Guide To The Conditions That Trachyonychia Can Indicate
Trachyonychia, which is also called 20-nail dystrophy, is a condition of the fingernails and toenails. It causes interference in the affected individual's nail matrix. All twenty of a patient's nails may be affected, or it may only affect a single nail. Straight, long lines that extend the length of the nail and end at variable heights are characteristic of trachyonychia. Other nail symptoms include sandpaper-like texture, lack of nail luster, brittle nature, and a rough appearance. While it is most prevalent in childhood, this condition can happen at any age. Most often, trachyonychia appears when an individual is born and progresses over time.
Thankfully, there as a few trachyonychia treatment options. Many patients experience some relief and success by taking corticosteroids for trachyonychia. These can be oral, systemic, or topical corticosteroids. Some patients may need antifungals for trachyonychia as well. However, treatment for trachyonychia often depends on the cause. Thus, patients must understand the cause behind their condition first.
Alopecia Areata
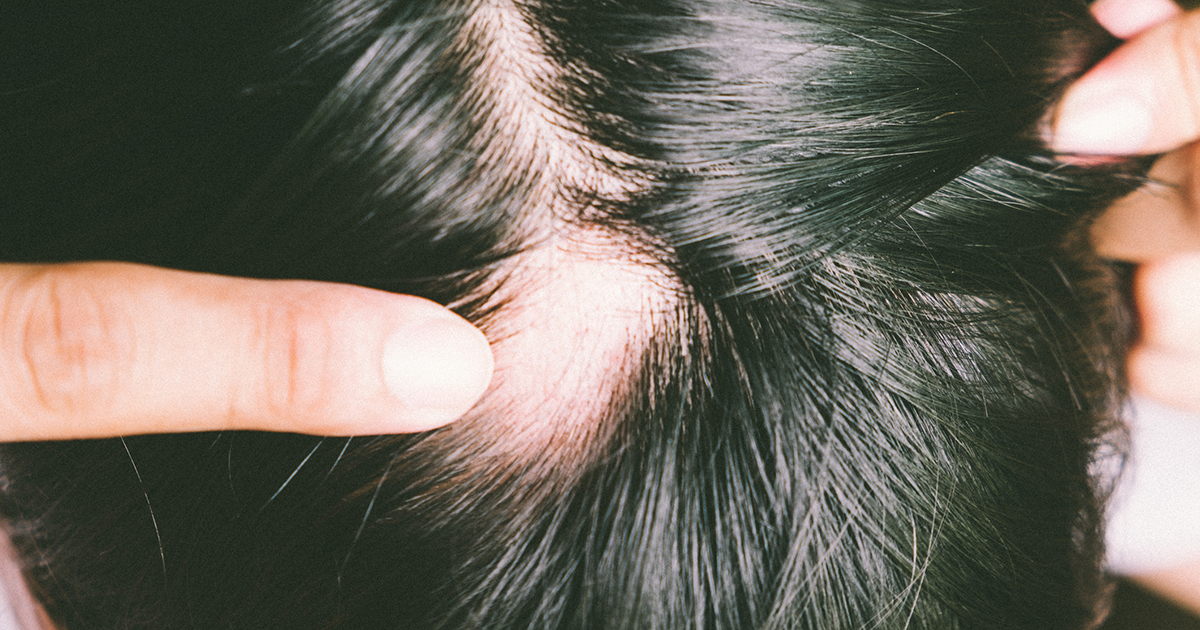
Trachyonychia has been strongly linked to individuals affected by a common autoimmune disorder called alopecia areata. The most characteristic symptom that occurs in alopecia areata is an unpredictable loss of hair. This disorder occurs when a patient's immune system inappropriately attacks their hair follicle cells. This malfunction causes the production of hair to lag and results in shrunken hair follicles.
The mechanism behind the abnormal immune system attack on such cells is unclear at this time. However, it does appear to harbor some genetic factors. Twenty-five percent of alopecia areata patients have a family member who is also affected. While hair loss is the most classic symptom in this disorder, changes in the fingernails and toenails are also common manifestations. Changes in the nails, including trachyonychia, are typically one of the very first indications that alopecia areata is developing. Between forty-five and eighty-three percent of all trachyonychia patients also have alopecia areata.
Atopic Dermatitis
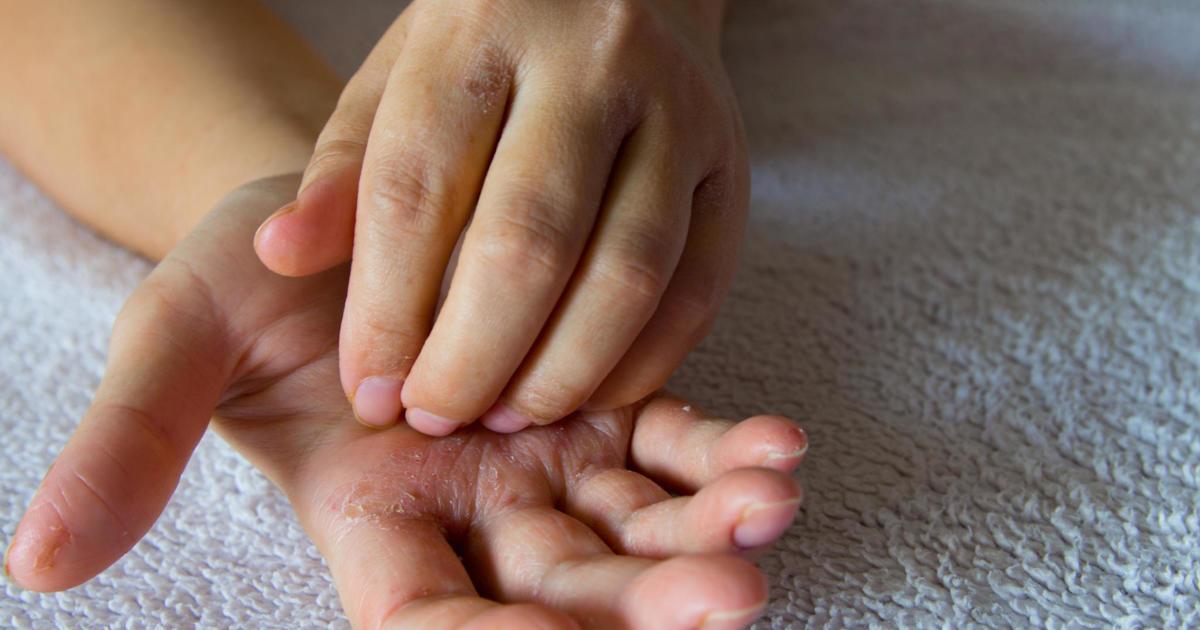

Eczema, also called atopic dermatitis, can cause an affected individual to develop trachyonychia. Atopic dermatitis affects the skin and causes the development of dry, scaly patches. These dry and scaly patches on the skin are often extremely itchy and are responsible for intense discomfort in affected individuals. Atopic dermatitis can happen in a child as early as two or three months old. Approximately ninety percent of atopic dermatitis patients will experience symptoms before they reach half a decade of life. Milder manifestations of atopic dermatitis continue from childhood into adulthood in around half of all patients.
The condition happens when the skin's ability to retain moisture becomes impaired. Without the protective moisture barrier function of the skin, external factors or changes can cause inflammatory lesions. Trachyonychia occurrence in eczema is the result of the individual's nail matrix being infiltrated by eczematous change. These skin changes around the nail and nail bed cause an interruption of nail synthesis, resulting in trachyonychia and other conditions that affect the nails.
