Important Symptoms, Stages And Treatment For Lyme Disease
Causes And Risk Factors For Lyme Disease
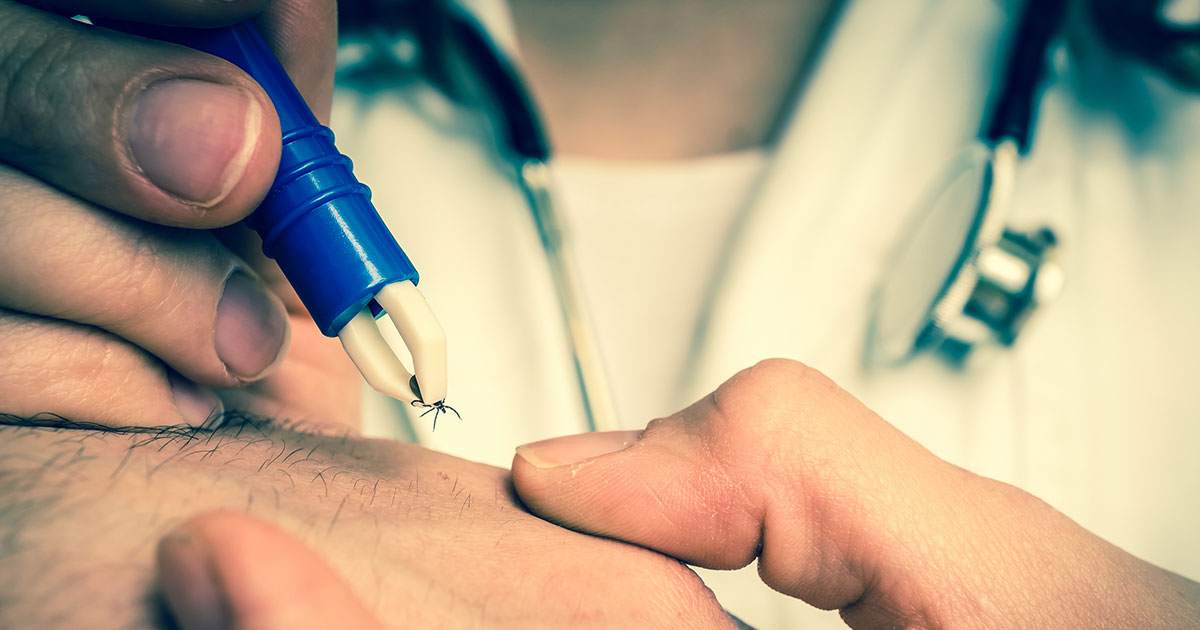
Lyme disease is an infectious disease spread from host to host through the bite of infected ticks. Ticks need blood to survive, so they attach themselves to hosts such as mice, deer, dogs, and humans to feed. Upon feeding on animals that are infected with the Lyme disease bacteria, ticks become infected, continuing to infect other animals and humans that they feed off of. In most cases, an infected tick must be attached for twenty-four hours before the bacteria can be transmitted.
Pets, particularly dogs, can increase the chance of being bitten by an infected tick, as they can carry the ticks into the home or yard.
Preventing Tick Bites And Lyme Disease

The best way to prevent Lyme disease and other bacteria caused illnesses, is by avoiding tick bites. Some ways to stay protected and to avoid tick bites while venturing into woodlands or forested areas include wearing light-colored long-sleeved shirts and pants and keep shirts tucked into pants and socks pulled over pant legs. Other ways to prevent getting bitten by ticks involves using bug spray containing DEET or Icaridin on clothing and skin, walking along cleared paths, showering within two hours after being outdoors, and doing a full-body check. If an attached tick is found, it is essential to remove it immediately with tweezers. It is also essential to check all outdoor gear and pets before returning home, as they could carry ticks inside the house.
