Treatments For Deep Vein Thrombosis
There are many reasons why individuals might experience deep vein thrombosis (DVT), including medical conditions, surgery, and not moving for long periods. Deep vein thrombosis happens when a blood clot forms in the deep veins in the body, usually in the legs. This condition can cause pain and swelling in the leg, but it is possible to have no symptoms. It can be very dangerous because part of the blood clot can break off and end up in the lungs, thus causing a pulmonary embolism, which can lead to death. It is critical for a patient with DVT to get medical attention. There are several methods to treat and prevent deep vein thrombosis. Learn about them now.
Blood Thinning Medication
If diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis, there are blood thinning medications available to help control the clot without any of it breaking off. The medications used are called anticoagulants, and they help stop the clot from growing, though they do not dissolve the clot. Using the medications properly will help patients avoid some of the complications of surgery, including bleeding problems. Many drugs are considered blood thinning medications, even though they do not actually thin the blood. If an individual in the hospital, heparin is the most common drug administered. This is given through a shot in the abdomen on a daily basis.
After leaving the hospital, or if diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis, medication will be in pill form and must be taken daily. A patient needs to work with their doctor to determine which medication will be right for them. Some medications come with warnings about what kinds of foods to avoid and other precautions. As with any medicine, it is crucial to take any medication given as directed and report any complications because there may be a better choice of medication for individual patients.
Compression Socks
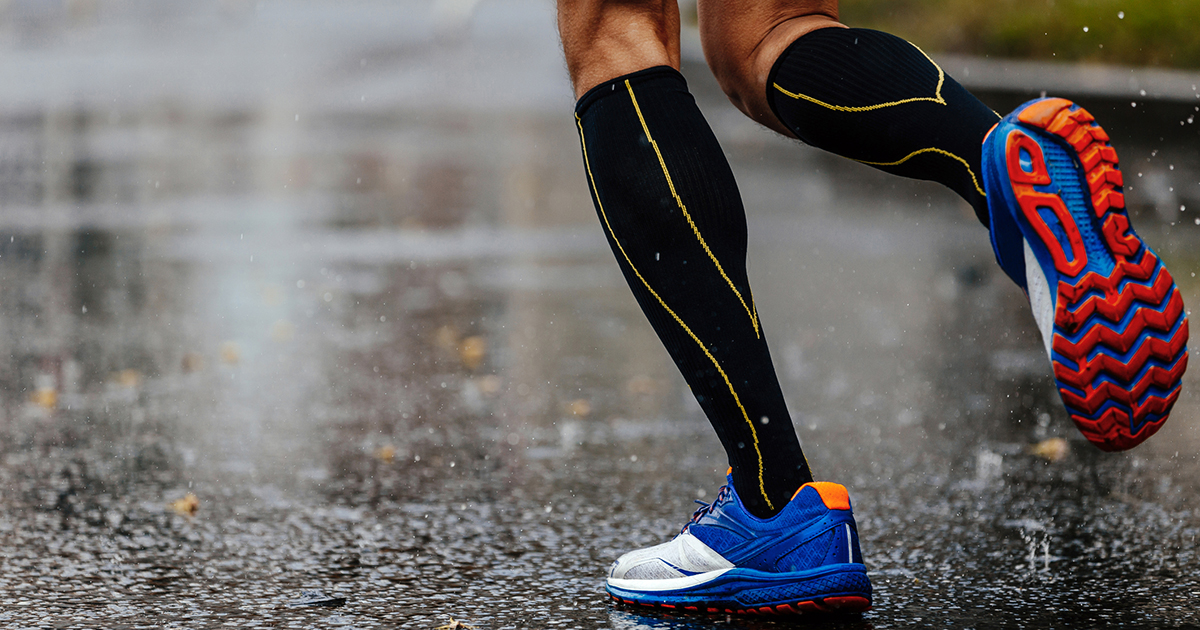

It is vital to wear compression socks to prevent and treat deep vein thrombosis, particularly after surgery. These are special stockings that squeeze the ankles, calves, and sometimes thighs. The way they work is by being tighter around the ankles, which pushes up fluid in the leg. This pressure allows blood to flow freely and prevents any pooling of blood that can cause a clot. If the compression socks are not worn, there is a higher chance of deep vein thrombosis, which will cause the leg to swell, hurt, and feel warm to the touch. Patients who are told to wear these stockings must wear them all day and then take them off when heading to bed. Unless advised, compression socks should not be worn at night because they can cut off blood flow in the leg. If you need to wear compression socks, know they are designed to be used when awake and moving. When sleeping, there is generally not a need to push fluid up the leg because there is no gravitational resistance when lying down.
Regular Doctor Visits
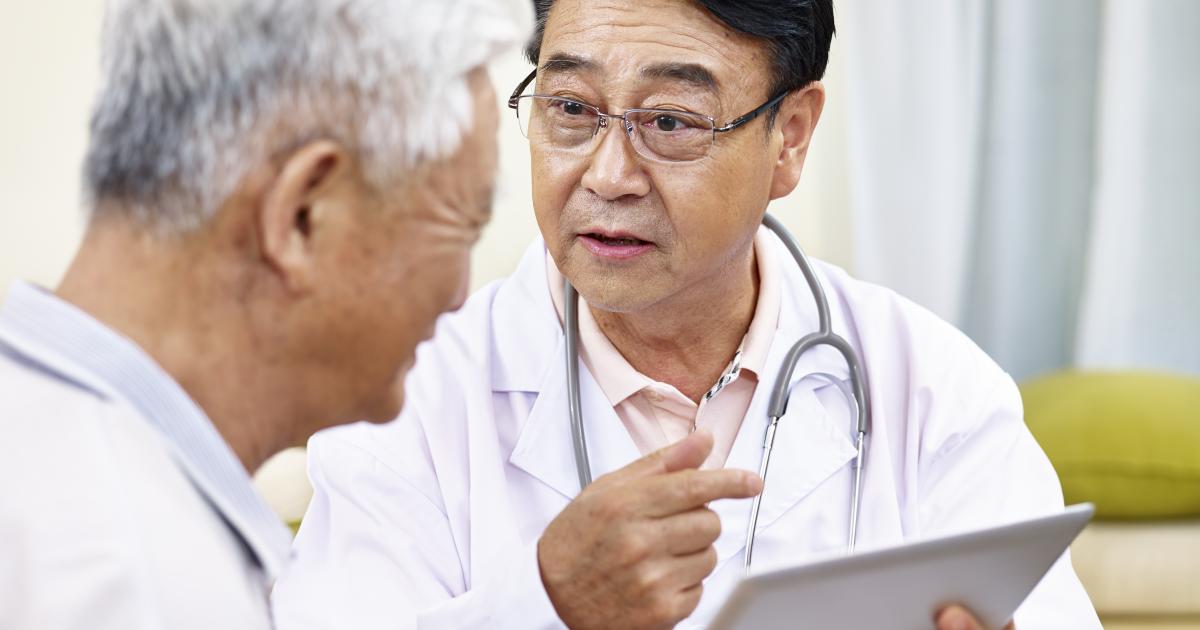

If a patient is diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis, it is critical to maintaining regular doctor visits. If they are prescribed medication, there may be a need to get routine blood tests to make sure the medication is at the appropriate levels. One of the most common medications for DVT is warfarin, though new medications have come on the market that do not necessitate getting blood tests or changing the dosage. Visits with the doctor will allow patients to express any complications they may be experiencing and get their questions answered. It will allow them to head off any issues they have and let the doctor alter the treatment plan if the current one does not seem like it is working effectively. By seeing the doctor on a regular basis, patients can keep up to date on new treatments and alternative treatments. If the blood clot does not dissolve or becomes larger, the doctor may need to be more aggressive with treatment. But, if patients do not go to see them regularly, the blockage may go untreated and end up in an emergency.
Clot-Busting Medication
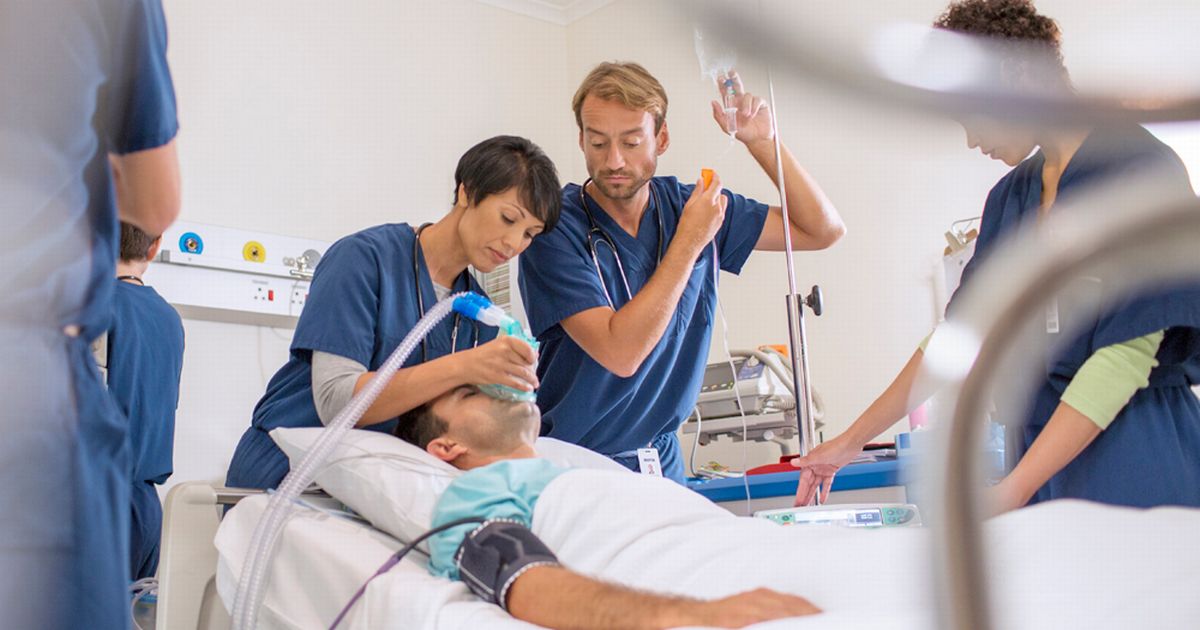

Clot-busting medication must be administered directly to the blood clot. This is achieved by going to the hospital and having a catheter inserted into the vein. The doctor will fish the catheter into DVT and send the drug directly into it, thus breaking up the clot. Additionally, the doctor can widen the vein using a stent or balloon angioplasty to help prevent clots in the future. This measure is sometimes risky, as it could cause part of the clot to break away and travel to another area of the body or it could cause bleeding problems. However, if a patient has a large blood clot, using the clot breaking procedure might be what is best because the benefits outweigh the risks. Furthermore, doctors can insert a filter that will prevent pieces of the clot from traveling to other parts of the body and causing damage that will necessitate other medical procedures to save the patient's life.
Monitor For Excessive Bleeding
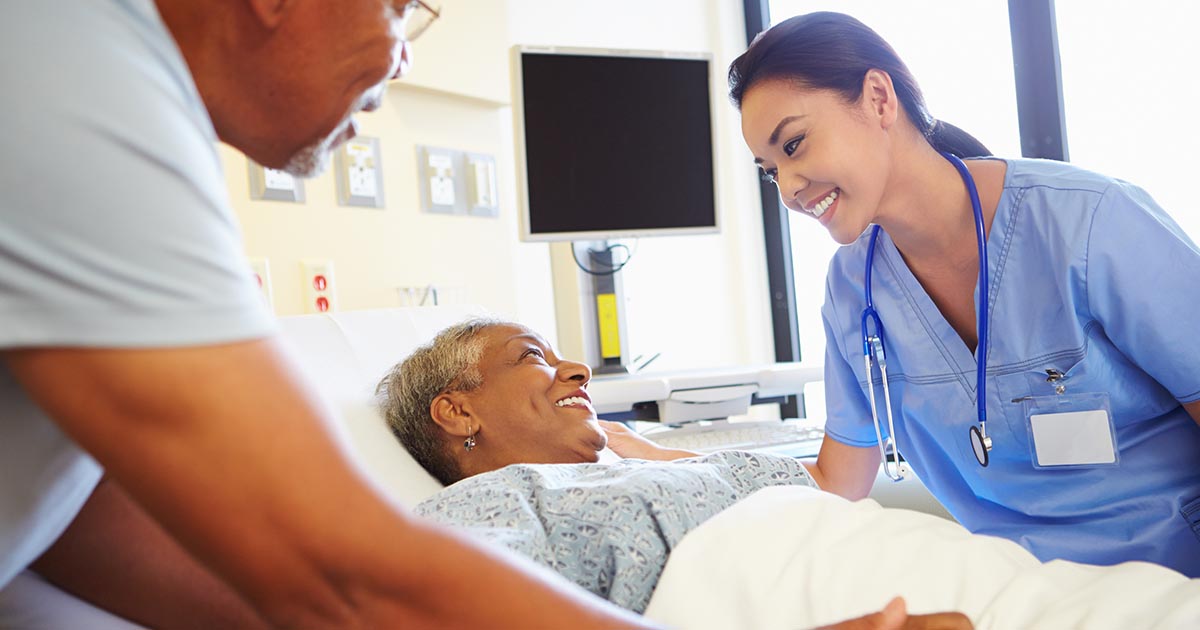

If a doctor monitors patients for excessive bleeding, they can help prevent clots from forming. Blood clots form in the deep veins in the limbs. So, if patients are subject to any of the conditions that can cause excessive bleeding, the doctor can monitor them and their symptoms so deep vein thrombosis is diagnosed as early as possible. With early diagnosis, more options for treatment are available. For instance, if a patient had surgery, they should be closely monitored for excessive bleeding that might cause DVT. Additionally, prophylactic measures, like compression socks and blood thinners, should be used to head off the possibility of developing deep vein thrombosis. This gives patients the best chances of eliminating the complications that can come along with developing a blood clot. Any way to prevent a life-threatening event should be taken.
