Treating And Preventing Cerebrovascular Disease
Cerebrovascular disease is used to describe any disease that causes the brain to become affected by bleeding or ischemia due to blood vessel involvement. Some of the conditions under the umbrella term are aneurysms, vascular malformations, strokes, vertebral stenosis, and carotid stenosis. Blood flow may become restricted due to many different factors including rupture, narrowing, and blockage of the blood vessels. Ischemia is the word for the lack of adequate blood flow. There are, thankfully, preventative measures patients can take to avoid developing cerebrovascular disease and treat the condition should it occur.
Carotid Endarterectomy
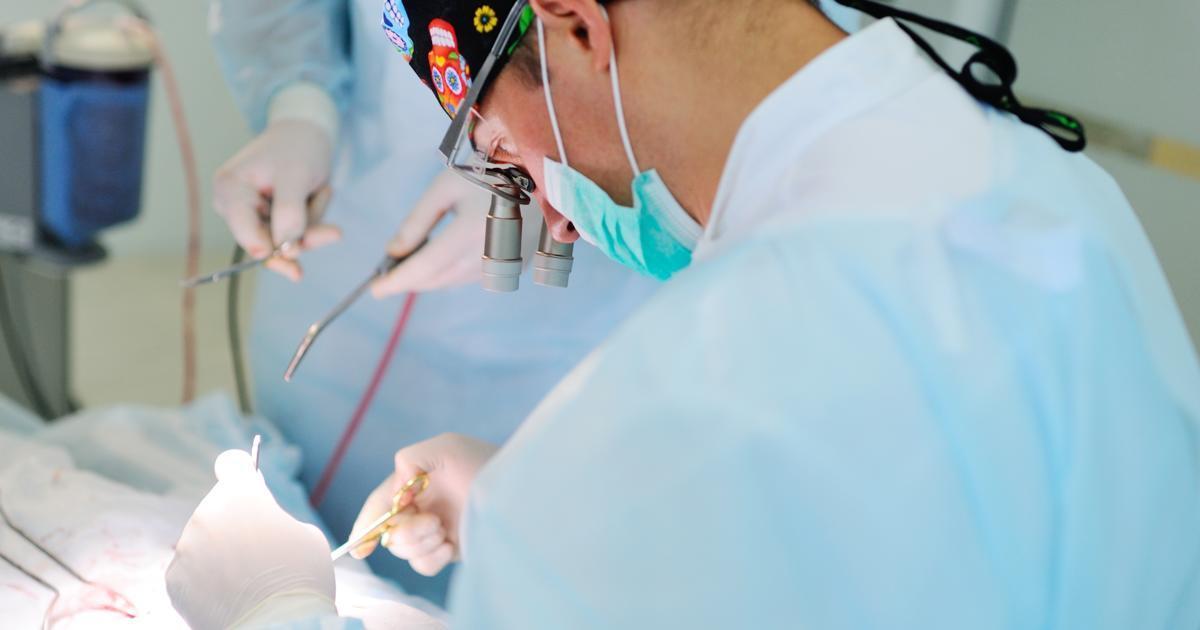
Carotid endarterectomy is surgery done in the hospital that removes a buildup of plaque from the carotid artery in a patient's neck. The surgery's goal is to restore blood flow to the brain so the patient does not have a stroke. It's often recommended for patients who already show signs of decreased blood flow. Depending on the circumstances, patients might have general anesthesia or local anesthesia. With local anesthesia, the doctor will have the patient remain conscious to check on their brain's reaction to different blood flow. If this is the case, they'll be given medicine to help them relax.
The surgeon makes an incision in the neck to expose the blocked portion of the artery. They will then remove the plaque buildup through their incision. Recovery time for this surgery usually takes one to two days. As with most major surgeries, there is the potential for complications. However, the procedure tends to be safe when an experienced surgeon operates. Older individuals, women, and those with chronic diseases have a higher chance of complications.
Carotid Angioplasty And Stenting
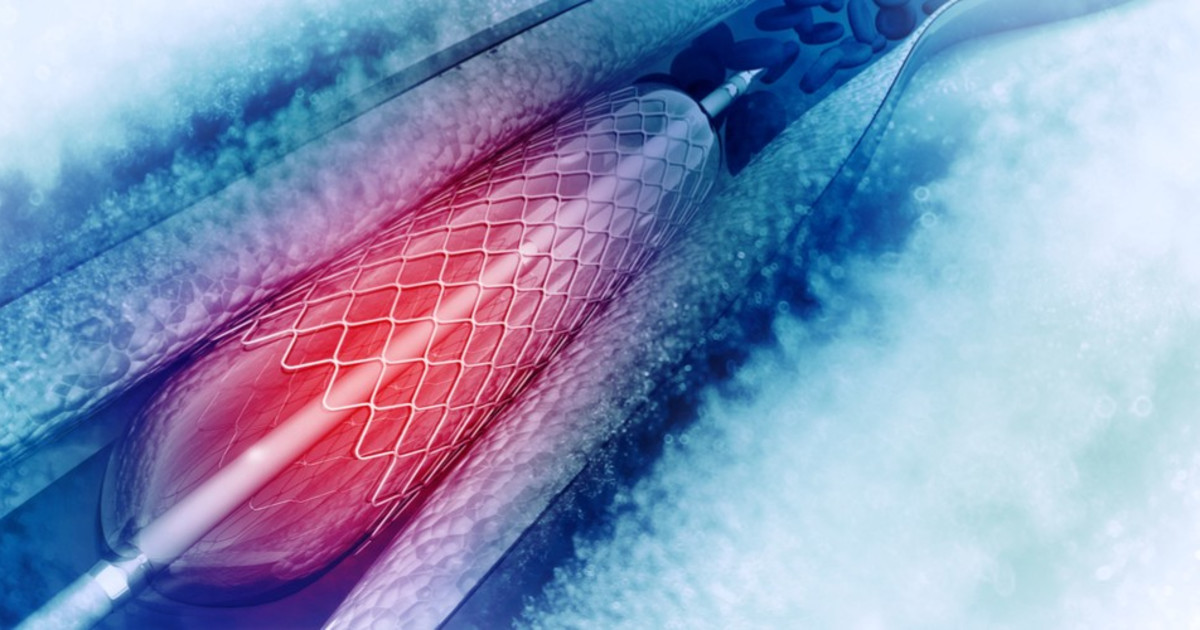
Carotid angioplasty and stenting are both procedures used to open a patient's clogged arteries. This helps restore the flow of blood to the brain after the flow was blocked. They're most commonly performed to help prevent stroke or treat stroke symptoms. This procedure also involves plaque buildups in the carotid artery.
However, instead of removing the plaque, the surgeon will insert a tiny balloon into the clogged artery and inflate it. This widens the artery so the blood can move past the plaque buildup and reach the brain. Stenting is often combined with a carotid angioplasty. A stent is a small coil of metal used to prop the artery open. These procedures are typically used if traditional surgery is either too risky or impossible.
Tissue Plasminogen Activator
Tissue plasminogen activator is considered a gold standard in stroke treatment. The FDA has approved this treatment for ischemic strokes. If the treatment is administered promptly, it can mitigate the stroke's long-term effects and save the lives of patients. The drug is administered through an IV and dissolves the clot causing the blockage of blood flow. This then allows blood to flow freely back to the oxygen-starved part of the brain.
The treatment must be used within the first three hours following the stroke to be effective. Certain patients may improve up to four and a half hours after a stroke. In many cases, patients wait too long to go to the hospital, and they lose the ability to receive this vital treatment. This is why stroke recognition is so important.
Blood Platelet Inhibitors
Blood platelet inhibitors are medications that prevent clots from forming. A blood clot forms when platelets in the blood stick together and create a clump, which can then block veins and arteries. When the blocked blood vessel is supposed to supply blood to the brain, it can lead to stroke and other cerebrovascular events. A blood platelet inhibiting medication will work during the clotting part of bleeding and prevent the platelets from adhering.
Therefore, clots won't form. The antiplatelet medication most commonly used is acetylsalicylic acid. This medication is so vital in many cardiovascular health regimens because it keeps arteries from becoming clogged, which can prevent heart attacks and strokes.
Cholesterol-Lowering Medication
Another treatment able to treat or prevent blocked blood vessels is cholesterol-lowering medication. The best way to prevent high cholesterol is by leading a healthy lifestyle. However, exercising and dieting isn't always enough. Cholesterol medications can help in a few different ways. They can decrease 'bad' cholesterol, which is what increases the potential risk of developing heart disease.
They're also able to decrease the total triglyceride amount. Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood that also increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. In addition, they can increase 'good' cholesterol. Good cholesterol helps to protect the cardiovascular system against blockage and disease. Doctors may suggest either one medication or a combination of several.
