12 Warning Signs of a Staph Infection — Don’t Wait!
In the intricate tapestry of human health, our skin serves as both a shield and a canvas, silently whispering tales of our well-being. Among the myriad of stories it tells, the subtle signs of a staph infection are particularly crucial to decipher. Staphylococcus aureus, commonly known as staph, is a bacterium that resides harmlessly on the skin and in the nose of many individuals. However, when it breaches the skin barrier, it can lead to infections ranging from mild to life-threatening. This article meticulously explores the top 12 red flags of a staph infection, signs that often go unnoticed until they escalate into serious health concerns. By understanding these silent whispers, we empower ourselves to act swiftly, ensuring that our skin remains a vigilant guardian of our health.
1. Understanding Staph Infections: The Basics

Staph infections are caused by the Staphylococcus bacteria, with over 30 types identified, though Staphylococcus aureus is the most common culprit. These bacteria can cause a variety of infections, from minor skin issues to severe diseases like pneumonia, endocarditis, and sepsis. The bacteria can enter the body through cuts, abrasions, or other breaks in the skin, leading to localized infections or, in severe cases, systemic infections. Understanding the nature of these bacteria is crucial, as it provides insight into how they operate and why certain symptoms manifest. With a deeper comprehension of staph infections, individuals can better recognize the red flags that indicate when a harmless skin resident turns into a formidable foe.
2. The First Red Flag: Unexplained Skin Irritation
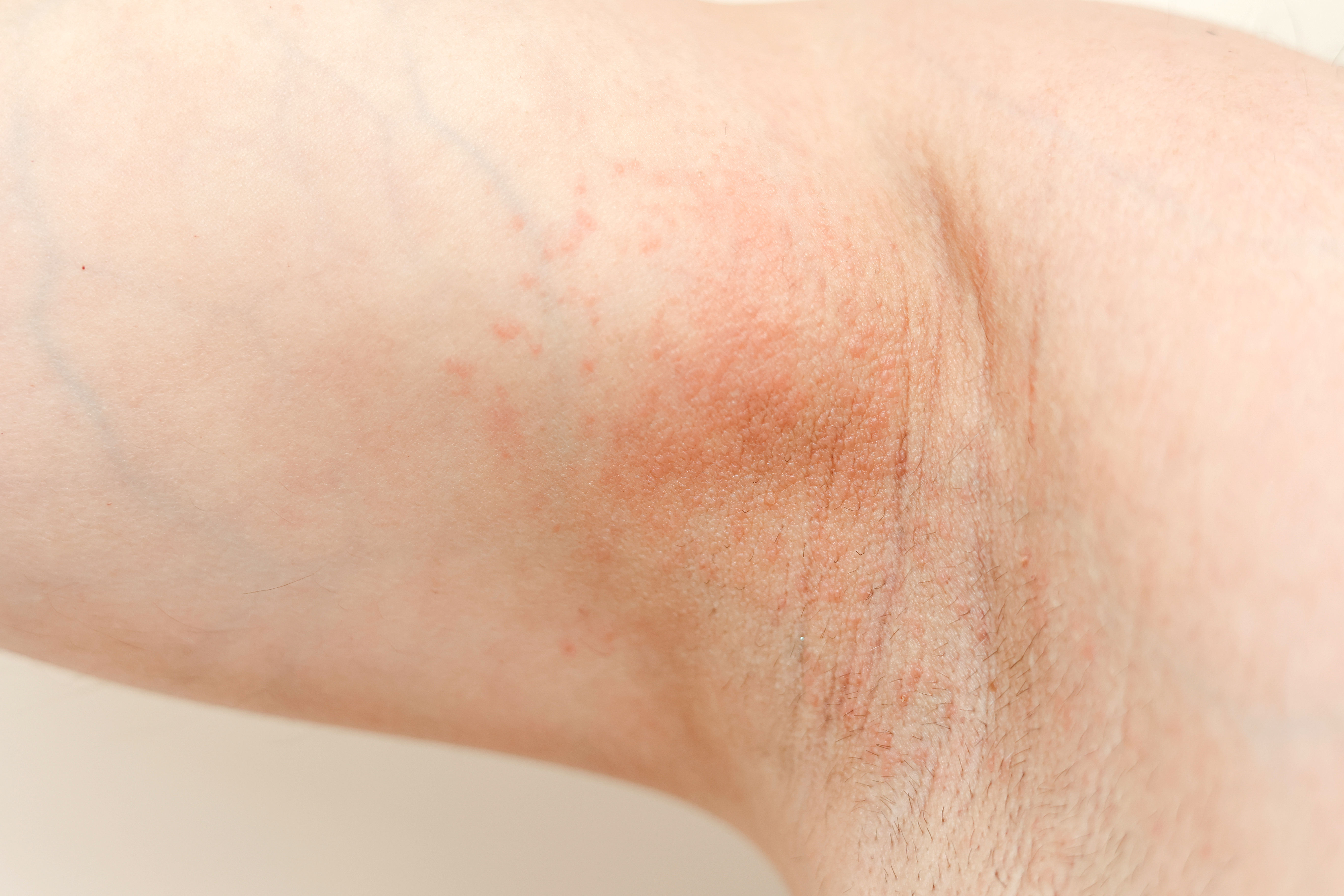
One of the earliest signs of a staph infection is unexplained skin irritation. This irritation often presents as redness, warmth, and swelling in a localized area and may be mistaken for an allergic reaction or insect bite. Unlike other irritations, this redness often intensifies, and the area may become increasingly tender to the touch. Such symptoms are the skin's way of signaling that something is amiss beneath the surface. Recognizing this red flag early can prevent the spread of the infection and avoid more severe complications. It is essential to monitor any persistent or worsening irritation, particularly if it is accompanied by other unusual symptoms.
3. Painful Boils and Abscesses: A Common Indicator
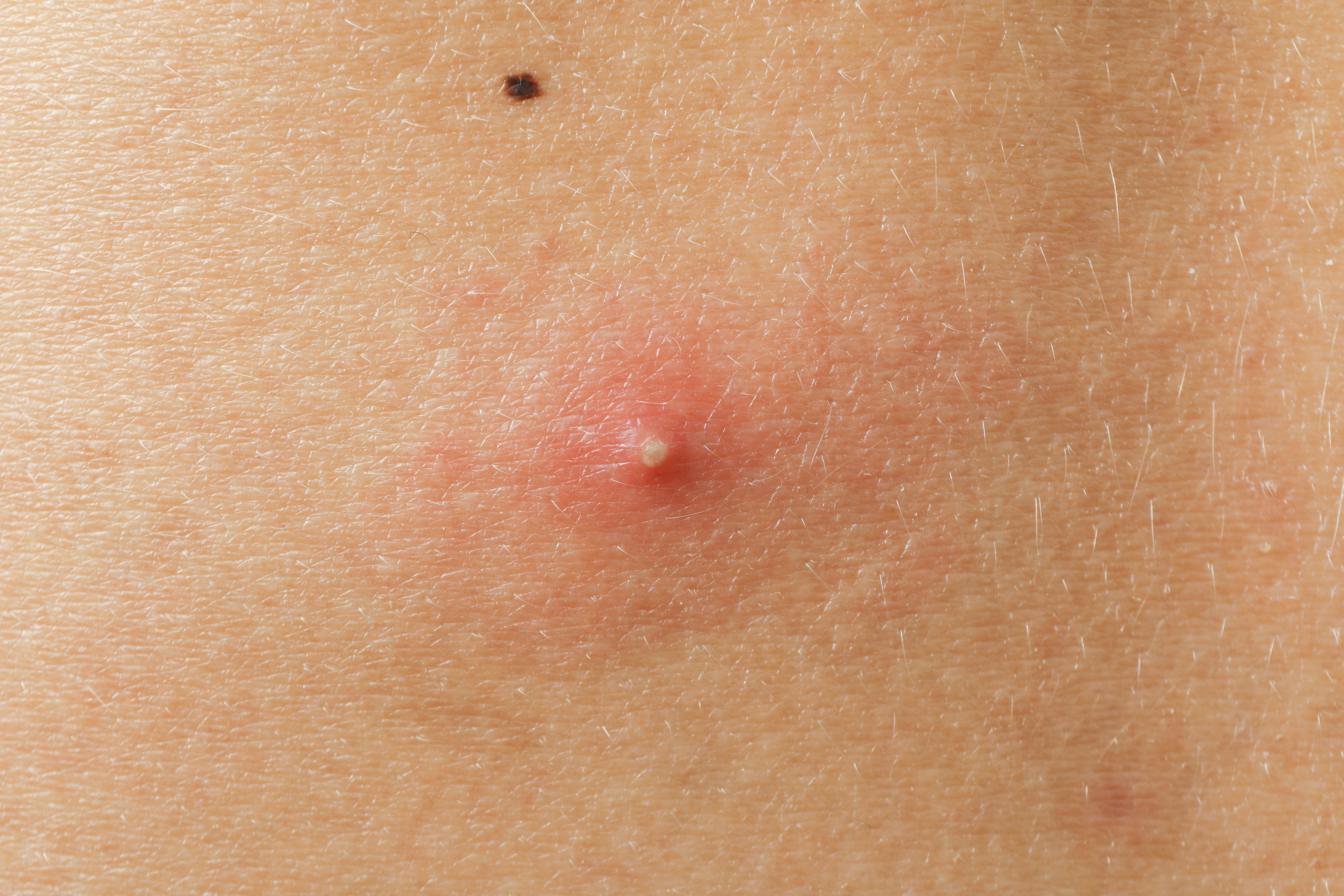
Boils and abscesses are common indicators of a staph infection. These painful, pus-filled lumps can form on any part of the body but are most frequently found in areas prone to friction and moisture, such as the armpits, groin, and buttocks. Boils begin as a red, tender bump that quickly fills with pus, growing larger and more painful. An abscess is a deeper infection that may require medical intervention to drain. These symptoms occur as the body attempts to isolate the infection, creating a barrier of pus. Early recognition and treatment of boils and abscesses are crucial in preventing the spread of the infection to other parts of the body or into the bloodstream.
3. Cellulitis: The Underestimated Threat

Cellulitis is a serious bacterial skin infection that often results from a staph infection. It appears as a red, swollen area that feels hot and tender, spreading rapidly if not treated promptly. Unlike superficial infections, cellulitis penetrates deeper into the skin and underlying tissues, posing a significant risk if left unchecked. This condition can lead to severe complications, including the spread of bacteria to the bloodstream or lymph nodes. Recognizing the symptoms of cellulitis, such as fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes, in conjunction with skin changes, is critical. Immediate medical attention is necessary to prevent the infection from becoming life-threatening.
4. Impetigo: A Contagious Concern

Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection commonly caused by staph bacteria, particularly affecting children. It is characterized by red sores that quickly rupture, ooze for a few days, and then form a honey-colored crust. These sores usually appear around the nose, mouth, hands, and feet but can spread to other areas through contact. Impetigo can be easily spread in crowded settings or through close contact, making it a public health concern. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is essential to prevent the spread of the infection to others and to avoid potential complications such as kidney inflammation.
5. Folliculitis: The Hair Follicle’s Hidden Struggle

Folliculitis is an infection of the hair follicles, often caused by staph bacteria. It presents as small, red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles, which can be itchy, sore, or filled with pus. While folliculitis is generally a mild infection, it can lead to more serious skin infections if not treated properly. The condition can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows, but it is most common on the scalp, face, chest, back, buttocks, and legs. Understanding the signs of folliculitis and seeking appropriate treatment can prevent the infection from worsening or spreading.
6. Fever and Malaise: Systemic Red Flags

Fever and malaise are systemic symptoms that often accompany more severe staph infections. When the body detects an infection, it raises its temperature to create an inhospitable environment for bacteria, resulting in fever. Malaise, a general feeling of discomfort or unease, often accompanies fever, signaling that the body is fighting an infection. These symptoms, when combined with localized skin changes, are significant red flags that a staph infection may have spread beyond the skin. Monitoring these symptoms and seeking medical advice can prevent complications such as sepsis, a potentially life-threatening response to infection.
7. Lymphangitis: The Pathway of Infection

Lymphangitis, an infection of the lymphatic vessels, can occur when a staph infection spreads. It is characterized by red streaks extending from the site of infection toward the lymph nodes, often accompanied by fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes. These red streaks indicate that the infection is advancing along the lymphatic system, a network that helps the body fight infections. Lymphangitis is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention to prevent the infection from reaching the bloodstream. Recognizing the symptoms of lymphangitis is crucial for preventing severe complications and ensuring timely intervention.
8. Recurring Infections: The Warning of an Underlying Issue

One of the most concerning signs of a staph infection—often overlooked until patterns emerge—is recurrence. If skin infections keep returning, especially in the same area, it may indicate an unresolved internal issue or a colonization of Staphylococcus aureus on the skin or nasal passages. These repeated outbreaks can be triggered by a weakened immune system, chronic skin conditions, or insufficient treatment of the original infection. In some cases, close contacts may be asymptomatic carriers, leading to a cycle of reinfection. Persistent or recurrent staph infections should never be dismissed—they warrant a thorough medical evaluation to identify root causes, assess antibiotic resistance, and implement long-term prevention strategies. By recognizing recurrence as a red flag, individuals can interrupt this cycle before it escalates into more serious health risks.
9. Toxic Shock Syndrome: A Rare but Serious Complication
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a rare but life-threatening complication of staph infections. It is caused by toxins produced by certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus and can develop rapidly. Symptoms include high fever, low blood pressure, rash, confusion, and organ failure. TSS is most commonly associated with the use of superabsorbent tampons but can also occur from skin infections, surgical wounds, or other sources. Early recognition of TSS symptoms is critical, as the condition requires immediate medical treatment to prevent severe complications or death. Understanding the connection between staph infections and TSS can aid in prompt diagnosis and intervention.
10. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA): The Resistant Strain
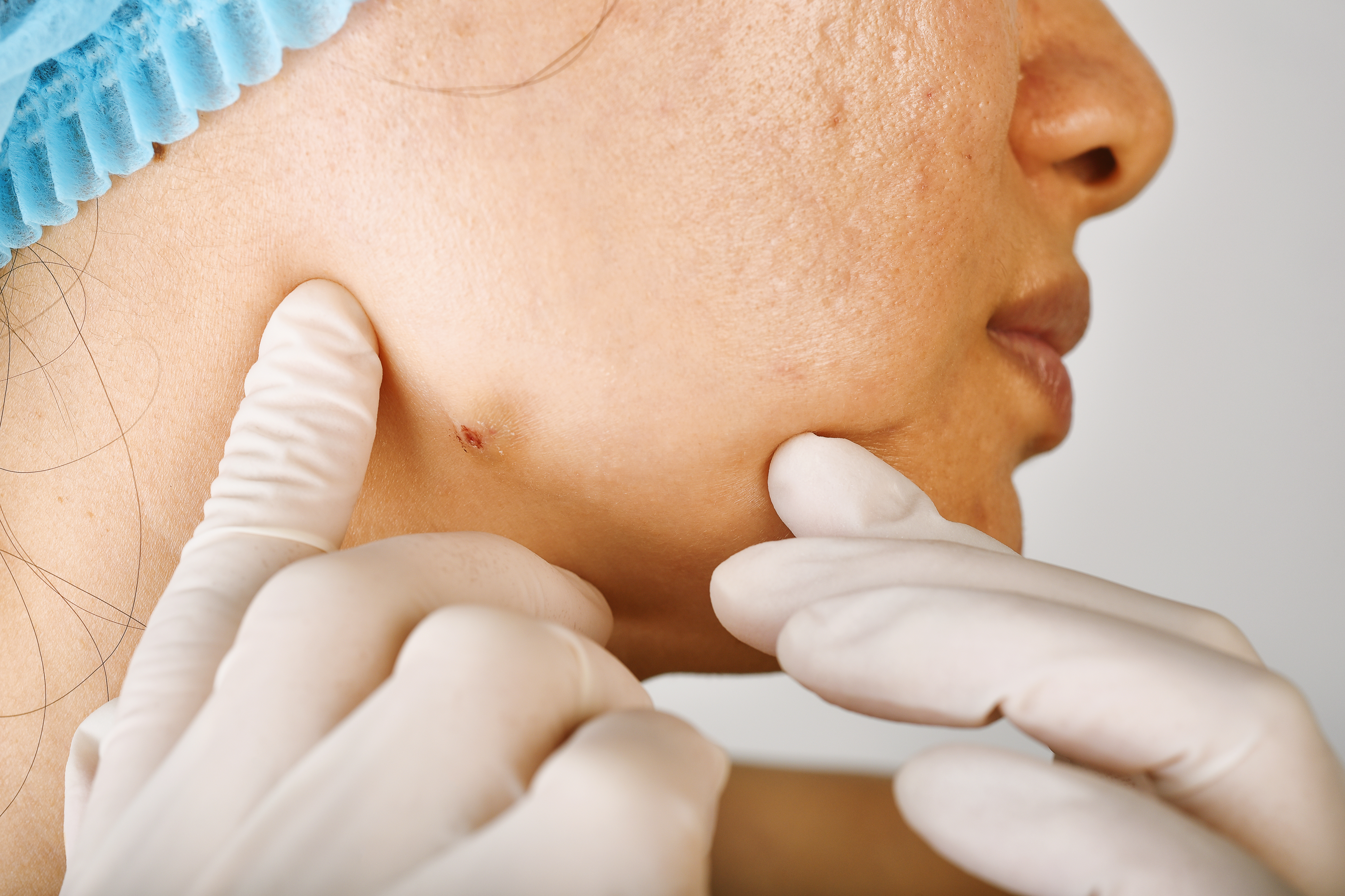
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a strain of staph bacteria that is resistant to many common antibiotics. MRSA infections can be challenging to treat and often require alternative antibiotics or more aggressive treatment strategies. The symptoms of MRSA are similar to those of other staph infections, including skin irritation, boils, and abscesses, but they may be more severe or persistent. MRSA is a significant public health concern due to its resistance to treatment and its potential to cause widespread outbreaks. Understanding the risks and symptoms of MRSA can help individuals take precautions to prevent infection and seek appropriate treatment if symptoms arise.
11. Preventive Measures: Guarding Against Staph Infections

Preventing staph infections involves maintaining good hygiene, promptly treating cuts and abrasions, and avoiding sharing personal items. Regular handwashing, particularly after contact with potentially contaminated surfaces, can reduce the risk of infection. Keeping wounds clean and covered can prevent bacteria from entering the body. Additionally, individuals should be cautious in communal settings, such as gyms or locker rooms, where staph bacteria may be present. Understanding and implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of staph infections and their complications, ensuring that the skin remains a resilient barrier against bacterial invaders.
12. Treatment Options: Navigating the Path to Recovery
Treatment for staph infections depends on the severity and location of the infection. Mild skin infections may be treated with topical or oral antibiotics, while more severe infections may require intravenous antibiotics or surgical intervention. In cases of MRSA, alternative antibiotics or combination therapies may be necessary. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing complications and ensuring a full recovery. Patients should follow their healthcare provider's instructions carefully and complete the entire course of antibiotics to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance. Understanding the available treatment options can empower individuals to take an active role in their recovery and prevent future infections.
The journey of deciphering the silent whispers of our skin reveals the critical importance of awareness and prompt action in the face of staph infections. By recognizing the top 12 red flags, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and prevent serious complications. Empowered with knowledge, we can listen to our skin's signals, respond appropriately, and maintain the integrity of our body's first line of defense. As we conclude this exploration, it is clear that vigilance and education are key to safeguarding our health against the silent threats posed by staph infections.
