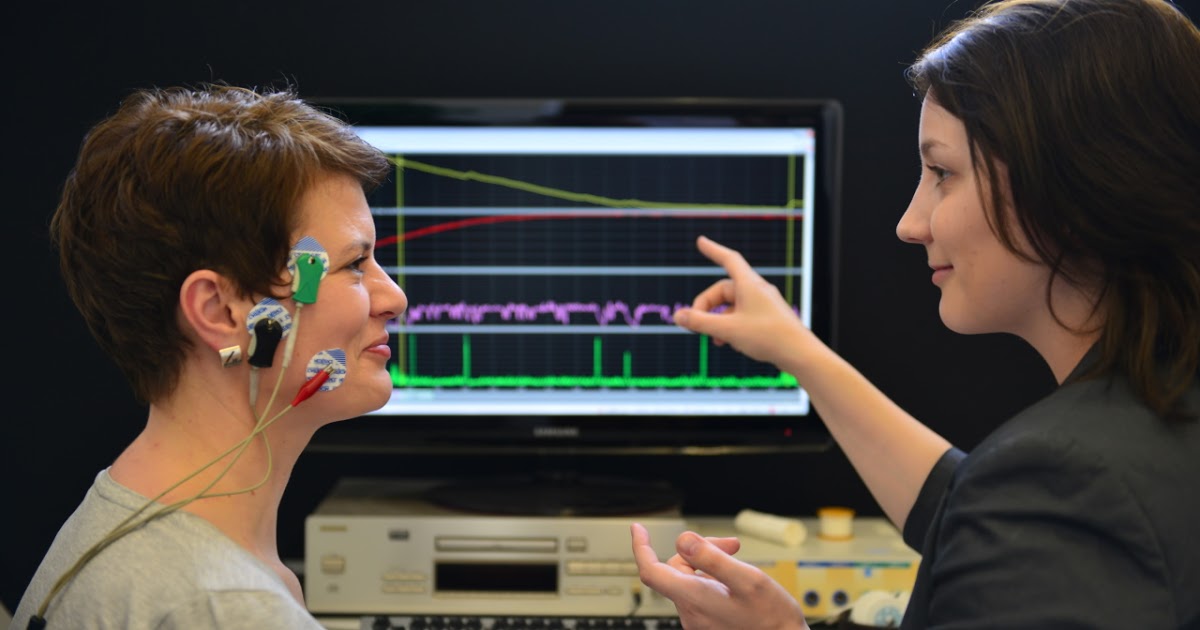

Anyone dealing with PTSD should seek help from a trained medical professional right away to control symptoms. Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing is a type of cognitive therapy that can be used to treat symptoms by asking the person affected to focus on a moving finger to help guide them through trauma. Behavioral behaviorists can assist in adjusting trauma-filled thoughts and guide the person affected by developing alternative interpretations and engaging in a new way of responding to negative or overwhelming feelings.
9. Medications
Medications are available and should be prescribed by a health professional only. Serotonergic antidepressants may include fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine. Drugs that help decrease physical symptoms may include prazosin, clonidine, guanfacine, and propranolol. Research indicates that patients who take an antidepressant for at least a year are less likely to develop a relapse. Antidepressants are also the only group of medications that have been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration for PTSD treatment. Mood stabilizers and antipsychotic medications are also available, especially for patients who experience paranoia.
