Signs And Symptoms Of Cystitis
Cystitis is a medical term for an infection of the bladder and is usually caused by bacteria such as E. Coli, though occasionally it may be caused by a fungus. Women are a fair amount more susceptible to cystitis than men, and obesity and diabetes are risk factors. Most of the time, cystitis is not serious and can be treated with a round of antibiotics. Many individuals will suffer from cystitis at some point in their lives, but not everyone knows the symptoms.
With this in mind, get familiar with the ajor symptoms linked to cystitis now.
Persistent Desire To Urinate

A persistent desire to urinate is an early symptom of cystitis, and someone suffering from this condition may feel a strong need to empty their bladder. Patients may urinate more frequently than normal or have trouble getting their bladder to empty. Having to strain to empty one's bladder is abnormal and needs to be checked out by a doctor before things get worse. Even though it might not seem like a big deal, this is one of the most common symptoms of a urinary tract infection. Eventually, the patient may experience pain when trying to urinate. Pain may be felt at the urethra, usually as a burning sensation, or further up in the pelvic area.
Continue for more symptoms of cystitis.
Cloudy Or Strong Smelling Urine

Cloudy or strong smelling urine can indicate the presence of bacteria in the bladder. In general, healthy urine does not have a strong or foul smell, so smelly or strangely colored urine is a cause for concern and should be investigated by a doctor. Bacterial colonies in the urine cause the cloudiness and smell. Although urine does not normally have a pleasant smell, a urinary tract infection causes it to have an especially foul odor, such as rotting fish or ammonia. Not everyone describes the smell the same way, but the point is that infected urine smells very different from healthy urine.
Keep going to uncover more symptoms of cystitis.
Pelvic Pain

Pelvic pain can be a symptom of many different medical problems, but cystitis is one of the most common causes. Some individuals with cystitis simply feel pressure or discomfort in the pelvic region, whereas others may report intense pain, especially if the infection goes untreated for too long. The pain is caused by bladder inflammation, which happens when the body reacts to the presence of harmful bacteria. Patients may feel pain in the lower back, the lower stomach, or near the pubic bone. Pain higher up on the torso can signal a kidney infection, which is more serious than most cases of cystitis.
Continue to learn more about additional symptoms of cystitis.
Hematuria
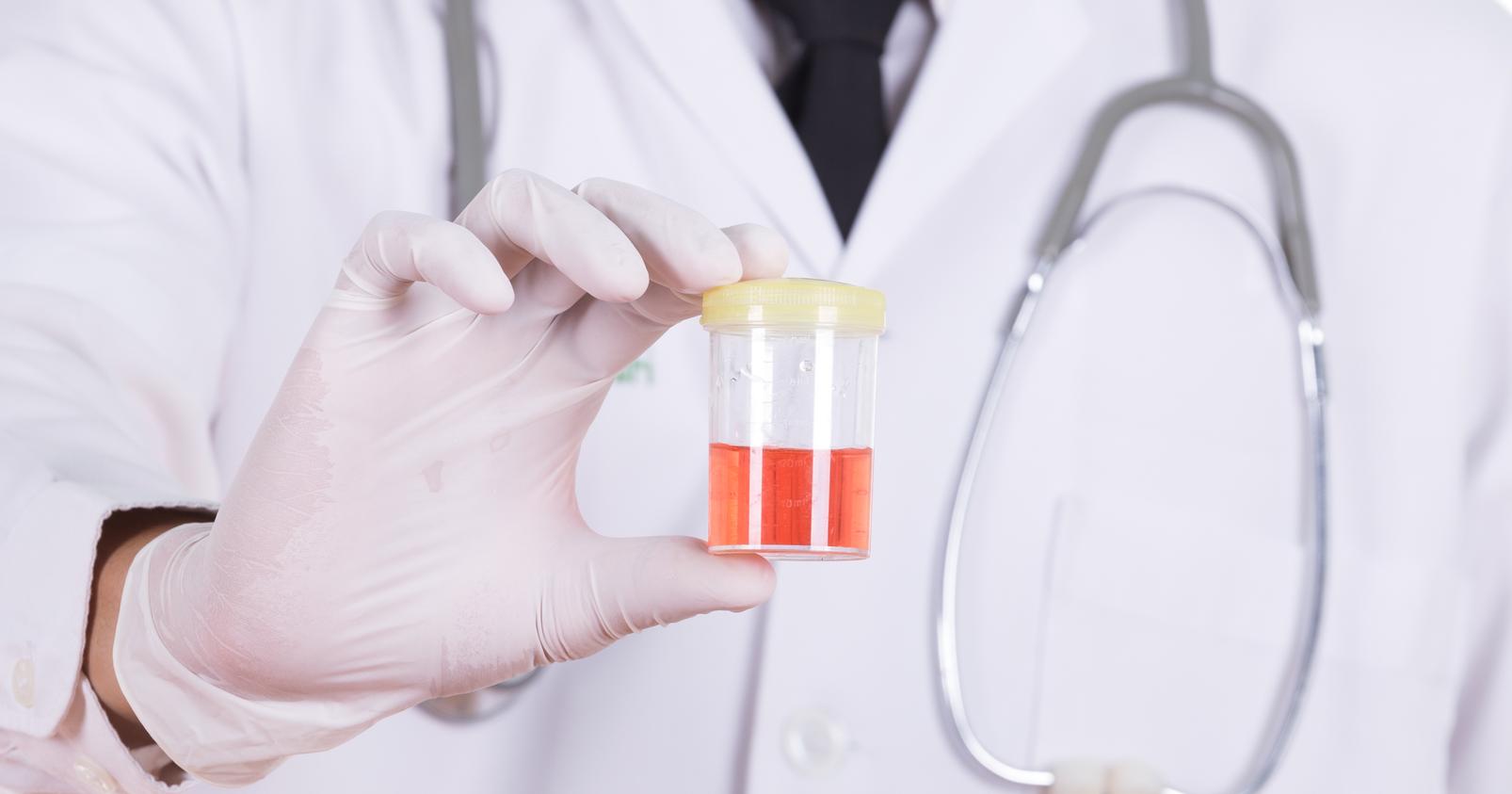
Hematuria means there is blood in the urine. Blood can cause the urine to be noticeably discolored and may appear pink, red or brownish. However, sometimes the blood is not visible and is only detected when the doctor runs laboratory tests on the patient's urine. Cystitis that involves blood in the urine is sometimes referred to as hemorrhagic cystitis and can indicate a more serious infection. Anyone who notices blood in their urine should see a doctor right away. The one exception is if a woman who is menstruating notices blood in her urine, as this is completely normal.
Continue reading for more on symptoms of cystitis.
Low-Grade Fever

As is the case with most infections, cystitis can cause a low-grade fever. For adults, a low-grade fever is about 100 to 101 degrees Fahrenheit. The fever is a sign the body is trying to fight off infection in the bladder and is one of several indicators of infection doctors check for. Other indicators include white blood cell count and the presence of bacteria in the urine. In many cases, the body cannot fight off cystitis on its own and needs help in the form of antibiotics, which is the typical treatment for cystitis and cures it most of the time.
Uncover additional symptoms of cystitis now.
Lower Abdominal Pressure
Lower abdominal pressure is a common symptom of cystitis, and it can occur with both mild and more advanced cases. Patients often describe the abdominal pressure as a cramping sensation, and it may be accompanied by pelvic discomfort and the sensation of pressure or fullness in the bladder. To ease the discomfort of lower abdominal pressure, it may help to apply a heating pad to the abdomen. Patients could also try gently massaging the area. Since lower abdominal pressure can occur with a serious case of cystitis or with another serious medical condition, individuals with this symptom might want to keep a journal of the times when they experience it and how long it lasts. If lower abdominal pressure persists for more than a week or if it occurs in conjunction with nausea, vomiting, or pain in the back or side, patients should make an appointment with their doctor.
Keep reading to learn more about the major indicators of cystitis now.
Passing Small Amounts Of Urine Frequently

Patients with cystitis may notice they are passing small amounts of urine frequently. They could feel a persistent urge to urinate, and they might even feel an urge to urinate after the bladder has already been emptied. The amount of urine passed will be much less than usual, and the urine could appear cloudy. Some may pass urine with a particularly strong odor. Pediatric patients with cystitis could start to experience wetting accidents in the daytime. Patients who notice frequent urination (more than eight times per day) should see their doctor for an evaluation. Since cystitis can progress quickly, patients should see their doctor if frequent, urgent urination persists for more than a few hours. They will ask questions about when the patient first noticed this symptom and if they have ever had a urinary tract infection. Tests such as a urinalysis and a cystoscopy may be necessary for diagnosis.
Discover more warning signs of cystitis now.
Burning Sensation While Urinating
A burning sensation while urinating typically occurs as a direct result of the bacterial infection that is present with cystitis. Doctors may prescribe medications such as acetaminophen with codeine and pentosan polysulfate sodium to relieve the pain, and tricyclic antidepressants are sometimes used for this purpose as well. These medicines are often prescribed with antibiotics to clear the bacterial infection from the body. Most patients find the burning sensation during urination resolves rather quickly once they begin taking these prescriptions. Some find drinking cranberry juice eases their symptoms as well, and physicians recommend drinking plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. Citrus fruits, tomatoes, artificial sweeteners, caffeine, and alcohol may irritate the bladder, and doctors recommend patients avoid these while receiving treatment for cystitis. Experts also suggest patients wear cotton underwear and loose-fitting trousers during their treatment.
Get more details on the symptoms of cystitis now.
Nausea And Vomiting

Nausea and vomiting tend to occur with more serious cases of cystitis, and they are usually an indication the infection has spread to the kidneys. If these symptoms are present, patients should seek emergency medical care. Some individuals could experience a fever and chills in conjunction with nausea and vomiting. At the emergency room, patients should let the physician know when they began experiencing nausea and vomiting and how many vomiting episodes they have had. The doctor may ask questions about if the patient has been able to keep food or liquid down and about symptoms such as painful urination or back or side pain. If a kidney infection is suspected, patients may have urine and blood tests, and some will need to have x-rays, ultrasounds, and CT scans. Patients with kidney infections may need to stay in the hospital to receive intravenous antibiotics, and anti-nausea medication may be administered as well. Patients will be monitored regularly, and they will be released from the hospital once the infection has resolved and they have stopped vomiting.
Read more about the symptoms of cystitis now.
Back Or Side Pain

Like nausea and vomiting, back or side pain could indicate a cystitis patient has developed a kidney infection. Individuals with pain in these areas should seek emergency treatment. Doctors will begin by taking the patient's vital signs and health history information. The patient will be asked about any history of urinary tract infections, as well as the precise location of any back or side pain. It can be helpful for the physician to know if the patient's pain is dull or sharp and if it persists or comes and goes. The doctor will lightly tap over the patient's kidneys to check for pain, and the patient's back and sides may be palpated to check for any masses or tenderness. An abdominal examination may be performed, and patients might need to have urine and blood tests and imaging studies. While being treated for a kidney infection, the patient should always let their medical team know if the back or side pain worsens or changes location. Patients might be offered prescription pain relievers to ease symptoms, and it can also help to use a heating pad on the back or sides.
