The Long-Term Effects Of Heavy Drinking
Dementia And Memory Loss

Heavy drinking over long periods can lead to a condition known as alcoholic dementia, which is most often associated with memory loss. And as a result, patients experiencing advanced dementia or memory loss typically lose their cognitive and learning skills. The reason behind this is because alcohol has a detrimental effect on brain cells resulting in temporary difficulty making decisions and poor judgment. Over time, as more and more brain cells are damaged, these temporary issues become permanent. Nutritional deficiencies, which are quite common in heavy drinkers, can also lead to brain cell damage resulting in dementia and memory loss.
Continue to learn more about the effects of drinking on the liver.
Fatty Liver Disease
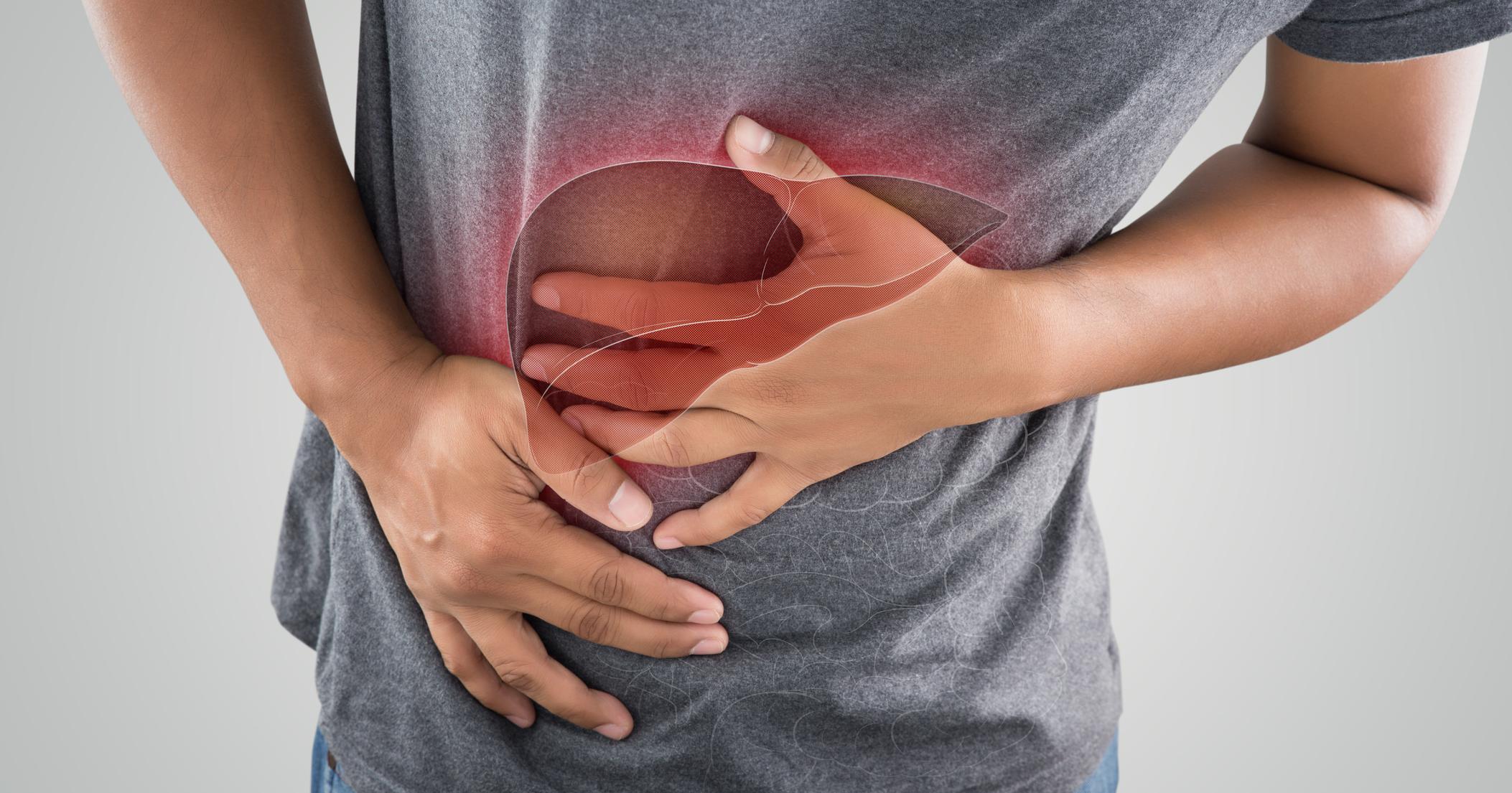
Fatty liver disease, medically known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition that can develop when excessive fat accumulates in the liver. Although it is normal for individuals to have small amounts of fat in their liver, large amounts can lead to serious health issues. While several things can lead to fatty liver disease, the most common cause is heavy drinking. Excessive drinking damages the liver, and as a result, the liver is unable to break up fat cells. If this occurs and heavy drinking continues, inflammatory alcoholic steatohepatitis often develops, which can lead to life-threatening cirrhosis of the liver.
Continue reading to learn about what serious condition heavy drinking is often linked to and how it increases an individual's risk.
