Options For Treating Hip Bursitis
Bursitis is a painful condition in which one or more bursae become inflamed. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions for the muscles, tendons, and bones close to joints, which are structures that connect bone to bone. Tendons connect muscle to bone. Bursitis can occur any part of the body where there are bursae, but the most commonly affected are the elbows, shoulders, and hips. Bursitis is often triggered by repetitive motion, but it can also be the result of infection, gout, and inflammatory types of arthritis. Obesity increases the risk of both knee and hip bursitis. Hip bursitis is generally self-limiting, but surgery to drain the bursae or correct a related tendon is sometimes required. This article will discuss some specific treatments for hip bursitis.
Cold Compress

The hip has two bursae, which help cushion bones, tendons, and muscles in the hips, thighs, and buttocks. Hip bursitis is most likely due to overuse of the hip joint. It is important to rest the area so the bursae can heal. If hip pain is due to bursitis, the most likely symptoms will be stiffness, pain, and swelling. The joint may ache, and it may hurt more if pressure is applied, or patients move a lot.
A simple and effective first-line treatment for hip bursitis is the application of a cold compress or cold pack to the affected area. It is best to do this for the first forty-eight hours after symptoms appear. The cold compress will soothe inflammation and relieve pain. Use the pack for up to twenty minutes at a time before taking a ten-minute break. Repeat this treatment multiple times throughout the day for the best results.
Anti-Inflammatory Medication

Anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen, reduce pain and inflammation in the affected area. Steroid medications like prednisone may also be injected directly into the affected bursae. Prednisone acts quickly to reduce inflammation and pain, and unless the problem happens again, typically, only one injection is necessary.
It is imperative to rest the affected area, as more exertion will only aggravate the problem. Try to recall the activity that caused bursitis to occur so it can be avoided in the future. If the hip is overused again, bursitis is likely to recur. Consult a doctor if pain escalates, if the joint cannot be moved at all, or if there is a fever. A rash or bruising over the affected area are also indicators professional medical care may be needed.
Physical Therapy
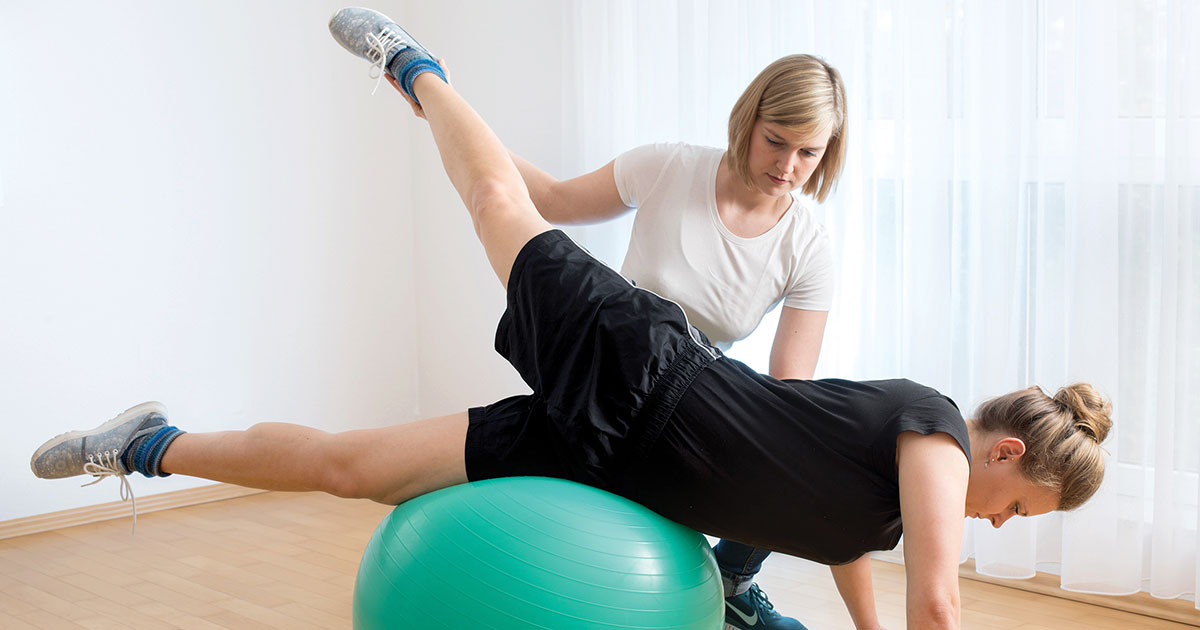

Most cases of hip bursitis improve and resolve on their own, if given time. However, if the condition persists or recurs, physical therapy may be an option. This involves heat treatment, massage, water therapy, and special exercises. Physical therapists are medical professionals trained to help the patient move better, relieve their pain, and prevent further damage and complications. The therapist is trained to develop an individualized treatment plan designed to restore normal movement. This plan may involve exercises that strengthen the muscles in the hip area. The therapist will also advise the patient on home care, which may involve cold packs, heat packs, or a cane or walker during the recovery period. Patients who sleep on their side may find it helpful to place a small pillow between their knees.
Tendon Repair Surgery
Trochanteric bursitis of the hip is sometimes treated with surgery when more conservative treatments have failed. The bump of bone over the front of the hip is called the greater trochanter. The tendon that passes over the greater trochanter is known as the iliotibial band. The bursa in this area is supposed to reduce friction as the iliotibial band glides over the greater trochanter. The iliotibial band joins up with the gluteus maximus muscle.
Walking causes this muscle to pull on the iliotibial band, and if the band is too tight, it causes friction as it passes over the greater trochanter and its bursa, the greater trochanteric bursa. This puts pressure on the bursa and causes pain as a result. The reasons why the iliotibial band may be too tight are not well understood. Tendon repair surgery to remove the damaged bursa and lengthen the tendon will relieve the pressure on the greater trochanter and its bursa.
Antibiotics

Antibiotics are drugs that kill the pathogens that cause disease. Most cases of hip bursitis are not related to infection and do not require antibiotics. However, when the bursae do become infected, the condition is called septic bursitis, which is a potentially severe complication. Bacteria may invade a bursa through a cut in the skin or by some other means. Individuals with diabetes, HIV, or cancer are at a higher risk for septic bursitis.
In addition to pain and swelling, this condition may also cause a fever, chills, redness in the affected hip area, and a general feeling of being unwell. To make the diagnosis and to find out which bacteria is causing the infection, physicians may draw a small amount of fluid from the bursa. If left untreated, septic bursitis can lead to septicemia, which is an infection of the bloodstream, though it can spread to other areas of the body. Prompt antibiotic therapy usually resolves septic bursitis without further related complications.
Take Some Time To Rest

The most common form of hip bursitis is noninfectious and involves an inflammation of a bursa without any underlying infection. It's generally considered less serious than the less common infectious bursitis. The most commonly recommended treatment for noninfectious bursitis is to take some time to rest. When individuals let their hips rest by staying at home and minimizing the time they spend walking around, the inflammation will eventually run its course and go away. Doctors may also recommend over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications to help with the pain. When the pain is more serious, they might prescribe stronger medication. It can also help to use ice on the affected area to help numb the pain.
Physical Activity Modification
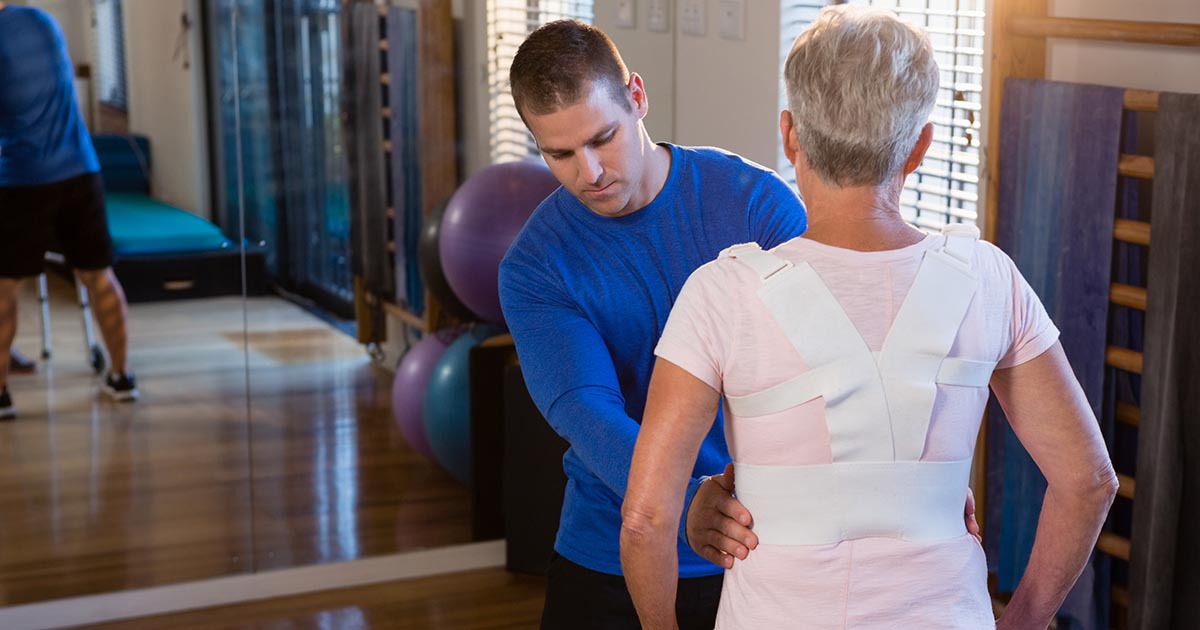

Hip bursitis patients may need to undergo certain physical activity modifications to help prevent a recurrence. A physical therapist can typically help with this. Individuals with hip bursitis can learn home exercise programs that help stretch and strengthen their leg muscles. It is important for each patient to consult a physical therapist about the best exercise routine for their body and condition, as overexercising could make the inflammation worse.
If an individual's lifestyle puts them at a higher risk of a recurrence, such as if they work manual labor or are an athlete, their physical therapist may teach them new ways of doing day-to-day tasks that minimize the risk to the hips. When the initial injury has subsided, the therapist might recommend a strengthening and flexibility program to prevent another injury.
Corticosteroid Injection
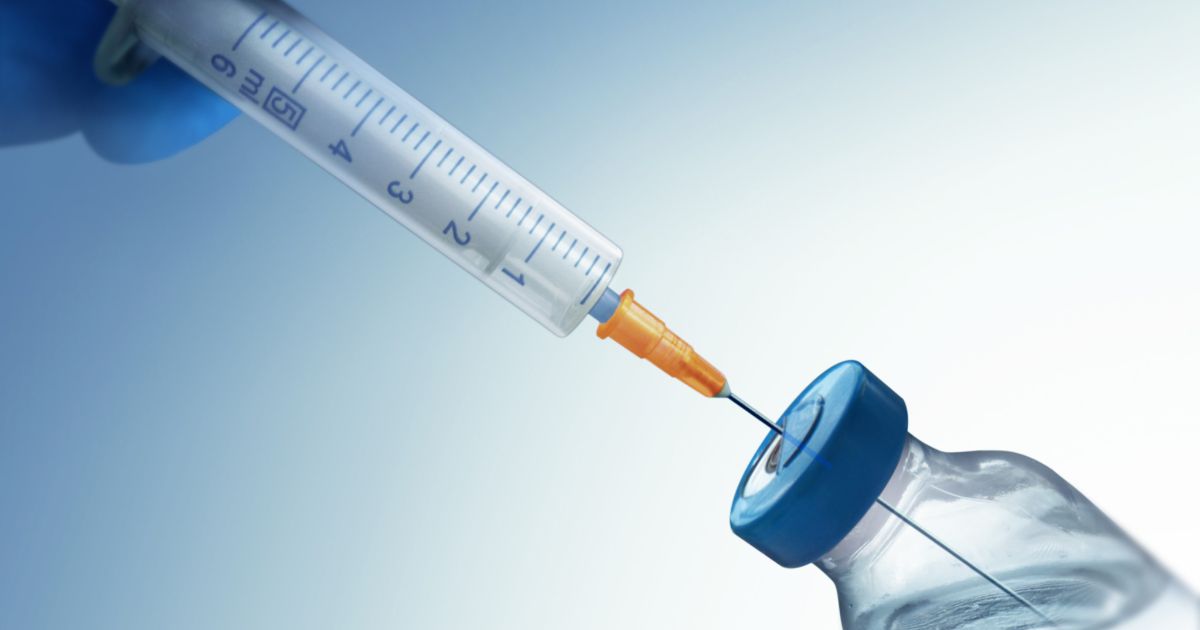
A corticosteroid injection may be used in cases where the patient's hip is significantly swollen and painful. During this procedure, a small amount of corticosteroid is injected into the bursa, along with local anesthetic. Corticosteroids are a class of medication that mimic the body's adrenaline-related hormones and act as an elevated amount of these hormones in the body. This suppresses the immune system and its inflammatory reaction. In addition to helping with hip bursitis, corticosteroids are also used to treat asthma and arthritis. Prior to an injection, patients should tell their doctor if they are taking any blood thinners. Patients may be asked to stop taking these medications for several days before the injection.
Use A Cane Or Crutch
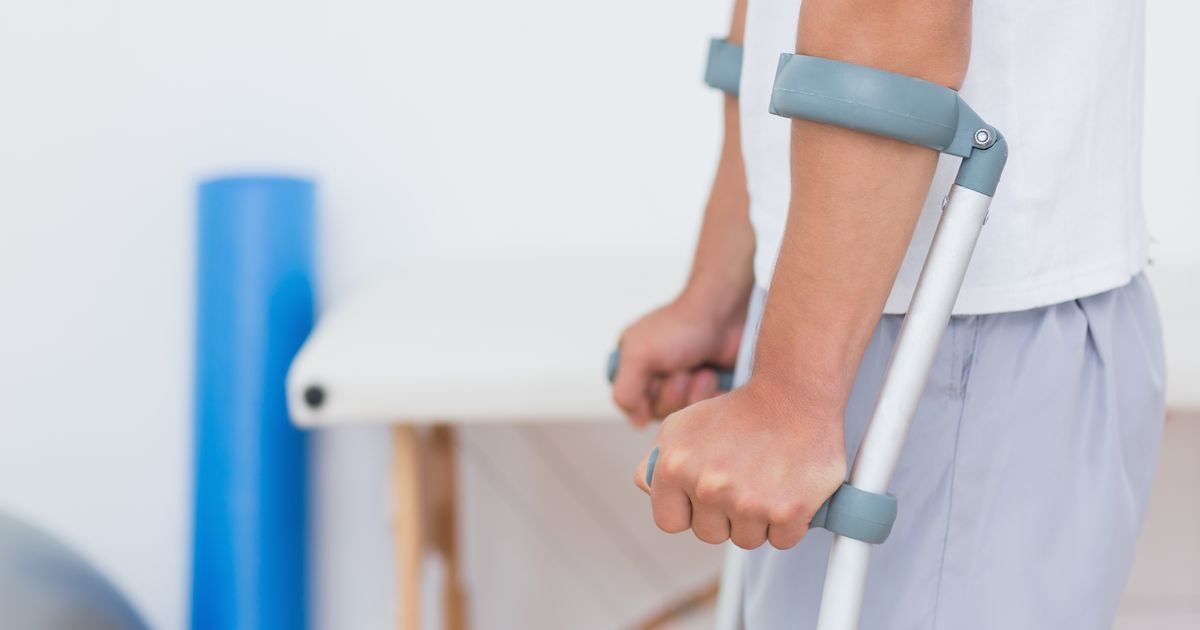
The swelling and inflammation from hip bursitis tend to cause more pain when individuals put weight on their affected leg. Doing so stresses the injury by putting pressure against it. If patients cannot rest entirely while they wait to heal, using a cane or crutch can help relieve pain. These mobility assistive devices are used for various forms of chronic pain relief and help with walking. If an individual with hip bursitis has never used a cane or crutch before, they should have their doctor teach them how to position and wield it properly. Otherwise, they may not get the right amount of pain relief and may have trouble balancing.
Lose Excess Weight

While there's no absolutely foolproof way to prevent bursitis, the chances of developing it or having a recurring episode are higher if there is excess strain on the hips. It can help for individuals to lose excess weight, as this reduces the amount of force being exerted against their hips and other joints. Weight loss should be secondary to a healthy exercise plan, though. Hip bursitis is more easily prevented and treated through careful physical movement than through extreme weight loss. It's important to avoid doing activities that cause extreme pain or difficulty, as these may make the injury worse instead of helping with the healing process.
