Guide To The Most Common Autoimmune Diseases
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
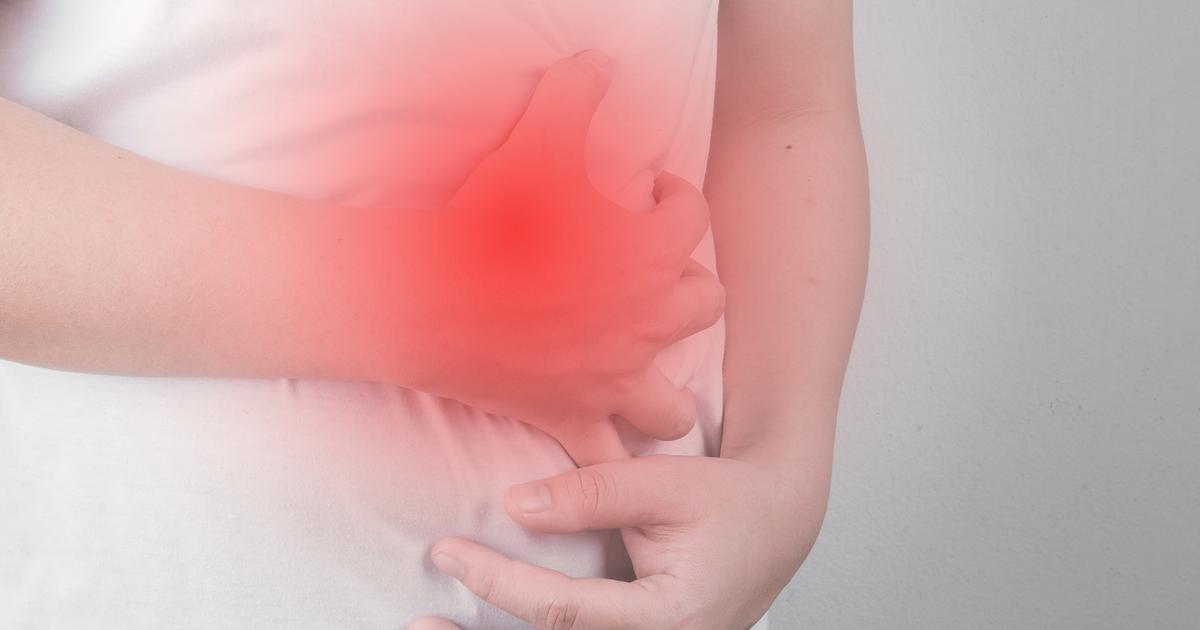
Inflammatory bowel disease is the umbrella term that refers to a group of disorders that cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract and organs. There are a few different types of inflammatory bowel disease, the most common of which are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Inflammatory bowel disease occurs when a trigger causes the affected individual's immune system to inappropriately produce antibodies programmed to destroy healthy intestinal tissues.
Both types of inflammatory bowel disease cause similar symptoms. Examples of these symptoms are fatigue, diarrhea, weight loss, blood in the stool, reduced appetite, fever, abdominal cramps, and abdominal pain. These symptoms vary depending on the location and severity of the inflammation. These conditions are diagnosed through blood and fecal occult blood tests, colonoscopy, and intestinal tissue biopsy. Additional tests that can help include flexible sigmoidoscopy, upper endoscopy, capsule endoscopy, and balloon-assisted enteroscopy.
Psoriasis
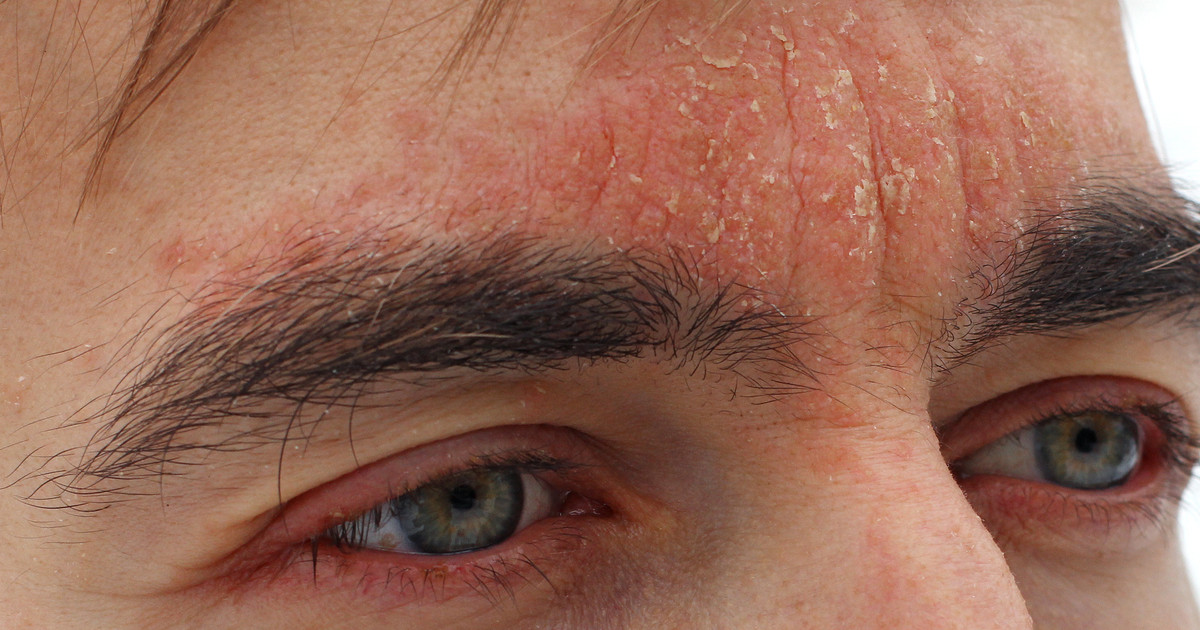
Psoriasis is a common skin condition. However, some individuals may not realize that it is an autoimmune disease, which means it is chronic. In addition, there is currently no known cure, though there are treatments. For reference, psoriasis causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, which often results in itchy and red scaly patches on the skin. The most common locations for these psoriasis patches are the scalp, elbows, knees, and trunk.
Besides the skin patches, patients often deal with stiff and swollen joints, cracked skin that can itch and bleed, as well as thickened or ridged nails. This condition has many triggers, including cold and dry weather, stress, infections, and certain medications. Treatments for psoriasis include corticosteroids, topical retinoids, salicylic acid, and light therapy.
