10 Key Facts About PolG Behind Frederik of Luxembourg’s Tragic Death
3. Diagnosis and Genetic Testing for PolG Disorders

Diagnosing PolG disorders can be a daunting task due to their diverse clinical presentations and overlap with other mitochondrial diseases. Genetic testing plays a pivotal role in confirming a diagnosis, allowing for the identification of specific POLG mutations. Next-generation sequencing technologies have revolutionized the field of genetic diagnostics, enabling the rapid and comprehensive analysis of the POLG gene and other related genes. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for managing PolG disorders, as it can inform treatment decisions and provide prognostic information. In addition to genetic testing, a thorough clinical evaluation is essential, often involving neurologists, geneticists, and other specialists. Biomarkers, such as elevated lactate levels in blood or cerebrospinal fluid, can also aid in the diagnostic process. Despite advancements in genetic testing, challenges remain, particularly in interpreting the clinical significance of novel or rare mutations. Continued research and collaboration among geneticists and clinicians are vital to improving diagnostic accuracy and outcomes for patients with PolG disorders.
4. The Pathophysiology of PolG Disorders
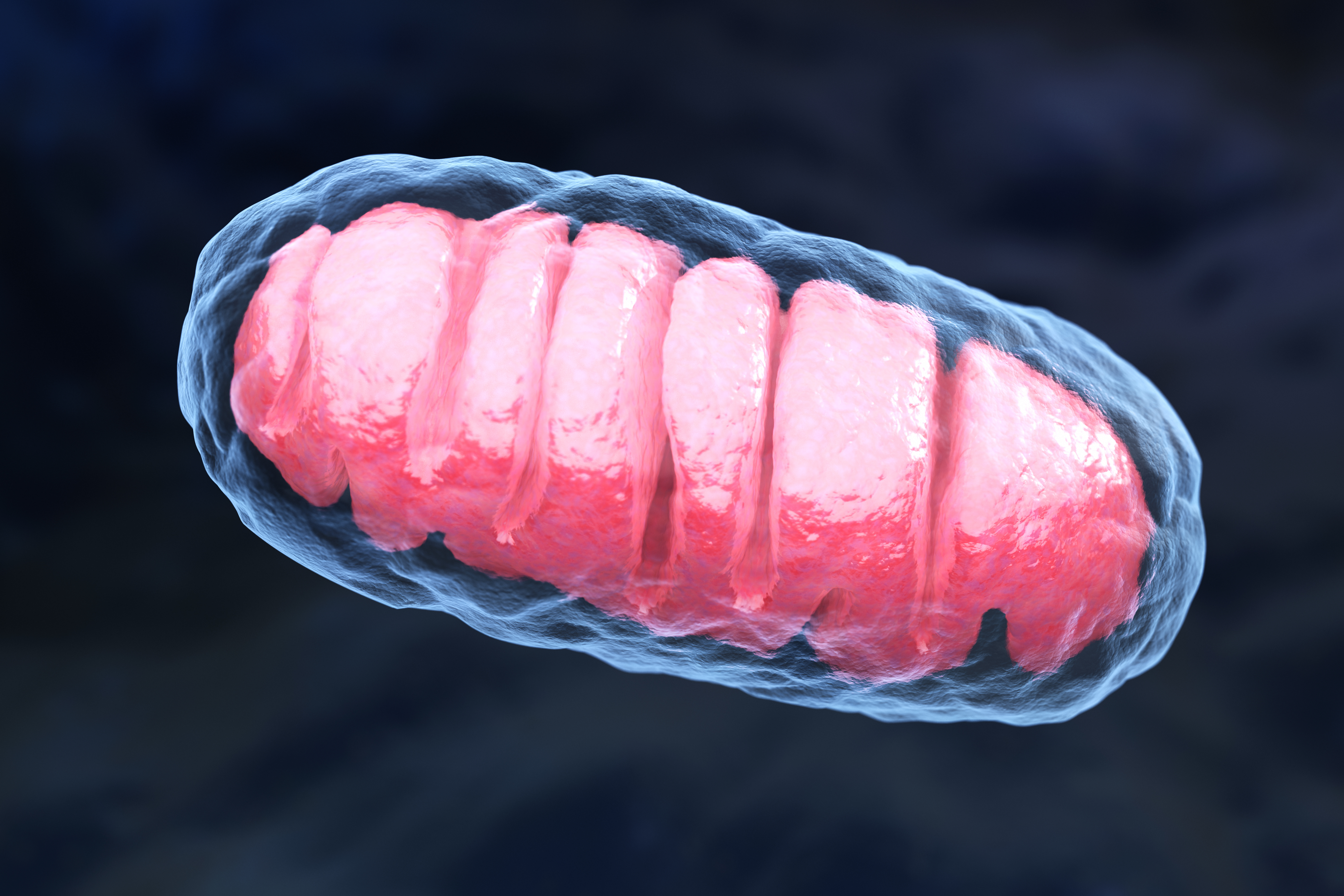
The pathophysiology of PolG disorders is rooted in mitochondrial dysfunction, which disrupts cellular energy production. Mitochondria are responsible for generating adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the cell, through oxidative phosphorylation. When POLG mutations impair mitochondrial DNA replication, it leads to a depletion of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) or the accumulation of mutations within mtDNA. This results in compromised mitochondrial function and reduced ATP production, affecting high-energy-demand tissues such as the brain, muscles, and liver. The accumulation of defective mitochondria can also trigger a cascade of cellular stress responses, including increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which further damage cellular components. Understanding the pathophysiology of PolG disorders is critical for developing therapeutic strategies that target the underlying mitochondrial dysfunction. Research efforts are focused on exploring potential interventions that can enhance mitochondrial function, reduce oxidative stress, and improve cellular energy metabolism.
