Guide To The Causes And Complications Of Anhidrosis
Anhidrosis is a condition in which the sweat glands do not function properly. Even in extreme heat, patients with anhidrosis are often unable to perspire at all, and this prevents the body from cooling itself effectively. While the condition can affect the entire body, some individuals might only experience symptoms in a few areas. Symptoms of anhidrosis generally include the partial or complete absence of sweat, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and flushing. Patients may feel very hot, and muscle cramps are common.
To diagnose this condition, doctors normally perform a sweat test. After being coated in a powder that changes color in response to the presence of sweat, the patient sits in a room warmed to a temperature that should produce perspiration. Photos are taken during the test to check for any color changes in the powder that indicate sweating. In certain cases, it may be necessary for the patient to have a biopsy of the skin or sweat glands. Treatment involves trying to determine the underlying cause and making lifestyle adjustments that could reverse or manage it. For example, patients who experience anhidrosis due to a particular medication may be switched to a different one, and individuals who develop the condition as a result of clogged sweat glands might be advised on exfoliation and other appropriate modifications to their skincare routine.
Some of the most common causes and complications associated with anhidrosis are discussed below.
Connective Tissue Diseases

Connective tissue diseases are one of the major potential causes of anhidrosis. These diseases result in inflammation to the collagen and elastin, two proteins that help tissues connect with body structures. Connective tissue diseases can damage the lungs, skin, nerves, gastrointestinal system, and other body areas. Rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and Sjogren's syndrome are a few of the connective tissue diseases currently recognized, and patients with these conditions may exhibit a range of symptoms, including dry mouth, dry eyes, reduced or absent sweating, fatigue, and shortness of breath. To diagnose these types of diseases, doctors perform a physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies. Patients who receive a positive diagnosis will be referred to a specialist who treats their specific type of connective tissue disease. Treatment for connective tissue conditions usually includes immunosuppressants, and some patients may benefit from physical therapy and lifestyle modifications.
Get more details on what can result in anhidrosis now.
Damage To The Skin
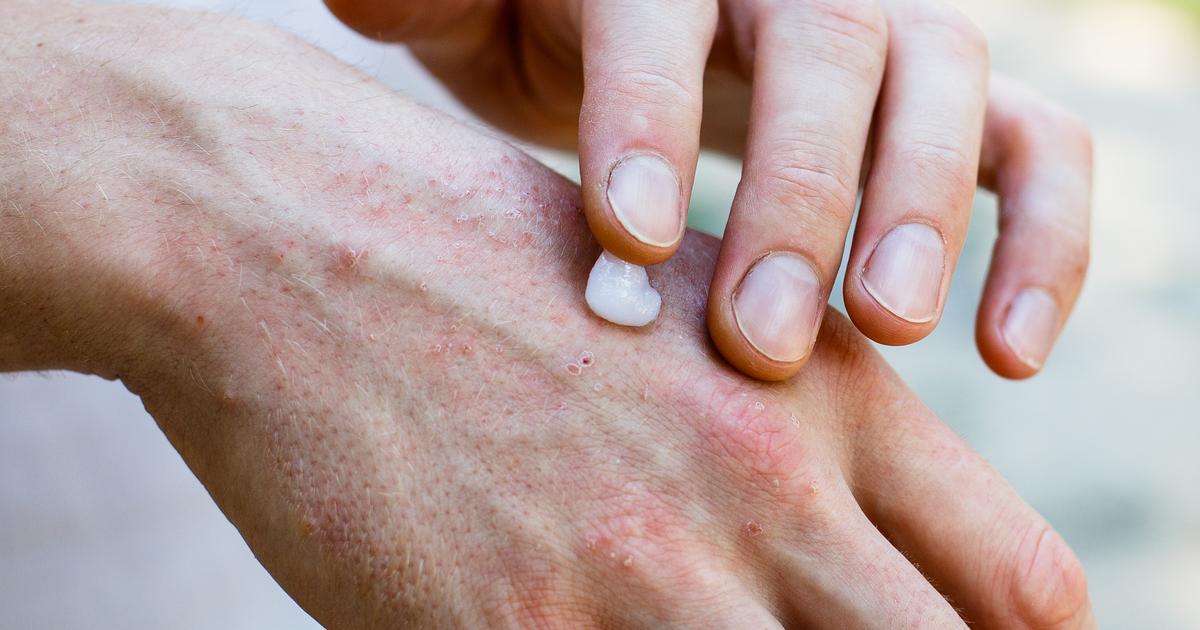
Some patients with damage to the skin could develop anhidrosis. For example, individuals who have burns or scars may notice these areas do not produce sweat, and anhidrosis is also common in patients who have had radiation therapy. Some surgical procedures carry the risk of damaging the sweat glands, and this is known to trigger anhidrosis. Diseases that clog the pores, including psoriasis, are recognized causes of the condition too. To minimize the risk of anhidrosis, patients having radiation therapy should ask their healthcare team about possible precautions to minimize skin damage. Individuals with conditions that affect the pores should also speak with their doctors about steps that might help reduce clogging. Patients with a burn may wish to go to an urgent care center so the burn can be properly evaluated and treated. Anyone who has any type of damage to the skin may want to consider visiting a dermatologist to investigate the latest treatment options as well.
Uncover more causes of anhidrosis now.
