What Is A Bitter Herb?
Although modern medicine has made leaps and bounds in advancements throughout time, the body is an incredible machine that can be healed and cared for with what Mother Nature provides us. Our ancestors even discovered some insights about how the human body reacts to natural medicines, and one of these was with the use of bitter herbs. Keep reading to reveal what a bitter herb is, how it heals and helps the body, and how to incorporate it into a healthy diet today.
What Is A Bitter Herb?

Bitters are plants with a sharp pungent taste or smell. Digestive bitters are within the category of plant stimulants and are far from the sweetest experience, and are likely disagreeable and harsh to many individuals' taste buds. The very word ‘bitter’ is even linguistically associated with expressions of anger, resentment, pain, and reactivity. Many may not be aware, but we may know some of these bitter herbs and might even use them in our daily lives. Some of the most common bitters include Barberry, Chamomile, Gentian, White Horehound, Wormwood, Goldenseal, Dandelion Root, Milk Thistle, Peppermint, and Yarrow to name a few.
How Do Bitters Work?
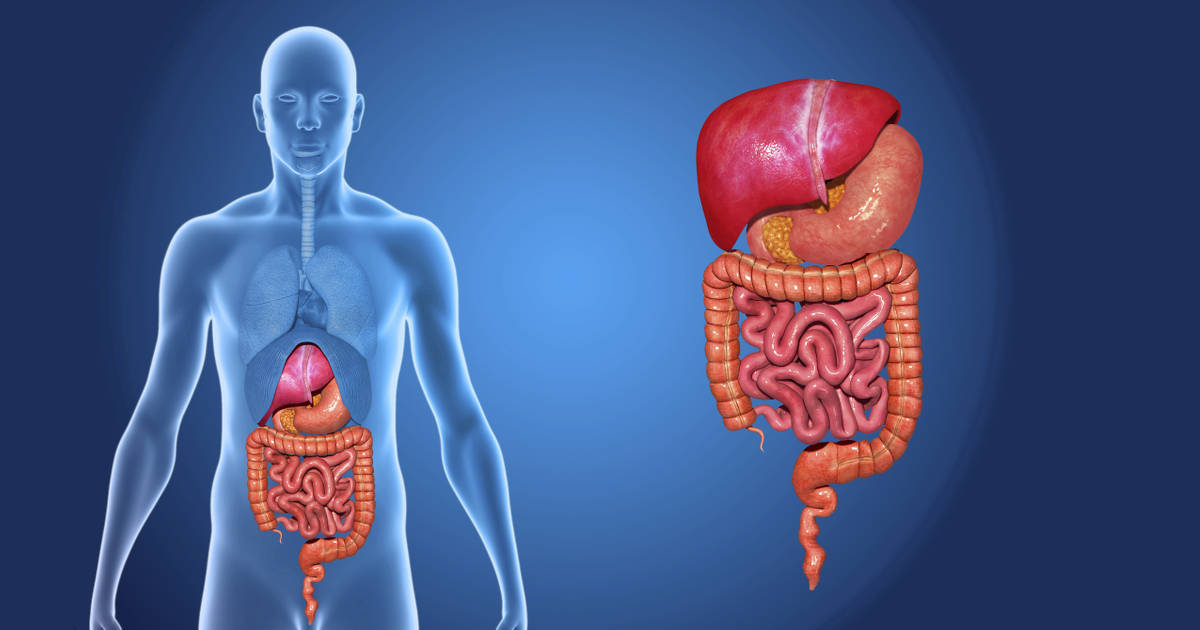
Bitters, as disagreeable as they may be, promote appetite and improve digestion. When a bitter hits our tongue, it is stimulated, and secretes digestive juices and stimulates the activities of the liver and pancreas. This is known as the "bitter reflex," that triggers specific actions in the body that prepares the digestive system for food. The taste of bitter alone stimulates the brain to release the digestive hormone, gastrin, which begins a chain reaction of neural and endocrine actions, such as appetite stimulation and the release of digestive enzymes. Hence, the reason why bitter flavored foods have a rich history in the healing arts.
