Serious Complications Of Cerebral Palsy
Contracture
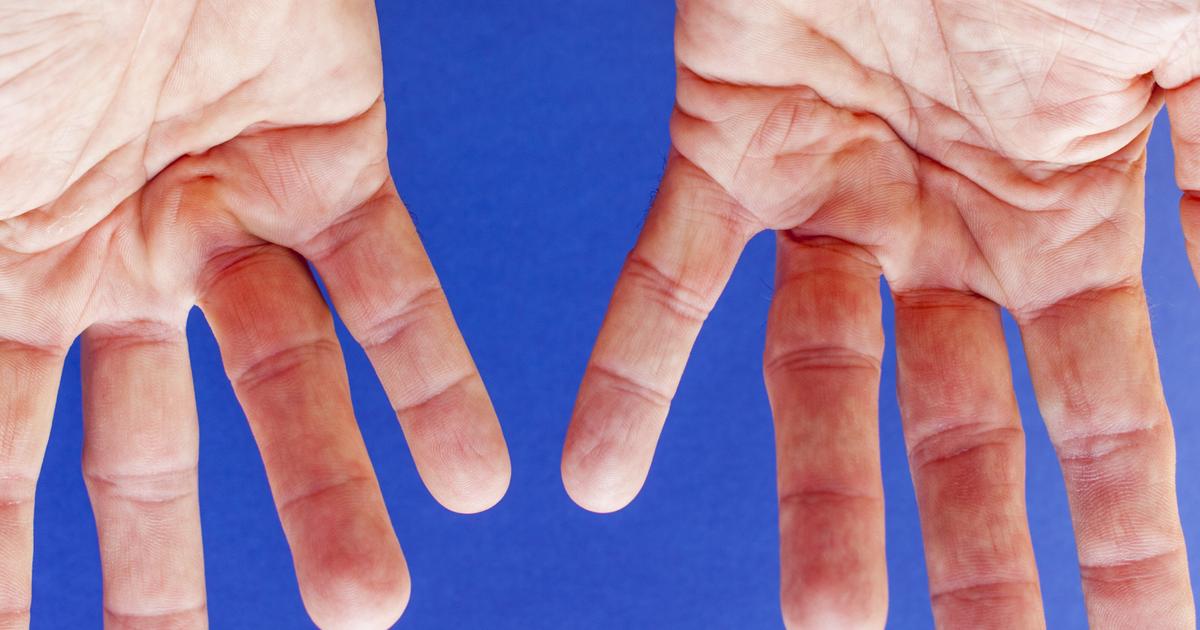
Cerebral palsy patients may develop contracture as a complication. This is a deformity that occurs when the connective tissues of an individual's body constrict and become stiff. Tissues that can be affected by contracture include joint capsules, ligaments, muscles, tendons, and skin. This complication can manifest as difficulty stretching the legs, moving the hands, and straightening the fingers.
There are several ways cerebral palsy can cause patients to experience this complication. The muscle of individuals with this disorder is structurally altered with fibers that have a small diameter, reduced muscle body size, and overly stretched sarcomeres. In addition, their muscle tissue has an abnormal arrangement of connective tissue and an altered extracellular matrix. Most of these abnormalities are caused by altered gene expression and a deficiency of muscle stem cells.
Osteoarthritis
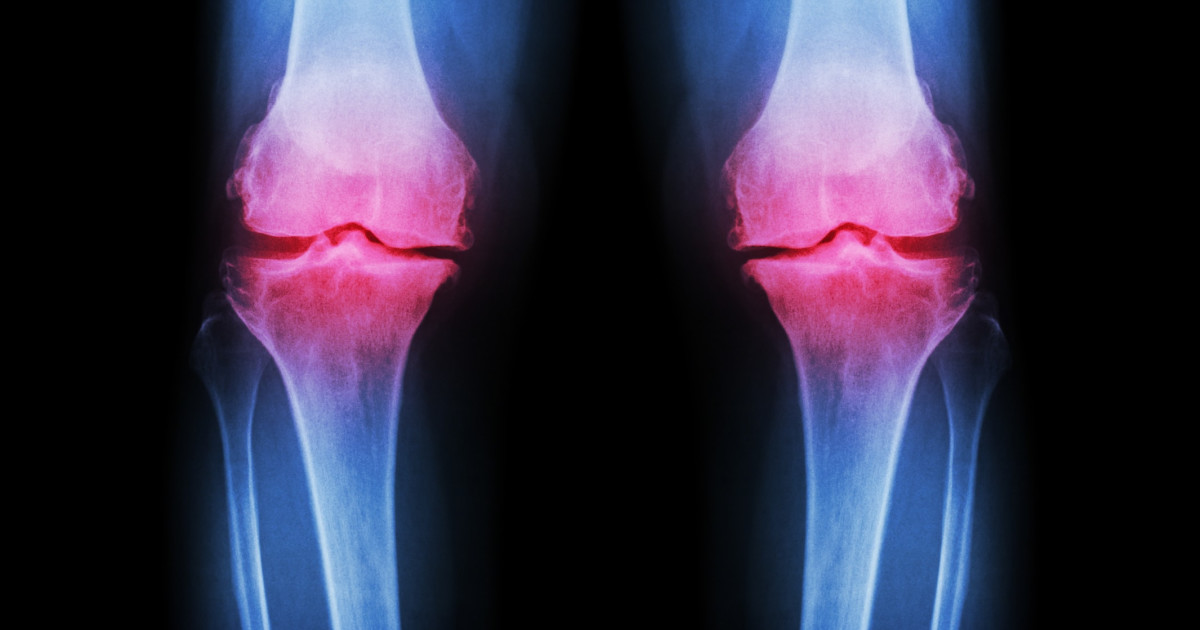
An individual with cerebral palsy may develop osteoarthritis due to their disorder. Osteoarthritis is a condition where the cartilage in a joint that protects the bones becomes eroded over time. This causes stiffness and pain in the affected joint. An individual with cerebral palsy is at an increased risk of developing osteoarthritis because of the abnormalities in the musculoskeletal system the disorder causes. Muscle imbalance is a common characteristic seen in these patients. It can cause the abnormal and unusual movement of one or more joints in the body.
A combination of the overuse of joints, compression in joints, unusual movements in the joints, and excessive wear on the cartilage in the joints are what cause a cerebral palsy patient to develop this condition. Symptoms in individuals with cerebral palsy precipitated osteoarthritis include pain with joint movement, joint tenderness, and a grating feeling in the joint upon movement. Others are joint stiffness, the inability to move the joint through its full range, and hard lumps felt around the affected joint.
