Guide To Effective Lung Cancer Diagnosis And Treatment
Radiation Therapy
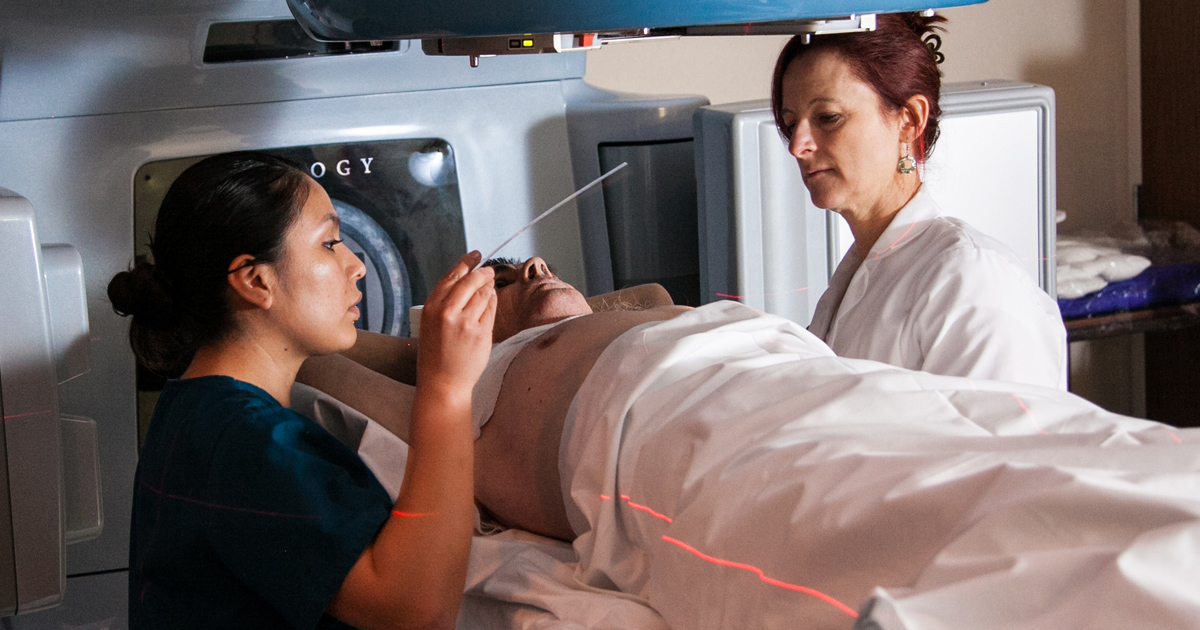
Radiation therapy uses concentrated beams or radioactive materials to destroy cancerous cells or stop them from growing. The most common form of radiation therapy used for lung cancer patients is referred to as external beam radiation. External beam radiation uses a large machine that aims the high-energy beams at the skin above the local area where the cancerous tissue is located. This is to minimize damage to healthy surrounding tissues.
Another form of radiation often used to treat lung cancer is brachytherapy. This form of internal radiation therapy uses a small quantity of radioactive material placed into the patient's airway close to the cancerous tissue. The pellets or seeds containing the radioactive substance are typically removed from the patient's body after a set amount of time. This is to allow the radiation to do damage and kill the malignant tumor cells.
Chemotherapy
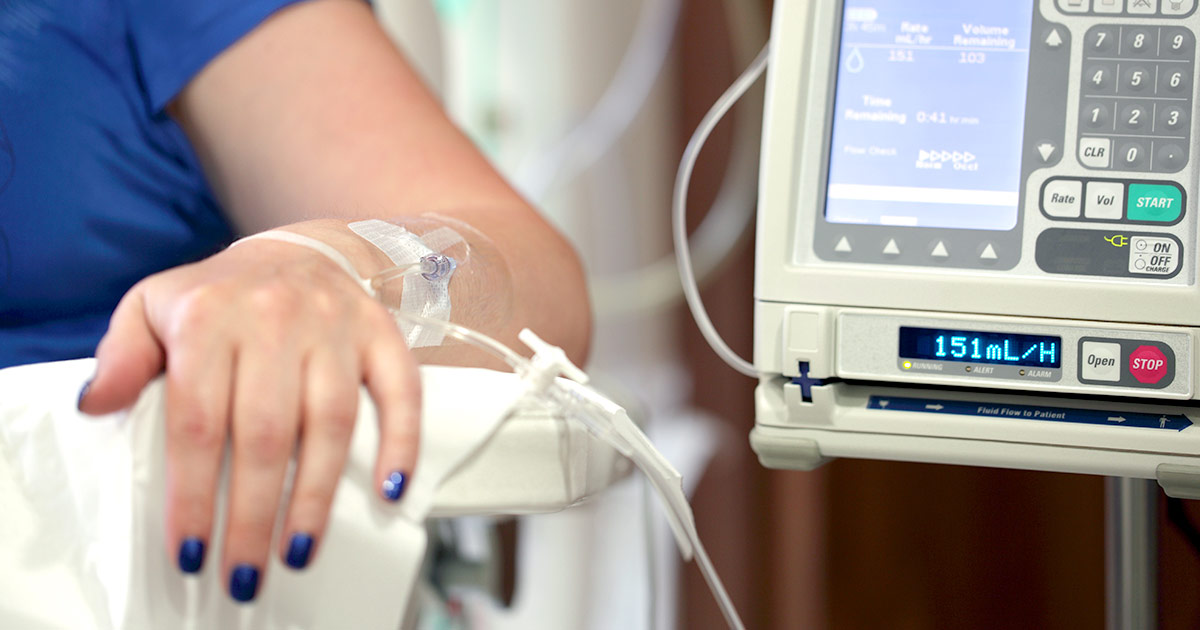
Chemotherapy refers to the use of a combination of potent medications to eliminate malignant cells in the body. This treatment works by targeting the cells in the body undergoing the cell division process and multiplying. Cancerous cells have specific characteristics where they grow faster, divide more often, and do not die at the same rate as healthy cells. Chemotherapy medications allow patients to take advantage of these properties of malignant cells because they are almost always in some stage of the cell division process.
Chemotherapy is typically administered intravenously through a vein in a chemotherapy clinic, medical office, or hospital setting. Some patients may need to receive chemotherapy through central venous catheters or central venous access devices. These devices offer a stronger and larger intravenous entry point than a traditional intravenous catheter. Chemotherapy may be administered independently in cases where the patient cannot undergo tumor excision surgery. In other cases, it can be combined with radiation therapy and surgical procedures.
