Important Information To Know About Liver Cancer
The liver plays an important role in the body because all blood in the system passes through it. While acting as a filter for blood, it has several functions, including eliminating toxins and converting nutrients into useful forms. When cancer cells are in the blood, the liver is an easy target for infestation. As a result, many individuals acquire liver cancer metastatically after it spreads from other areas, although it can also originate in the liver itself.
Symptoms
Symptoms of liver cancer are similar to other medical conditions and other forms of cancer as well, so it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Often in the early stages of liver cancer, symptoms are not present, but later they will often include abdominal pain, bloating, a lump in the abdomen around the liver, a full feeling like after consuming a large meal (but without consuming a large meal), weight loss, fatigue, weakness, nausea and vomiting, jaundice, light-colored feces, dark urine, and fever. These symptoms can lead to serious conditions, and early diagnosis of liver cancer is critical for treatment and survival.
Cancer Stages
The staging of liver cancer is based on how much the disease has spread both within the liver as well as if it has invaded other parts of the patient's body. Liver cancer has the potential of spreading to the individual's lungs, bones, and lymph nodes. If liver cancer does happen to spread to any of these parts, and a new tumor affects another area of the body, it does not take on a new name (e.g. liver cancer that has spread to the lungs is not called lung cancer) and it is not referred to as two separate types of cancer, because the abnormal cells are the same cancerous ones found in the liver. Instead, it is called metastatic liver cancer and treated in a similar way, though often with more aggressive approaches.
Benign And Malignant
Abnormal growths in the liver are categorized as either benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous). Benign forms of cancer rarely pose a threat, and thus, they typically do not need to be treated, though they can be removed as a precaution to avoid potential future health issues, cancer-related or not. Benign forms can include hemangioma, hepatic adenoma, focal nodular hyperplasia, cysts, lipoma, fibroma, and leiomyoma. Malignant liver cancer includes hepatocellular carcinoma, primary liver cancer, and cholangiocarcinoma, cancer affecting the bile ducts. Hepatoblastomas are rare childhood malignant tumors. Malignant tumors are categorized as primary and secondary, according to their cause, size, and other factors.
Aflatoxin Exposure

While there are numerous chemicals and toxins that will increase the risk of a wide range of different cancers, among the most common risk factors for liver cancer is aflatoxin exposure. Aflatoxins are substances known to cause cancer and are created from a fungus that can contaminate a variety of different foods like wheat, peanuts, corn, soybeans, rice, and ground nuts. As with most types of fungus, the aflatoxin fungus can grow on these foods when they are stored in a warm and moist environment, which makes it particularly common in warm or tropical countries.
Both the United States and Europe are required to test foods to check the levels of aflatoxins. As such, it's important for individuals to minimize their consumption of these foods if they're visiting a warmer country outside of the United States or Europe. With long-term exposure to aflatoxins, the chances of an individual suffering from liver cancer will greatly increase. This risk goes even higher when aflatoxin exposure is combined with the development of a hepatitis B or C infection.
Hemochromatosis

Hemochromatosis is an inherited metabolic disease that can possibly lead to cirrhosis and eventual liver cancer. When affected by this hereditary condition, the individual's body will absorb too much iron from the food they eat. This iron will settle in various tissues around the body, which includes the liver. While this likely doesn't sound too harmful, the buildup of iron within the liver increases the likelihood an individual will develop cirrhosis, dangerous scarring of the liver that can bring about liver failure and liver cancer.
The main symptoms of hemochromatosis include abdominal pain, fatigue, joint pain, and general weakness. When this condition has progressed to a later stage, you might experience such symptoms as diabetes, impotence, heart failure, and liver failure. If treated early enough, it's possible to prevent damage to the liver as well as liver cancer.
Wilson's Disease

There are a variety of very rare diseases known to substantially increase the risk of liver cancer, the primary of which is Wilson's disease. This is a rare kind of inherited disorder that leads to the accumulation of copper within the brain, liver, and other organs. If an individual is affected by this condition, it's likely they will be diagnosed with it between five and thirty years old. While copper plays an important role in an individual's ongoing health, any excess amounts of copper are supposed to be excreted from the bile in their liver.
When affected by this disease, the patient's body will be unable to eliminate copper properly, which means it will instead accumulate in the body and eventually cause many harmful complications. If this disease is caught early enough, the treatment options available to patients should greatly reduce the potential complications and may allow them to lead a normal life free from liver cancer.
Chronic Hepatitis B Or C Infection
A chronic hepatitis B or C infection always heightens the risk of an individual suffering from liver cancer. As mentioned earlier, hepatitis B and hepatitis C are infections that can develop from a contaminated needle, because of unprotected sex, or during childbirth. These liver infections will heavily damage the overall condition and function of an individual's liver, which will invariably put the patient at a greater risk of developing liver cancer. Keep in mind hepatitis B can't be wholly cured.
On the other hand, it's possible to get rid of a hepatitis C infection. In order to reduce the possibility of suffering from hepatitis B, it's important that all children and adults obtain the HBV vaccine, which will automatically lower their risk of hepatitis B and liver cancer. Currently, there's no vaccine available for hepatitis C. Early treatment of hepatitis C will oftentimes eliminate the virus altogether. As for hepatitis B, certain medications can reduce symptoms and lessen the likelihood of liver cancer.
Diagnosis
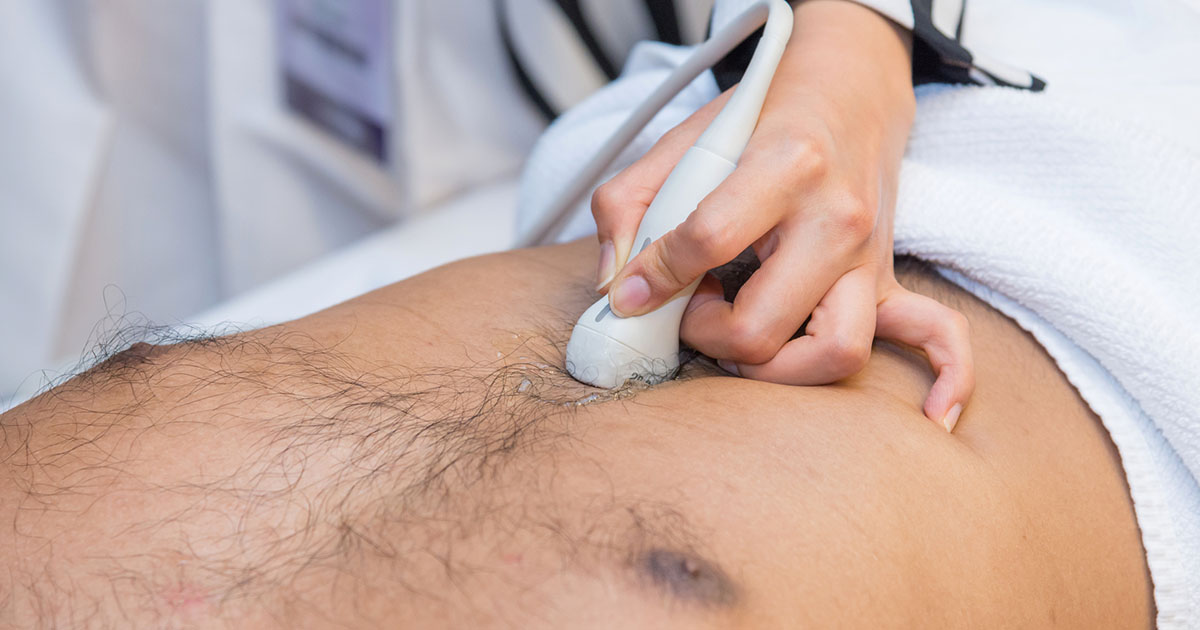
When symptoms arise, a proper diagnosis can be made and is accomplished in several different manners. Blood tests measure the levels of alfa-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin, both of which, if elevated, is cause for concern. CT scans, ultrasounds, and MRIs allow doctors to see any abnormalities in the liver in addition to other body parts through medical imaging. These imaging tests are particularly important when determining whether liver cancer has spread to other parts of the body. A liver biopsy involves the examination of a small sample of the suspicious tissue, but comes with the risk of bleeding, infection, and spreading of potentially infected cells.
Treatment
Traditional treatment options depend on the stage of liver cancer and the overall health of the patient’s liver. Surgery can remove a tumor on the liver if it is small and can have risks. A liver transplant is often necessary when a small tumor is not able to be removed, and the liver is severely scarred. Ablation therapy is the process of killing cancer cells by heat, laser, or specific substances and embolization denies cancer of blood needed for its survival.
The most common treatments for cancer, including liver cancer, are chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In many cases, these treatments are used in conjunction with others for the best results. For instance, chemotherapy or radiation might be used prior to surgery to shrink a tumor as much as possible, in an effort to make the surgery go easier.
Alternative Treatments
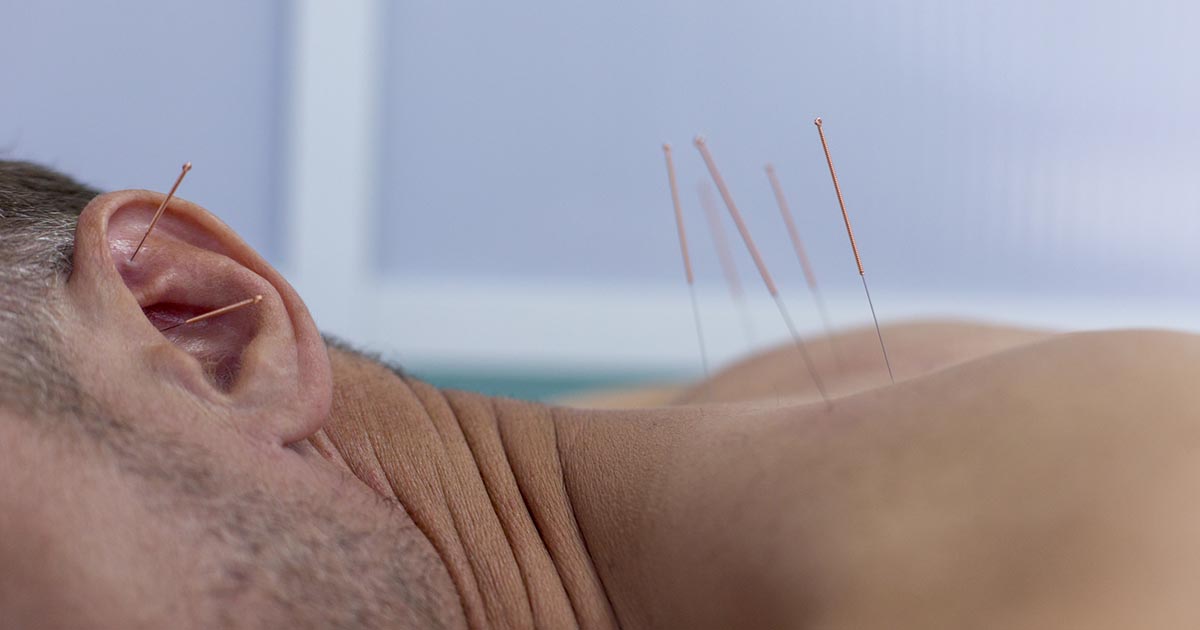
In the medical field, there are not yet any naturopathic treatments approved for the treatment of liver cancer, but some complementary therapies might help patients undergoing conventional treatments for their liver cancer. Acupuncture has been shown to help with side effects, such as nausea and vomiting, associated with chemotherapy and similar cancer treatments. Milk thistle is a herb with a history linked to liver health and mistletoe has been used as an herbal remedy on many occasions as well. Of course, when looking at any alternative treatments, liver cancer patients should always discuss anything they might wish to try with their primary doctor before taking any action to reduce interactions and unwanted effects.
Nutrition

As with all illnesses, it is important for individuals with liver cancer to maintain a healthy eating plan to help during their treatment and recovery. Getting adequate vitamins and minerals is accomplished best through food, and patients must meet caloric needs with a balanced diet. When nausea and vomiting prevent challenges, a dietitian or health care provider can help by providing suggestions and advice on how to remain healthy through nutrition. Weight and energy levels are often monitored and accessed. Good nutrition not only puts the body in its optimum working condition, but it also helps with treatment tolerance, which is crucial as some treatments for liver cancer can be quite harsh.
Pain Control

Liver cancer and its subsequent surgery or therapy may cause the patient considerable pain, so it is important to use the appropriate safety measures to manage any discomfort. Pain medication with advice from a doctor can help, and although side effects include fatigue and constipation, they can be remedied. Radiation acts to reduce the severity of liver cancer, such as by reducing the size of a tumor on the liver, and therefore can minimize associated pain. Certain kinds of injections can help manage pain associated with liver cancer by blocking nerve function in the abdomen. Natural methods of pain relief for liver cancer patients include relaxation, massage, and acupuncture.
Prognosis

The outcome of liver cancer depends largely on the stage at which the cancer was caught, and from there what treatment options are available and recommended to the patient in question. Other factors include if the disease has metastasized to other parts of the body (and the extent of this as well as what other parts are affected), the size and number of tumors, and the health of the liver and surrounding abdominal tissues. According to the American Cancer Society, there is a fifteen percent average five-year survival rate for all stages of liver cancer. This number, however, varies among patients and the stage of their cancer.
Prevention Tips

While it's very difficult to prevent most cancers from developing in the body, it's possible for individuals to lower their risk of liver cancer by following some standard guidelines and prevention tips. The main focus they'll need to have to prevent liver cancer is to avoid being exposed to the known risk factors. For instance, the most notable risk factor associated with liver cancer is a chronic infection that has occurred from either hepatitis B or hepatitis C, which are typically spread via contaminated needles or unprotected sex.
Additional prevention tips to follow include limiting tobacco and alcohol use, losing excess weight, limiting exposure to harmful chemicals, and treating inherited diseases that can increase the risk of liver cancer. When an individual is obese, they are more likely to suffer from fatty liver disease or diabetes, both of which are linked to liver cancer. When individuals drink too much alcohol, they put themselves at risk of developing cirrhosis, which is a severe condition in the liver that may eventually turn into liver cancer.
