Guide To The Types Of Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a skin condition in which a hair follicle becomes inflamed. It is typically related to a fungal or bacterial infection. The infection might look like white-headed pimples or red bumps around a hair follicle. If the infection spreads, it can turn into sores that scab over and take a long time to heal. Folliculitis does not typically have life-threatening consequences, but it can cause itching and soreness.
An effective treatment option is an antifungal shampoo for folliculitis. In some cases, anti-dandruff shampoo may be used. Some individuals may mistake certain types of this condition for acne. However, malassezia acne treatment must be treated differently than other forms of acne. This may mean medicated shampoos and a prescription for folliculitis. Thankfully, there are also antibiotics for folliculitis, including antibiotic creams. Some patients may also be able to employ natural remedies for folliculitis, though it is vital to determine which type they have first.
Pityrosporum Folliculitis

Pityrosporum folliculitis occurs when malassezia, a natural yeast, infects hair follicles. This common skin condition is often misdiagnosed or goes undiagnosed. Many patients with this condition may be under the mistaken impression that they have acne. However, treating the condition as an acne breakout will not help. One way to tell the difference between folliculitis and acne is to consider the symptoms. With folliculitis, patients will not see the blackheads and whiteheads that acne causes. Acne also does not tend to itch, but folliculitis can be itchy.
An individual with this type of folliculitis may be more likely to have dandruff and other skin conditions caused by malassezia. Dandruff and pityrosporum folliculitis also tend to be treated with the same antifungal shampoos. This form of folliculitis most commonly appears on the shoulders, chest, and upper back.
Continue reading to uncover the next type of folliculitis now.
Bacterial Folliculitis
Bacterial folliculitis is one of the most common types of folliculitis. In fact, this is the form that most individuals are referring to when they talk about folliculitis. Rather than being caused by yeast or another fungus, this type of folliculitis is caused by a bacterial infection. The most common bacteria that causes this infection is Staphylococcus aureus. It is common for bacterial folliculitis to affect both adults and children all over the world. Certain ointments and types of clothing can heighten an individual's risk of developing this condition.
Patients may also be at an increased risk of developing this condition if they wax, shave, or otherwise remove their hair frequently. Doing so can lead to irritation and allow bacteria to infect the hair follicles. Tight clothing might also cause friction that can lead to this infection. Some individuals develop infections after they have used antibiotics for long periods. Individuals may also be at a high risk of developing this condition if they use topical corticosteroids. Patients with chronic illnesses that compromise the immune system may see more severe breakouts from this condition.
Discover more types of folliculitis now.
Hot Tub Folliculitis

Hot tub folliculitis occurs when individuals spend a significant amount of time relaxing in a hot tub. This skin infection appears in the lower part of the hair follicle. However, some patients may develop hot tub folliculitis without being near a hot tub. The bacteria responsible for the infection work best in wet and warm areas. Though the bacteria can occur in any wet and warm place, infestations are particularly likely in wooden hot tubs as opposed to hot tubs made from other materials.
The main symptom of this type of folliculitis is a red and bumpy rash that itches. In rarer cases, the rash will not itch. Some of the bumps are filled with pus, and the rash may look like acne. Typically, the rash will develop a few hours or days following exposure. Following the formation of the rash, the symptoms might progress to painful and tender dark red bumps. Patients might see the rash in areas underneath their swimsuit or on their chest underneath where the water level hits.
Get more information on the different forms of folliculitis now.
Sycosis Barbae
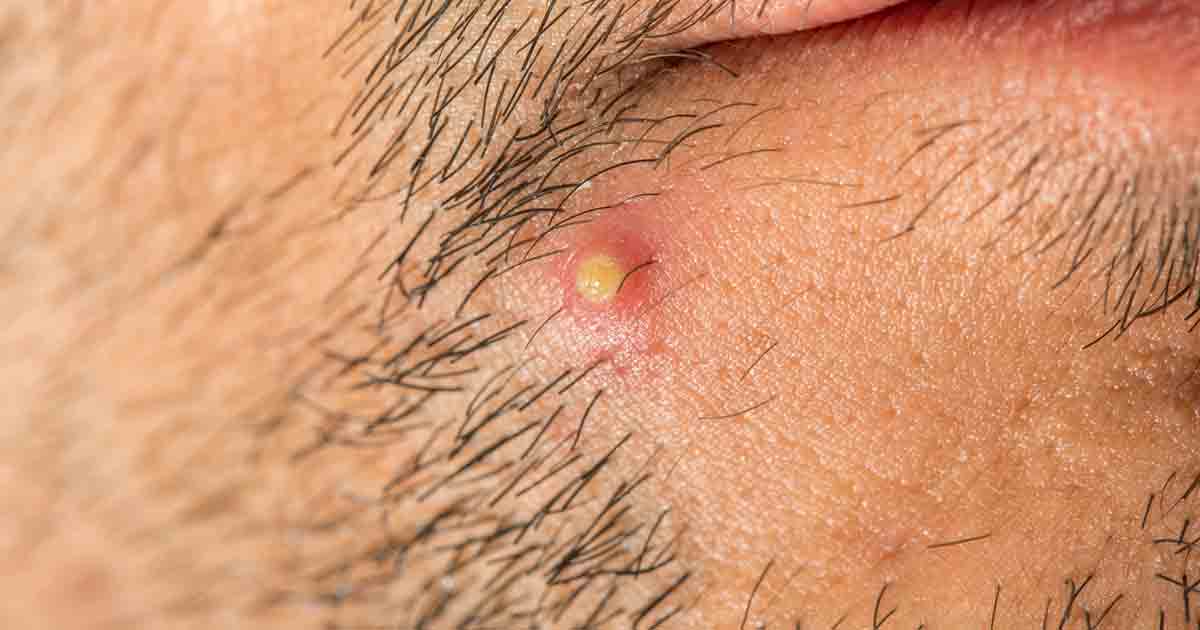
Folliculitis barbae occurs when the beard area becomes infected with Staphylococcus aureus. It may occur in both men who shave and those who do not shave. When the infection becomes deep-seated, it is called sycosis barbae. Sycosis barbae does not tend to be life-threatening. However, it can lead to permanent hair loss and deep scarring in the affected areas. Another condition that occurs is called pseudofolliculitis barbae. This appears when shaving leads to ingrown facial hair. The immune system sends up an inflammatory response to the affected hairs.
This type of folliculitis can occur wherever the hair is plucked or shaved. Individuals can have both pseudofolliculitis and sycosis barbae at the same time. Men who have African ancestry are more likely to develop this condition than other ethnic groups. Women can also be affected by both conditions. Patients are more likely to develop one or both of these conditions if they use a bladed razor than if they use an electric razor when shaving.
Keep reading to learn more about the various types of folliculitis now.
Boils And Carbuncles

Boils and carbuncles are types of folliculitis. Boils occur when a pus-filled and painful bump forms below the skin. They are caused by a bacterial infection of at least one hair follicle, though some boils may involve infections of multiple hair follicles. A carbuncle forms when clusters of boils connect below the skin and form a larger infected area. Most boils begin as tender, red bumps. The bumps swell with pus until they eventually rupture.
The most commonly affected areas with this condition are the armpits, buttocks, thighs, back of the neck, and the face. When a boil forms, there will often be swollen and red skin surrounding the bump. Unlike typical acne, boils swell as they are filled with more pus. They begin red, but then form a whitish-yellow tip that ruptures so that the pus can drain. Carbuncles cause deeper infections and increase an individual's risk of permanent scarring.
