What Causes Myelopathy?
Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition in which the immune system attacks the membranes around the joints. This condition can be found in the hands, knees, hips, neck, and back. When it affects the membranes between vertebrae, it leads to constant inflammation and myelopathy. Unfortunately, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to permanent joint damage. Treatments for this condition are improving, but most of the focus is on controlling the symptoms, especially pain and joint damage.
In the early stages of this disorder, back pain can be relieved through self-care with ice packs, over-the-counter pain medication, and light stretching. In more serious cases, a surgical procedure may be recommended to reduce swelling. Because of the risks of back surgery, this procedure is normally reserved for patients whose quality of life has been compromised by the condition.
Spinal Stenosis
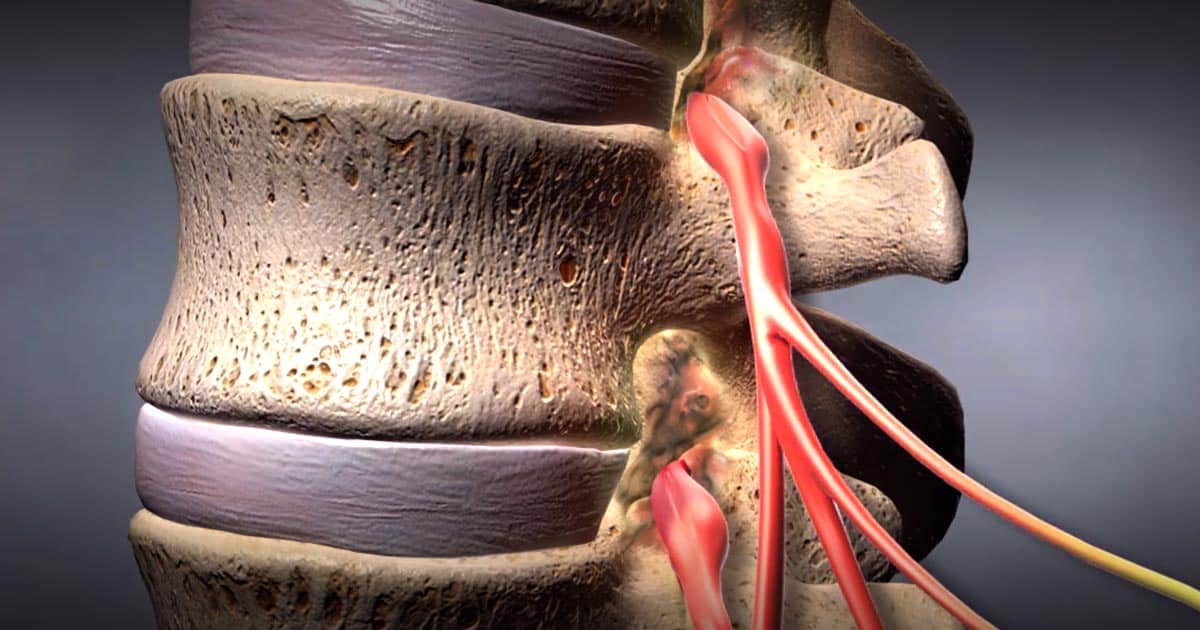
Spinal stenosis is a common cause of myelopathy in older individuals. This condition is most often found in the lower back and involves a narrowing of the spinal canal, the hollow tube within the vertebrae where the spinal cord is found. Because it typically involves thoracic myelopathy, spinal stenosis is marked by pain in the legs and difficulty with walking. It is frequently caused by osteoarthritis in the back, especially when there is a buildup of bone or bone spurs.
In the beginning, spinal stenosis is treated with physical therapy, stretching, and exercise. Symptoms get worse if the patient reduces the amount of daily activity. Cortisone injections can bring temporary relief for the pain of spinal stenosis. Back surgery to remove excess bone may be recommended, though this is normally done in more extreme cases due to the risks.
